Carbohydrates are a major source of food and an important form of energy for most living organisms. A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The two basic compounds that makeup carbohydrates are – Aldehydes and Ketones.
Carbohydrates are found in all-natural and processed foods. The three types of carbohydrate are:
- Monosaccharides– Glucose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides.
- Disaccharides–Sucrose and maltose are examples of disaccharides.
- Polysaccharides– Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are examples of polysaccharides.
Here, in this article, let us explore in further detail about the Polysaccharides, its types, properties and its functions.
Table of Contents
What are Polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are major classes of biomolecules. They are long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides. These complex bio-macromolecules functions as an important source of energy in animal cell and form a structural component of a plant cell. It can be a homopolysaccharide or a heteropolysaccharide depending upon the type of the monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides can be a straight chain of monosaccharides known as linear polysaccharides, or it can be branched known as a branched polysaccharide.
Also Read: Biomolecules
Characteristics Of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides have the following properties:
- They are not sweet in taste.
- Many are insoluble in water.
- They are hydrophobic in nature.
- They do not form crystals on desiccation.
- Can be extracted to form a white powder.
- They are high molecular weight carbohydrates.
- Inside the cells, they are compact and osmotically inactive.
- They consist of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. The hydrogen to oxygen ratio being 2:1.
Types Of Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are categorized into two types:
- Homopolysaccharides.
- Heteropolysaccharides.
Homopolysaccharidesn
A polysaccharide that contains the same type of monosaccharides is known as a homopolysaccharide. Some of the important homopolysaccharides are:
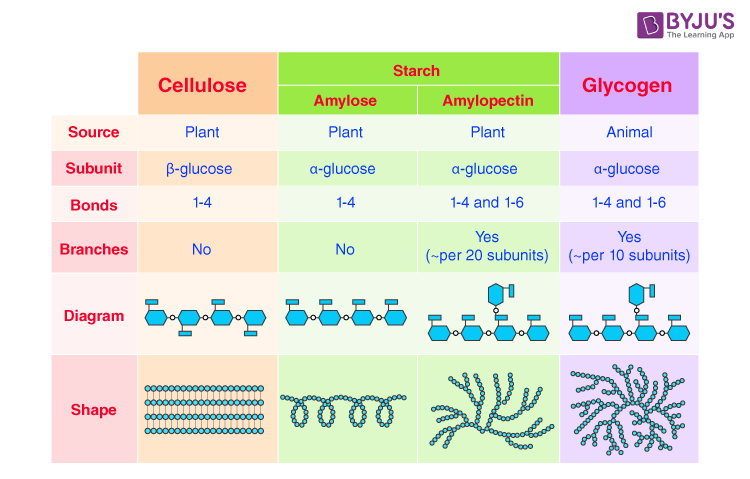
- Glycogen: It is made up of a large chain of molecules. It is found in animals and fungi.
- Cellulose: The cell wall of the plants is made up of cellulose. It comprises long chains of ꞵ-glycosides.
- Starch: It is formed by the condensation of amylose and amylopectin. It is found largely in plants, fruits, seeds, etc.
- Inulin: It is made up of a number of fructofuranose molecules linked together in chains. It is found in the tubers of dahlia, artichoke, etc.
Heteropolysaccharides
A polysaccharide that contains different types of monosaccharides is known as a heteropolysaccharide. Some of the important heteropolysaccharides are:
- Hyaluronic Acid: It is made up of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-glucosamine. It is found in connective tissues and skin.
- Heparin: It is made up of D-glucuronic acid, L-iduronic acid, N-sulfo-D-glucosamine and is largely distributed in mast cells and blood.
- Chondroitin-4-sulfate: Its component sugars are D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine-4-O-sulfate. It is present in the cartilages.
- Gamma globulin: N-acetyl-hexosamine, D-mannose, D-galactose are the component sugars of this polysaccharide. It is found in the blood.
Functions Of Polysaccharides
The polysaccharides serve as a structural organization in animals and plants. Other functions of polysaccharides include:
- They store energy in organisms.
- Due to the presence of multiple hydrogen bonds, the water cannot invade the molecules making them hydrophobic.
- They allow for changes in the concentration gradient which influences the uptake of nutrients and water by the cells.
- Many polysaccharides become covalently bonded with lipids and proteins to form glycolipids and glycoproteins. These glycolipids and glycoproteins are used to send messages or signals between and within the cells.
- They provide support to the cells. The cell wall of plants is made up of polysaccharide cellulose, which provides support to the cell wall of the plant. In insects and fungi, chitin plays an important role in providing support to the extracellular matrix around the cells.
Also Read: Proteins
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about the carbohydrates, its types, structure, sources and other related topics.

Good explanation of everything