Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a herbaceous flowering plant that belongs to the family Zingiberaceae. They are perennial plants that live for more than two years. Ginger is a rhizome which is a modification of the stem. It is native to Southeastern Asia and is known for its pungent smell.
Classification
|
Kingdom |
Plantae |
|
Clade |
Monocots |
|
Order |
Zingiberales |
|
Family |
Zingiberaceae |
|
Genus |
Zingiber |
|
Species |
Z.officinale |
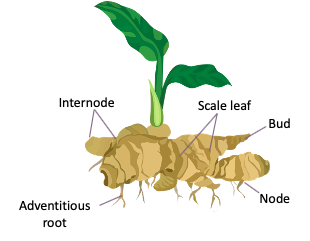
Well-Labelled Diagram of a Ginger Rhizome
Morphology
- It is a herbaceous perennial plant that grows upto 1 metre high.
- The leaves grow in an alternate manner and are long and elongate in nature.
- It produces white and pink clusters of flower buds that grow into yellow flowers on maturity.
- The flowers are arranged in a cone-like spike that is covered with overlapping green bracts.
- It is a monocotyledon plant.
- The underground stem modification forms into a rhizome that is widely used as a spice.
- The rhizome is palmately branched and bears leafy shoots. The leafy shoots are a pseudostem formed from the leafy sheaths and bears 8-12 distichous leaves.
- The inflorescence arises directly from the rhizome.
Production and Cultivation
Ginger is mainly cultivated in Southeast Asian countries such as China, India, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, Nepal and Bangladesh. China and India are the major suppliers of the spice all over the world.
The plant is cultivated by planting root stalk cuttings and does not require seeds for propagation. The rhizome is harvested by simply lifting it from the soil, cleansing it and drying it in the sun. The dried rhizome is irregular, palmate and branched in appearance. Its colour varies from dark yellow to light brown to pale buff.
Uses
The ginger rhizome is an aromatic condiment that is available as fresh ginger, preserved ginger, ginger powder, ginger oil, dry ginger, ginger oleoresin and ginger paste.
Use in Food Processing: Fresh ginger, ginger paste and oleoresin has carminative properties that is used in all kinds of food giving it a biting taste, flowery and spicy flavour. Ginger preserve and candy are used as confectionery items. It is also used in pickling, teas and making soft drinks. It is used in heavy food items as it possesses digestive properties.
Medicinal Uses: Ginger rhizome is a rich source of zingiberene, α-curcumene, gingerols, and shogaols. These phytochemical components give it antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antilipidemic properties.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S Biology for more such information.
Also Read:
Comments