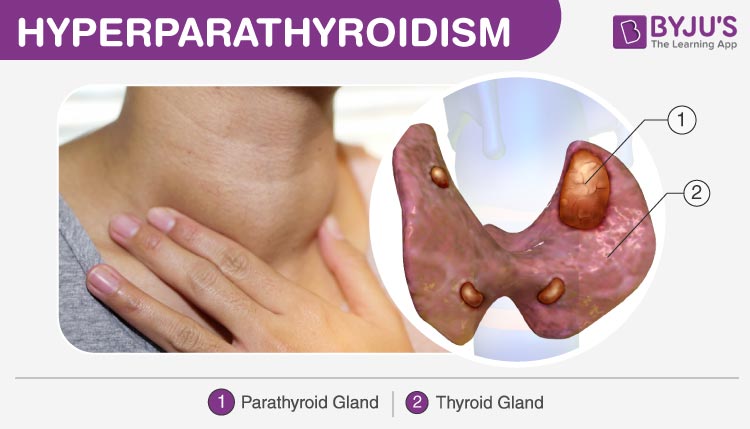
When there is an excess of parathyroid hormone produced in the patients, they are said to suffer from Hyperparathyroidism. The parathyroid glands are found in a pair on both the sides of the cricoid cartilage. They are small, almost the size of a pea and are fixed to the back of the thyroid gland.
The hormones produced by endocrine glands are essential for the regular operation of our bodies.
The parathyroid and thyroid glands are unlike organs, in spite of comparable terms and being adjacent to each other in the neck. The proportions of phosphorus, vitamin D, and calcium are regulated in our blood and bones by parathyroid hormone.
Types of Hyperparathyroidism
There are three types of hyperparathyroidism:
Primary hyperparathyroidism
This syndrome is mainly caused when one of our parathyroid glands becomes overactive and secretes an excessive amount of hormone. Some of the reasons for parathyroid ailments include non-threatening tumours on the glands and swelling in the pair of the gland. This condition could also be caused due to cancerous tumours, which would be counted as exceptional situations.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
This disorder is mainly observed when the calcium proportion in our body is dropped or reduced due to certain core ailments. Prolonged kidney illness also results in lowering Vitamin D and calcium, which results in secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Individuals with kidney ailments usually suffer from this syndrome. During tertiary hyperparathyroidism, the parathyroid gland becomes overactive and secretes an excessive amount of hormone despite the calcium proportions being normal.
Causes of Hyperparathyroidism
- Overactivity of parathyroid glands results in the surplus production of parathyroid hormone. This process takes place simultaneously either in one or in all glands. This main cause of this syndrome is related to several structural problems to parathyroid glands such as swelling of glands or a tumour.
- The intestine and kidney start absorbing huge quantities of calcium and sometimes also remove calcium from the bones. As the calcium proportion in our body is dropped, it results in increasing the production of parathyroid hormone by parathyroid glands. The production and discharge of this hormone will be standardized only when the calcium proportions in our blood are accurate.
Symptoms of Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism may or may not show any symptoms. When symptoms appear, they are often mild, or extreme or even severe. Below are a few symptoms of this condition:
- Exhaustion.
- Body pains.
- Loss of appetite.
- The weakness of muscle and joints.
- Constipated bowels.
- Motion sickness.
- Fatigue.
- Increased thirst for more urine production.
- Unable to concentrate and confusion.
- Depression.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of clarity.
- Recollection difficulties.
- Kidney stones.
- Osteoporosis- weakness and thinning bones.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
There are several tests and examinations available to conclude the symptoms as hyperparathyroidism. They include-
- General medical examination of the skin, eye, throat, pulse rate, etc.
- A blood test is performed to detect the calcium level and hormone level of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone including T3 and T4.
- CT, MRI, Thyroid, and Ultrasound Scans are conducted to detect the presence of a tumour or the swelling of the gland.
- Bone density test is done to calculate the mineral density in a bone by X-ray absorptiometry.
- A urine test is done to check the functioning of kidneys.
Treatment and Precautions for Hyperparathyroidism
There are few treatments available for this syndrome. Few antithyroid and radioactive iodine medication is taken to control the overproduction of parathyroid hormone. In extreme cases, surgery is performed to remove the thyroid gland. Before treating a patient with hyperparathyroidism, it is more important to check the age of a patient, type and causes of this syndrome, and functioning of the gland.
There are certain safety measures to be followed to control or to reduce the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism, which include:
- Practising meditation for stress and anxiety.
- Regular walk and exercise for stronger and healthy bones.
- Intake of more water and fresh fruit juice to avoid dehydration.
- Having a balanced diet including Vitamin D-rich food and calcium supplements to avoid weakness and thinning of bones.
- Avoid the use of tobacco, alcohol, and caffeine food products, which makes the symptoms worse.
To know more about the thyroid gland and thyroid diet, visit BYJU’S.

Comments