Table of Contents
Introduction
Germination is the fundamental process in which the sown plant seeds are grown into young plants or seedlings. Based on their growing conditions and the fate of the cotyledons, the process of germination is classified into two main types:
- Epigeal Germination
- Hypogeal Germination
Explore more: Seed Germination
Let’s learn more in detail about the types of Germination – Hypogeal Germination
What is Hypogeal Germination?
Hypogeal germination is a type of seed germination, which is typical for both the monocot and dicot seeds, where the cotyledons remain inside the soil.
The term Hypogeal germination is derived from the ancient Greek word, which refers to the below ground.
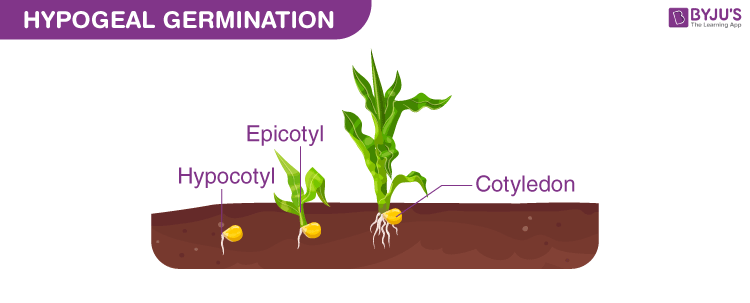
The Process of Hypogeal germination is described as:
During hypogeal germination:
- The cotyledons – a significant part of the seed embryo that remains under the soil.
- The plumule– the rudimentary shoot tip arising from the seed embryo emerges above the ground.
- The plumule arises out by pushing itself in the upward direction.
- This continues with the epicotyl- the seedling stem above the cotyledon, which rapidly elongates its structure.
Also Read: Cotyledon and their Types
Pros and Cons of Hypogeal Germination
The advantage of hypogeal germination is that the plant or the seedlings are protected from early grazing and the drawback or the disadvantage of hypogeal germination is that the plant cannot begin to synthesize its own food or photosynthesize until the true leaves have completely appeared.
Also Read: Photosynthesis
Hypogeal germination occurs in both monocotyledonous seeds including paddy, wheat, maize, etc. and dicotyledonous seeds, including pea, mango, groundnuts, etc.
Explore more: Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Seeds
This article concludes with an introduction to hypogeal germination. To know more about hypogeal germination, other related topics and important questions, keep visiting our website at BYJU’S Biology.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How do you distinguish between hypogeal germination and epigeal germination?
What is the role of the cotyledon(s) and the endosperm in the germination of seeds?
Role of the endosperm: Endosperm provides food or nutrition to the zygote during the process of embryogenesis (formation of embryos).

Comments