What are Algae?
An alga is a singular form, and Algae is plural.
An alga is the living, eukaryotic, and photosynthetic organism usually grown in moist areas. Hence, they are called the members of aquatic organisms. Alike plants, these organisms also contain chlorophyll and other biological pigments that act as a primary colouring agent and also helps in absorbing energy from light.
Also read: Algae
Types of Algae
These diverse group of aquatic organisms is neither plant nor animals. Based on their general features, algae are grouped into Kingdom Protista. According to the records, there are more than 50,000’s known species of Algae and based on their habitat, presence of biological pigments and other characteristics they are classified into seven different types.
- Pyrrophyta
- Euglenophyta
- Red algae or Rhodophyta
- Brown algae or Phaeophyta
- Green algae or Chlorophyta
- Yellow-green algae or Xanthophyta
- Golden-brown algae or Chrysophyceae
Here, let us learn more about the Red algae, its general characteristics and uses.
Also refer: Thallophyte
Rhodophyta
The scientific name of Red Algae is Rhodophyta and they belong to Class Rhodophyceae. There are two classes of red algal namely the Florideophyceae and Bangiophyceae. Both Florideophyceae and Bangiophyceae comprise 99% of red algal diversity in marine and freshwater habitats.
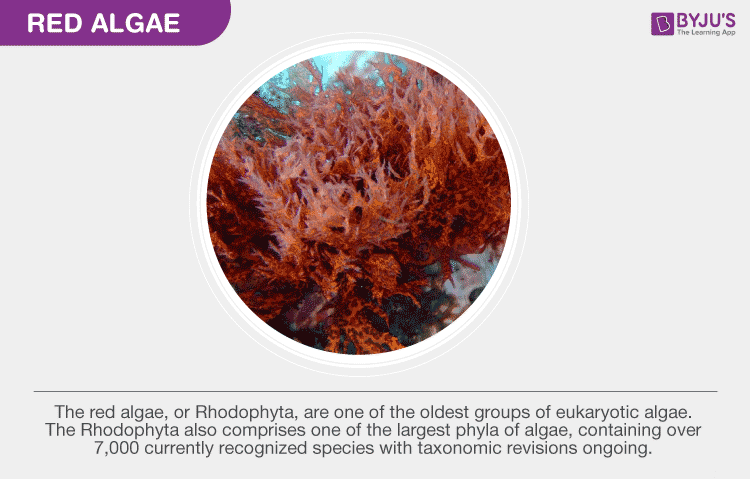
Red algae or Rhodophyta – It is a distinctive type of species that are mostly found in the freshwater lakes and are the oldest type of eukaryotic algae. They are red in colour due to the presence of a pigment called chlorophyll A, phycocyanin, and phycoerythrin. They are the member of the tribe Amansieae (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales, Rhodophyta), in which only Aneurianna and Lenormandia Sonder have foliar blades. They are the distinctive type of species, mostly found in the deep freshwater bodies.
According to the original description of the genus (Phillips, 2006), Aneurianna differs from Lenormandia in having endogenous branching and elliptic surface pattern with various irregularly ordered ellipses on the blade (so-called “elliptical areolation”) and incurved or inflexed apices, in contrast to the absence of endogenous branching, rhombic surface pattern with regularly arranged rhombi (“rhombic areolation”).
General Characteristics of Red Algae
Red algae are different from other groups except for diatoms. Listed below are general characteristics of Red Algae.
- Lack of flagella and centrioles
- Presence of photosynthetic pigments
- Found both in marine and freshwater
- They show biphasic or triphasic life cycle patterns.
- They are a multicellular, filament, blade structure.
- Stored food is in the form of starch and polymers of galactan sulphate
- A pit connection (hole in the septum) is formed between two algal cells.
- Have a diffuse growth pattern- Apical growth, Complex oogamy (triphasic)
- These group of red algae is generally found in tropical marine locations
- The mode of nutrition may either be saprophytic, parasitic or also epiphytic.
- Their cell walls consist of cellulose and many different types of carbohydrates.
- Grow on solid surfaces independently or sometimes found attached to other algae.
- Presence of pit in the cell walls, through which cytoplasmic connections are maintained.
- The male sex organs are known as spermatangium and the female sex organs are called carpogonia or procarp.
- Mode of Reproduction: It takes place by all the three means: vegetative, asexual and sexual. Asexual mode of reproduction is by monospores and during the sexual mode of reproduction, they undergo alternation of generations.
Uses of Red Algae
Red Algae has great ecological importance. They form a vital part of the food chain and are also involved in producing about 40 to 60 per cent of the total global oxygen for both terrestrial habitat and other aquatic habitats. Listed below are a few ecological and commercial importance of red algae.
- Algae provide natural food for fish and other aquatic animals.
- Red alga is the most important commercial food in Japan and in the region of North Atlantic.
- Agar or agar-agar, a jelly-like substance which is used in puddings, dairy toppings and other instant food products is extracted from Red algae.
- Red algae are used as the source of food for thousands of years as they are high in vitamins, minerals, a rich source of calcium, magnesium, and antioxidants.
- They are sources of dietary fibre as they have the ability to promote healthy circulation, lower bad cholesterol and regulate blood sugar levels.
- They are also involved in nourishing your skin, boosting the immune system and contributing to bone health.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to know more about the algae, their types, general characteristics, important facts about the algae, red algae, and blue-green algae.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are red algae?
Red algae are the oldest group of eukaryotic algae containing over 6000 species. They fall under the kingdom Protista and phylum Rhodophyta. They contain chlorophyll and can prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
Why are red algae named so?
Red algae are named so because of their red colour which they obtain from the pigment Phycoerythrin. The pigment reflects red light and absorbs blue light and hence give a reddish appearance to the algae.
What distinguishes the red algae from other algae?
The only difference between the red algae and other algae is that the red algae lack flagella, the whip-like structures that help in locomotion and perform sensory functions.
What is the importance of red algae?
Red algae form an important part of the ecosystem and are consumed by various organisms such as crustaceans, fish, worms and even humans. Red algae are also used to produce agar that is used as a food additive. They are rich in calcium and also used in vitamin supplements.
Give a few examples of red algae.
- Irish moss
- Dulse
- Laver (Nori)
- Coralline algae
Where are red algae found?
Red algae are commonly found in coral reefs and tide pools. They have the ability to survive at a greater depth than other algae because the pigment Phycoerythrin absorbs the blue light that can penetrate deeper than any other light wave. This allows red algae to carry out photosynthesis at a greater depth.
What are the different pigments present in red algae?
The different pigments present in red algae are:
- Red Phycoerythrin
- Blue Phycocyanin
- Zeaxanthin
- Carotenes
- Lutein

Nice information …keep it up
good useful article