Table of Contents
- Reproduction Definition
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
- Reproduction in Plants
- Reproduction in Animals
Reproduction Definition
“Reproduction is the process of producing offspring that are biologically or genetically similar to the parent organism.”
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is a biological process by which an organism reproduces an offspring that is biologically similar to the organism. Reproduction enables and ensures the continuity of species, generation after generation. It is the main feature of life on earth.
Let us have a detailed overview of reproduction, its types and the modes of reproduction in plants and animals.
Types of Reproduction
There are basically two types of reproduction:
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
“Asexual reproduction refers to the type of reproduction in which only a single organism gives rise to a new individual.”
Binary Fission (Asexual Reproduction) – Diagram
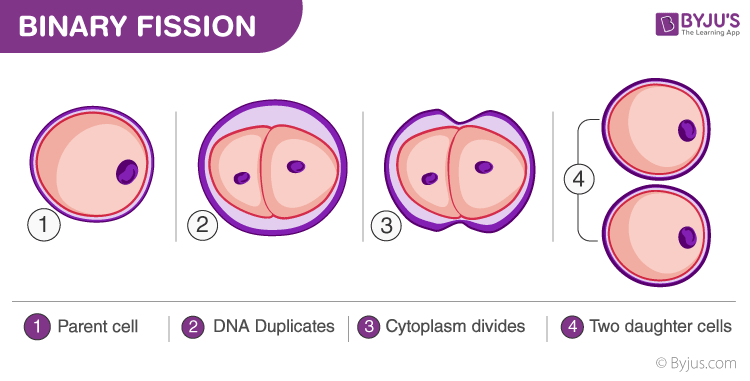
Asexual reproduction does not involve the fusion of gametes, and therefore, the offsprings produced are genetically identical to the parent. The organisms produced by asexual reproduction are less diverse in nature. This type of reproduction is practised widely by unicellular organisms.
The process involves rapid population growth and no mate is required for the process. However, a lack of genetic diversity makes organisms more susceptible to diseases and nutrition deficiencies.
Asexual reproduction is further divided into:
- Binary Fission: In this, the cell splits into two each cell carrying a copy of the DNA from the parent cell. For eg., amoeba.
- Budding: In this, a small bud-like outgrowth gives rise to a new individual. The outgrowth remains attached to the organism until it is fully grown. It detaches itself and lives as an individual organism. For eg., hydra
- Fragmentation: In this, the parent organism splits into several parts and each part grows into a new individual. For eg., Planaria
- Sporogenesis: In this type of reproduction, a new organism grows from the spores. These can be created without fertilization and can spread through wind and animals.
Also Read: Modes of reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
“Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves the production of an offspring by the fusion of male and female gametes.”
Sexual Reproduction Diagram
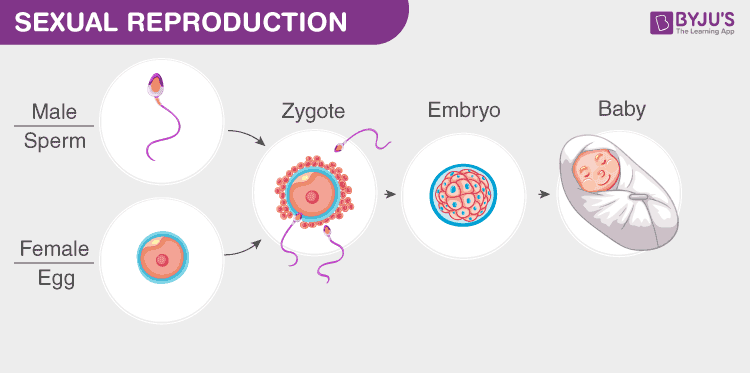
In sexual reproduction, male and female gametes are formed to produce an offspring. These gametes are either formed by the same individual or by different individuals of the opposite sex.
This process is usually slow and complex compared to asexual reproduction. The organisms so produced are genetically diverse. Thus, they can evolve along with the changing climatic conditions. Humans and many multicellular organisms exhibit a sexual mode of reproduction.
Reproduction in Plants
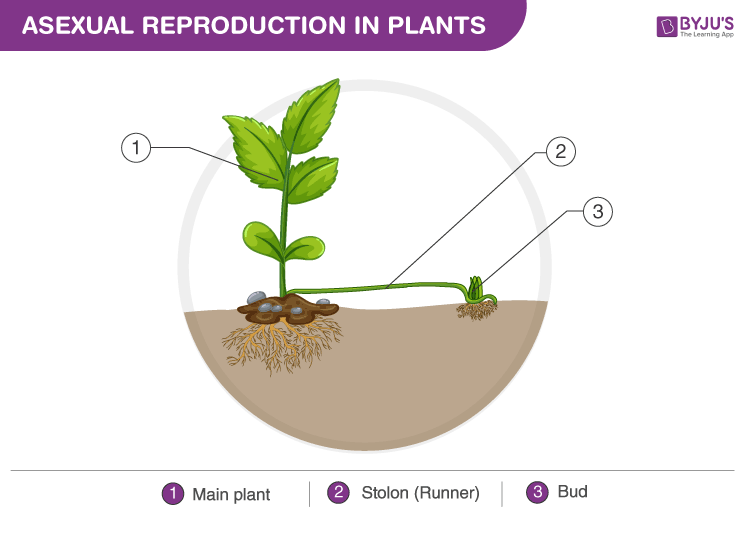
Plants reproduce by sexual and asexual means. Vegetative reproduction is the main mode of plant reproduction. Roots such as a corm, stem tuber, rhizomes and stolon undergo vegetative propagation.
Diagram of Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual reproduction in plants takes place through pollination in which the pollen grains from the anther of a male flower transfer to the stigma of the female flower.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants – Diagram
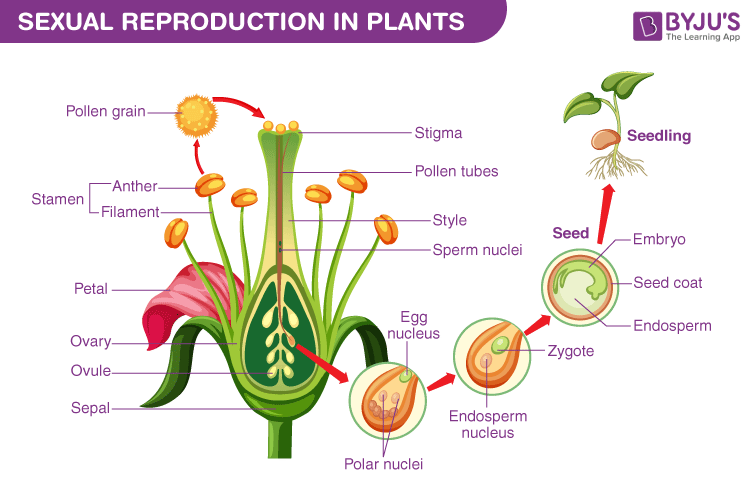
A few plants produce seeds without fertilization and the process is called apomixis. Here, the ovule or the ovary gives rise to new seeds.
Also Read: Reproduction in plants
Reproduction in Animals
Animals reproduce sexually as well as asexually. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes. This process is known as fertilization. Fertilization can be external or internal. External fertilization is the process in which the male sperm fertilizes the female egg outside the female’s body. On the contrary, in internal fertilization, the fusion of male and female gametes takes place inside the body of the female.
Asexual reproduction involves reproduction processes such as binary fission, budding, fragmentation, etc. The organisms have no reproductive systems and therefore no formation of male and female gametes takes place.
Thus, we see how beneficial reproduction is to continue life on earth.
Recommended Videos:

Also Read: Reproduction in animals
To know more about reproduction, and different types of reproduction, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download the BYJU’S app for further reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Define Reproduction.
Define Asexual Reproduction.
What are the types of Asexual Reproduction?
Different types of Asexual Reproduction are:
a) Binary Fission
b) Budding
c) Fragmentation
d) Sporogenesis
What are the advantages of Sexual Reproduction.
Variations: Due to recombination and crossing over, sexual reproduction brings about variations in species. Variations are essential for the individuality and evolution of species.Better adaptability: Increased variability due to sexual reproduction helps in better adaptability of species.Evolution: It helps in the evolution of species.
Harmful traits can be removed by a selection of better-adapted individuals or maybe not be expressed due to the reshuffling of gene pairs.
What is the difference between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction?
The differences between Sexual and Asexual reproduction are:
| Sexual | Asexual |
| Two parents take part | Single parent |
| Variation occurs in offspring | Offspring are genetically identical to each other and to their parent |
| Fertilization takes place | No Internal fertilization or External fertilization |
| Gametes are involved | No gametes |
| Mixing of hereditary material | No mixing of hereditary material |

Thank you
Nice class
Good class
Very Well written document.
Proudly to be a biologist. Thank u
So easy explanation
Very good class
super
So easy explanation Thank you
Very very easy explanation
This is great
Excellent
Thank you I love biology it’s my favourite subject
Thank you for helping us
very helpful 🙂
thank you
Very easy explanation
it was very helpful
Excellent
Very good explanation
Keep it up.
Nice class