Table of Contents
Introduction
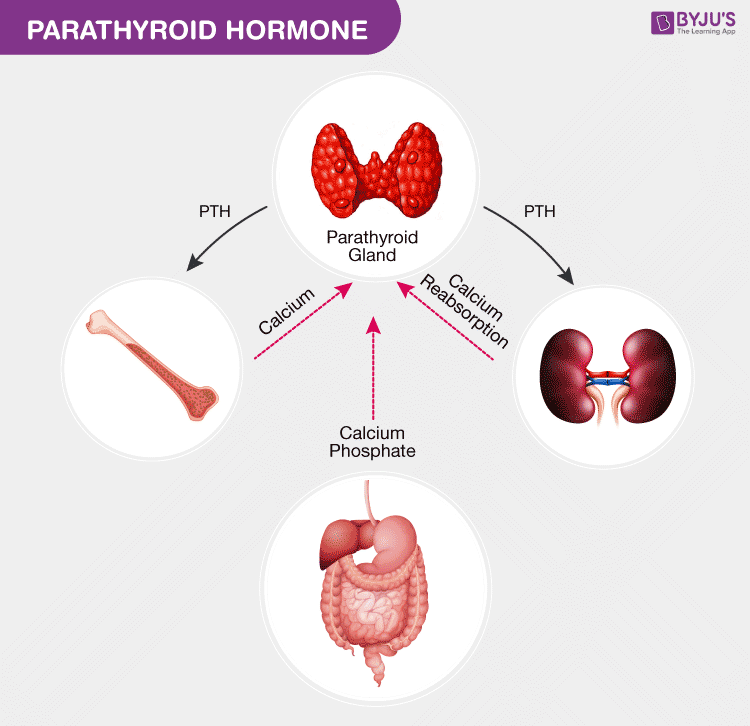
Parathyroid hormone is secreted by the four parathyroid glands. These tiny glands are present in the neck behind the thyroid glands. Parathyroid hormone controls and regulates the levels of calcium in the blood and raises their levels when they are too low. This gland performs its function through its actions on the bones, intestines, and kidneys.
There are two main types of Parathyroid hormone:
- Parathormone
- Calcitonin
The primary purpose of parathyroid glands is to regulate calcium in the blood in a very strict range between 9.0 and 10.1 mg/dL. Parathyroids also manage the amount of calcium in the bones and determine their strength.
Bones – The parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates the release of calcium from stores of calcium present in the bones into the bloodstream.
Intestine – PTH increases the calcium absorption in the intestine by food through its impacts and affects the metabolism of vitamin D.
Kidneys – PTH minimizes the calcium loss in the urine and also stimulates active vitamin D formation in the kidneys.
Parathyroid hormone Levels
What if the parathyroid hormone is too high?
Hyperthyroidism is an endocrine disorder which causes oversecretion of parathyroid hormone in the body. This oversecretion of PTH causes an abnormal rise in the blood calcium levels.
Oversecretion of parathyroid hormone can make a person depressed, irritable, insomnia, memory loss, lack of energy and worried are the most common symptoms in patients with parathyroid disease.
It is of three types.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
In primary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism, the level of calcium is high due to excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone.
In secondary hyperparathyroidism, the level of calcium is low due to other factors like kidney disease.
What if the parathyroid hormone is too little?
Hypoparathyroidism is a rare condition in which there is low production of parathyroid hormone in the body this condition results in abnormally low levels of calcium in the blood. It is treated medically with vitamin D analogues and oral calcium supplements.
When the calcium level falls down people get a tingling sensation or cramps in the hand muscles. A sudden drop can cause an individual to feel weird, foggy and the brain not functioning accurately.
To learn more about Parathyroid hormone, visit BYJU’S.
Related Links:
| Hypothyroidism |

Comments