Spores are haploid unicellular bodies that are produced as a result of sexual or asexual reproduction in eukaryotic organsims such as algae, bacteria, fungi and some plants. The process of formation of spores is referred to as sporogenesis.
Spores are reproductive cells that are capable of giving rise to a new organism as compared to gametes that require to fuse with another gamete to give rise to new individuals.
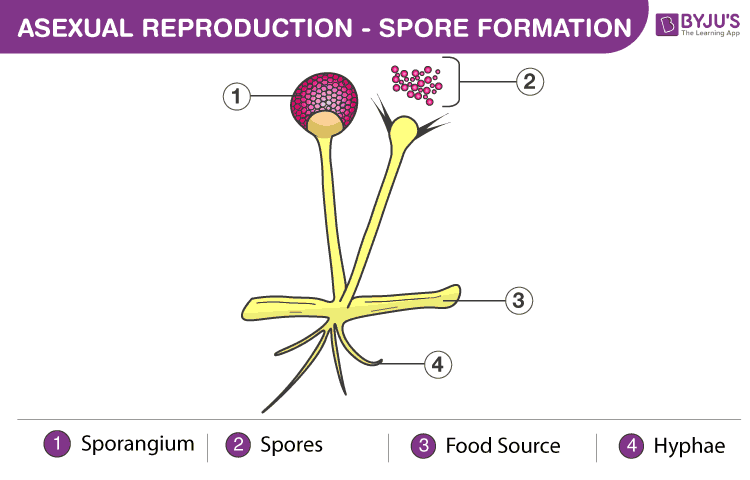
Below is a diagram of a fungal species showing formation of spore through asexual reproduction.
Examples
- In fungi, the spores are formed on a reproductive knob-like structure known as the sporangium. They produce minute haploid spores that grow into new organisms in favourable conditions. E.g., Aspergillus, Penicillium.
- In bacteria, another type of spores called endospores are formed as a result of unfavourable conditions. It is a non-reproductive structure that is not a true spore. E.g., Bacillus, Clostridium.
- In plants, spore formation is the sole means of asexual reproduction. Plants follow an alternation of generation life cycle, where diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores and ultimately gives rise to haploid gametophyte. E.g., liverworts, mosses and hornworts.
Also Read:
Comments