Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Sexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction: Male and Female Reproductive Organs
- Male Reproductive Organs
- Female Reproductive Organs
- Fertilization
- Viviparous and Oviparous Organisms
Introduction
All living things including, humans, animals, and plants reproduce offspring of their own kind. Few lay their eggs, few reproduce by giving birth to their young ones and few living things like plants reproduce by producing seeds.
Reproduction is the fundamental biological process of producing individuals of the same kind of species. This process enables and ensures the continuity of species, generation after generation. There are two types of reproduction: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction
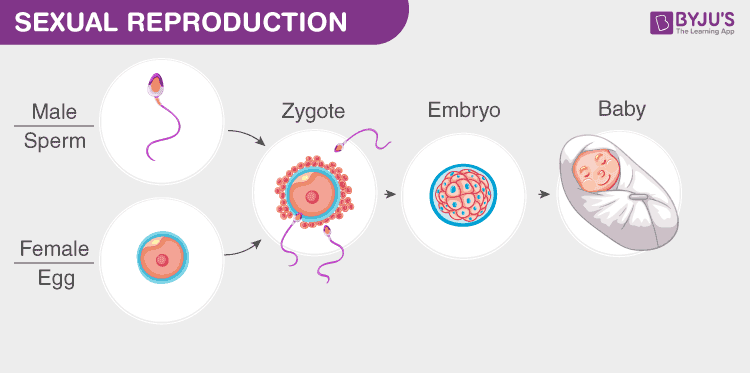
In this mode of reproduction, there is an involvement of two parents and the offspring has a fusion of the characteristics of both parents.
Recommended Video:

Sexual Reproduction Male and Female Reproductive Organs
Sexual reproduction is a general and fundamental mode of reproducing young ones in animals, humans, and plants. Compared to asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction is lengthy and more complex. An organism that follows sexual reproduction has specific reproductive organs. Both males and females have different sets of reproductive organs in their respective systems.
Male Reproductive Organs
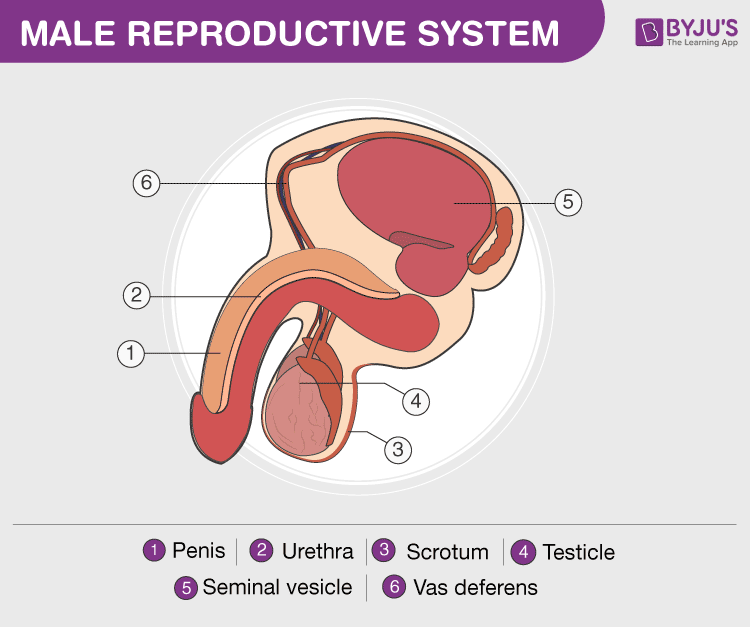
The male reproductive organs are located in the lower abdomen around the pelvic region. The major function of the male reproductive organs is to deliver sperm for fertilization. The male reproductive system is mainly composed of:
- Scrotum– A small muscular sac-like organ which is located below and behind the penis. It consists of the testes and is mainly involved in maintaining the temperature required for sperm production.
- Testes – It is also called testicles. They are a pair of oval-shaped organs which are mainly responsible for the sperm production and synthesis of testosterone- male hormones.
- Penis– It is the primary sexual organ which serves as both a reproductive organ as well an excretory organ and is used for the purpose of sexual intercourse. It is a cylindrical tube-like organ with a small opening at the top and is extremely sensitive as it becomes vertical when a person is sexually aroused. Semen, containing sperm, is ejaculated from the opening at the top when the person reaches sexual climax.
- Urethra– A narrow tube-like structure that conducts urine and semen from the urinary bladder to the penis.
- Vas Deferens– It is a muscular tube that carries mature sperm produced in the testes to the urethra.
Female Reproductive Organs
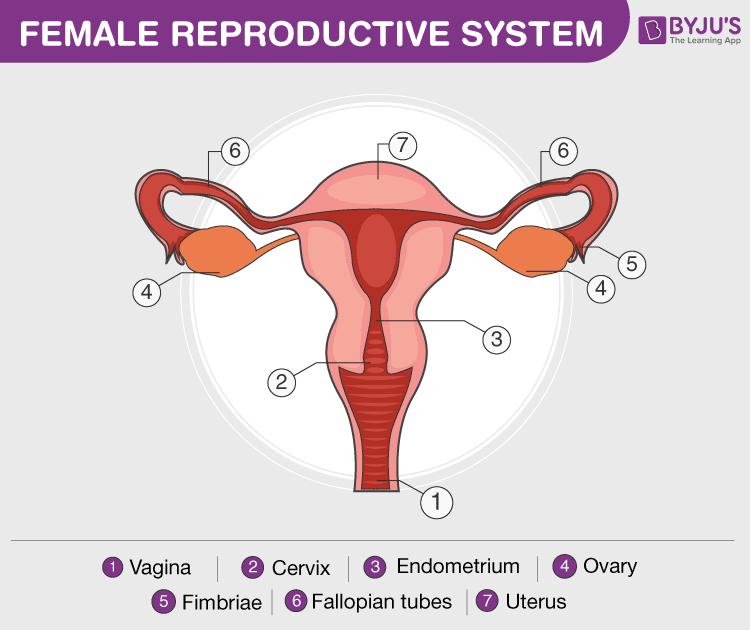
The female reproductive organs are located near the lateral walls of the pelvic cavity which consists of the following major organs:
- Ovaries– They are a pair of organs which are mainly responsible for the production and storage of the ovum, or egg, which are the sex gametes in a female.
- Uterus– It is commonly known as the womb. It is a pear-shaped muscular bag-like organ with a strong muscular lining that holds the baby after fertilization. The uterus is referred to as the site for embryo development as it protects the fertilized ovum and holds it till the baby is mature enough for birth.
- Cervix– A cylinder ring-shaped tissue which is composed mainly of fibromuscular tissue. It is located at the lowermost portion of the uterus and is involved in connecting the uterus and the vagina.
- Vagina– – The primary sexual organ which serves as both excretory organ as well as a reproductive organ. It is a muscular and tubular part of the female genital tract that opens outside the body and the opening of the vagina is called the vulva, which also includes the clitoris, labia, and urethra. The vagina connects the cervix to the external female body parts and it is the path for the penis during coitus as well as a fetus during delivery.
Fertilisation

Fertilisation is the fusion of haploid gametes- sperm with egg to produce the diploid zygote. It is the crucial stage of reproduction as, without fertilisation, sexual reproduction is futile. This process is of two types.
- Internal fertilisation:
In internal fertilisation, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place within the female parent. In this process, the sperms are released into the body of the females during copulation and the resulting zygote develops internally within the mother and gets its nourishment from her. This type of fertilisation is found in all humans, and in most animals like cats, dogs, cows, lions, etc.
- External fertilization:
In external fertilization, the fusion of sperm and egg is carried outside the female parent. This type of fertilization is found in a minority of organisms. In this process, the female parent lay her eggs and later, these eggs are fused by the male parent by ejecting his sperms over the eggs.
- Development of embryo
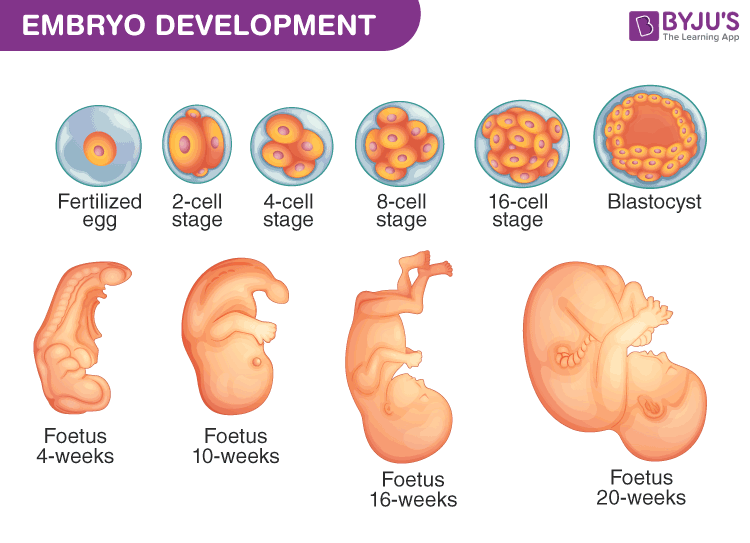
After the process of fertilization, the formed diploid zygote divides mitotically and develops into an embryo. This process is called embryogenesis in which the cell differentiates and modifies accordingly. Embryogenesis is carried out in the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week, the embryo is called a fetus.
Viviparous and Oviparous Organisms

Animals are classified into oviparous and viviparous based on the zygote development that is internal fertilization and external fertilization.
In oviparous organisms, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place outside the female parent by laying eggs. Birds, reptiles, and egg-laying mammals are classified as oviparous.
In all viviparous organisms, the fusion of sperm and egg takes place within the female parent and gives birth to young ones. All mammals excluding egg-laying mammals are classified as viviparous.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about sexual reproduction and reproductive organs.

good matter
Helpful for students learning online at home.