As we all know plant growth regulators are simple organic molecules which play a vital role in the growth and development of plants. Apart from these plant hormones or phytohormones, plant growth is also influenced by the certain external factors like temperature, length of a day, light and dark exposures, etc.
From the observation of W. W. Garner and H. A. Allard, every plant does not require the same amount of light and dark for their flowering. Plants require only a specific phase of light and darkness for their flowering and this term is known as the critical period. Based on the observations, they classified plants into three categories.
- Long day plants — Plants which require longer exposure to light than their critical period. eg. oats, wheat
- Short day plants– Those plants which require a shorter period than their critical period. eg. Chrysanthemum, tobacco, etc.
- Day-neutral plants –The plants in which flowering is unaffected by the photoperiod. eg. maize, sunflower, etc.
Here we will discuss three phenomena- photoperiodism, vernalization and seed Dormancy which influences the growth of a plant.
Photoperiodism
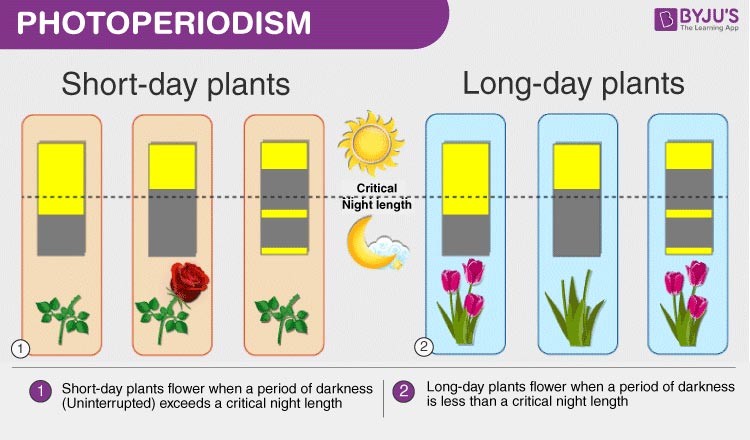
Photoperiodism is the phenomenon which is seen in most of the plants. It is the developmental responses of plants in which they are exposed either more towards the day or night for a particular length of day to induce flowering.
The continuation of the dark period is of equal importance. Therefore, it can be said that in certain plants, flowering depends on the duration of the light and dark exposures. This particular response to light and dark is known as photoperiodism.
The plants which require more exposure to the light are called long-day plants while those which require less exposure to the light are called short-day plants. The length of day or night varies from plants to plants.
Examples of long-day plants include irises, lettuce, spinach, radishes, etc. Christmas cactus, poinsettias chrysanthemums, etc are few examples of short-day plants.
Vernalisation
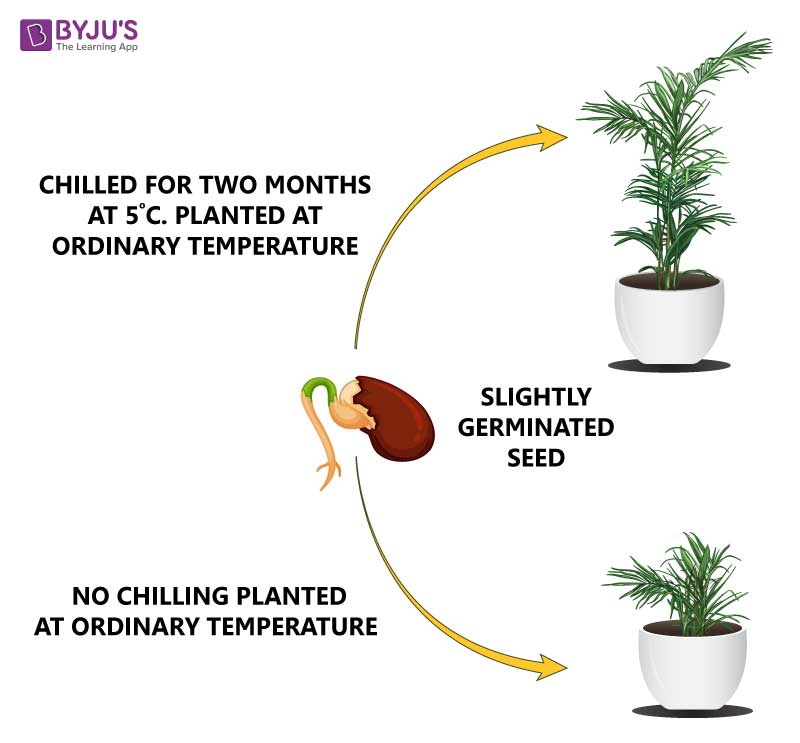
This term is used to describe the dependence of certain plants on exposure to low temperature for flowering qualitatively or quantitatively. It inhibits the development of reproductive organs in the growing season and permits the plant to have adequate time to reach its maturity stage.
Vernalisation is the phenomenon practised for the production of earlier crops. They are mainly cultivated in places where they naturally do not grow. Vernalisation helps in accelerating the plant breeding.
For example – the wheat plants which has two varieties – winter and spring. Beets, cabbage, turnips onions, are examples of vernalization.
The winter variety is planted in autumn; they get time to germinate and come out as small seedlings in winter, continue to grow in spring and are harvested in mid-summer.
Recommended Video:
Dormancy of Seeds
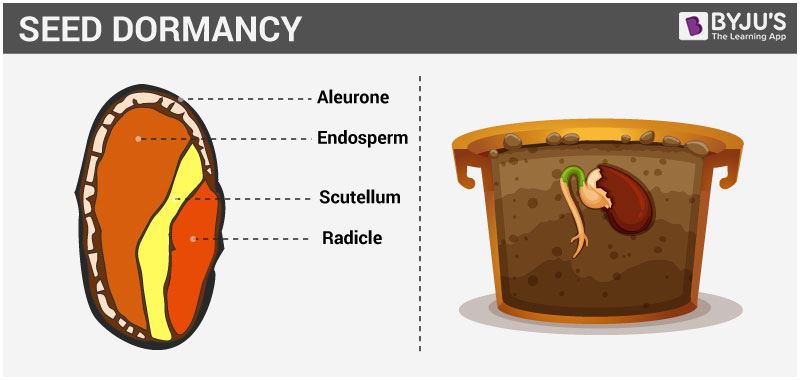
We often notice that seeds of some plant species do not germinate even after providing favourable conditions. This state of the seed is known as dormancy. The reason for this condition is that they need a period of rest or storage before becoming capable of germination. This period may vary from a few days to years.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Photoperiodism, Vernalisation and Seed Dormancy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is photoperiodism?
Photoperiodism refers to the flowering response of the plant to the lengths of the dark and light periods. This helps the flower to bloom in different seasons.
How is photoperiodism different from vernalisation?
Vernalization is the process of inducing flowering in plants by exposing them to low temperatures. On the contrary, photoperiodism is the process by which the flowering in the plants is affected by the relative lengths of dark and light periods.
What is photoperiod?
Photoperiod is the time each day when a plant or animal is exposed to light in a 24-hour period. Different plants require a specific length of light exposure to enter different stages of life cycles.
How are photoperiodism and vernalization important?
Photoperiodism is required to regulate flowering in plants. On the contrary, vernalization allows the plant to reach vegetative maturity before reproduction could occur.
How is seed dormancy caused?
The seed coat prevents oxygen and water from permeating into the seed. This makes the seed dormant. Seed dormancy is also caused by preventing chemicals from entering inside the seed.

Comments