The waste produced by a nuclear power plant or lab is referred to as radioactive waste. They include radioactive substances that are dangerous to the environment and the majority of biological forms. The wastes degrade over time. Therefore, they would be kept in a secure location until they lose their radioactivity and cease to be a danger to the environment. The time frame mentioned before is dependent on the radioactive isotopes and type of waste.
These include substances that are radioactive, such as radium, carbon, radon, uranium, and thorium. The soil, water, and rock all contain traces of these elements. While nuclear fuel manufacturing, mining, explosions at nuclear power plants, and the production of radioactive isotopes and nuclear fuels are all examples of man-made radiation.
Nuclear Waste Management
A person’s health may be in danger if they are exposed to radioactive wastes at levels higher than the background radiation. High-level radioactive waste exposure can lead to cancer, birth deformities, and other problems. The government is responsible for the safe disposal of radioactive waste. The collection, transportation, storage, and disposal of trash constitute the waste management cycle.
Radioactive waste Pollution

Water and air contamination caused by radioactive elements is known as radioactive pollution. It can produce dangerous pollution if radioactive waste is not disposed of properly. An illustration would be the significant aftereffects of the first atom bomb during the Second World War, which the world will never forget. Animal and plant life were totally decimated. The radiation from the bomb caused over 30% of the population to be either burned or killed, while another 30% suffered catastrophic injuries. Even with these outcomes, various countries are still engaged in a nuclear arms race that is also contributing to radiation pollution.
Types of Radioactive Wastes
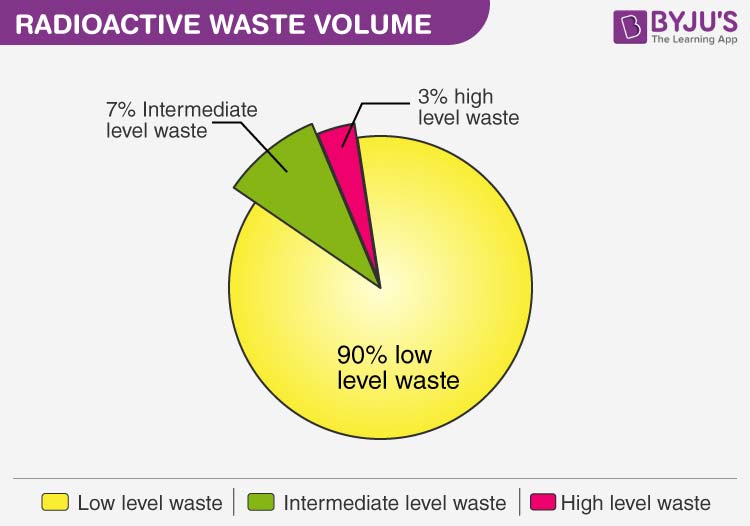
Exempt waste or Very low-level waste
Very low-level wastes are the least dangerous wastes (VLLW). Examples of VLLW include the materials that have been destroyed during demolition or rehabilitation projects, such as concrete, plaster, brick, metals, valves, and pipelines.
Low-Level Wastes: Typically come from the industrial and hospital waste streams. contains transient radiation and is made up of paper, rags, tools, garments, cotton, filters, etc. Before disposal, it is frequently burned or cremated.
Intermediate level waste
High levels of radioactivity are present in this form of trash, which must be buried. They include resins, metal fuel, and chemical waste. For disposal, the nonsolids are occasionally turned into bitumen.
High-Level Waste
High -Level waste is produced when uranium fuel in a nuclear reactor is burned. They need cooling and shielding because they are hot and very radioactive.
Major reprocessing facilities with an annual capacity of around 5000 tonnes exist in France, the UK, and Russia. India is looking into and exploring safe trash disposal on land. To lessen the consequences of radioactive elements, the government must take action to confine the waste.
To learn more about Radioactive wastes and Pollution, visit BYJU’s.

Comments