Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Characteristics of Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Gram-Positive Cell Wall
- Benefits of Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Risk Factors of Gram-Positive Bacteria
Introduction
Gram-positive bacteria are the genus of the bacteria family and a member of the phylum Firmicutes. These bacteria retain the colour of the crystal violet stain which is used during gram staining. These bacteria give a positive result in the Gram stain test by appearing purple coloured when examined under a microscope, hence named, gram-positive bacteria. Actinomyces, Clostridium, Mycobacterium, Streptococci, Staphylococci, and Nocardia are a few examples of Gram-positive bacteria.

Characteristics of Gram-Positive Bacteria
- They have a thick peptidoglycan layer and cytoplasmic lipid membrane.
- These bacteria lack an outer membrane.
- Have a lower lipid content and more teichoic acids.
- They move around with the help of locomotion organs such as cilia and flagella.
- The walls of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis contain teichoic acid.
Also Read: Difference between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria
Gram-Positive Cell Wall
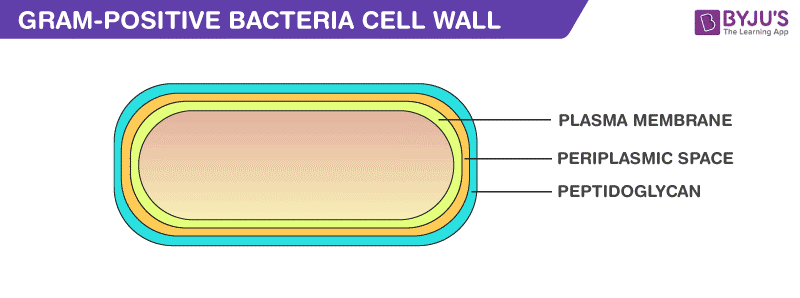
Peptidoglycan
It is a permeable, cross-linked organic polymer and rigid structure which plays an important role in providing shape and strength to the cell wall. It makes up about 90% of the cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane and protects the cell from the environment. Peptidoglycan is composed of three main components including Glycan backbone, Peptide, and Tetra-peptide.
Lipid
The lipid element found in the gram-positive bacteria cell wall supports its anchoring to the membrane. The total percentage of lipid content in a gram-positive bacterium cell wall is 2 – 5 per cent.
Teichoic acid
It is water-soluble and a polymer of glycerol. Teichoic acid is the major surface antigen of gram-positive bacteria and it makes up about fifty per cent of the total dry weight of the cell wall.
Benefits of Gram-Positive Bacteria
- These species of bacteria are non-pathogenic and reside within our body including the mouth, skin, intestine, and upper respiratory tract.
- They are an essential ingredient in producing Emmentaler or Swiss cheese.
- The species of Corynebacterium are used in the industrial production of enzymes, amino acids, nucleotides, etc.
- Various Bacillus species are used in the secretion of large quantities of enzymes.
- A few species of gram-positive bacteria are also involved in cheese ageing, bioconversion of steroids, degradation of hydrocarbons, etc.
- Bacillus amyloliquefaciens of gram-positive bacteria are a good source of a natural antibiotic protein – Barnase.
Risk Factors of Gram-Positive Bacteria
The substantial increase in skin and mucous infections in all humans are caused by staphylococcal species. These organisms are mainly transmitted through skin contact, fomite contact, inhaling infected aerosolized particles, by pets, etc. Other risk factors include food poisoning, Respiratory Diseases, tooth cavities, Diphtheria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc.
Also Read: Gram-negative bacteria
For more information on various topics like Bacteria, gram-negative bacteria and other Bacterial Diseases, keep visiting BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where are the gram-positive bacteria found?
The spores of gram-positive bacteria can be found in the soil, air and inside the human body.
Name the types of gram-positive bacteria.
Gram-positive bacteria can be staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, Bacillus anthracis, and Corynebacterium diptheriae.

I am thankful for your very good explanation. Your site is a good reference for high school and college.