Virology Definition
“Virology is the branch of science that deals with the study of viruses.”
What is Virology?
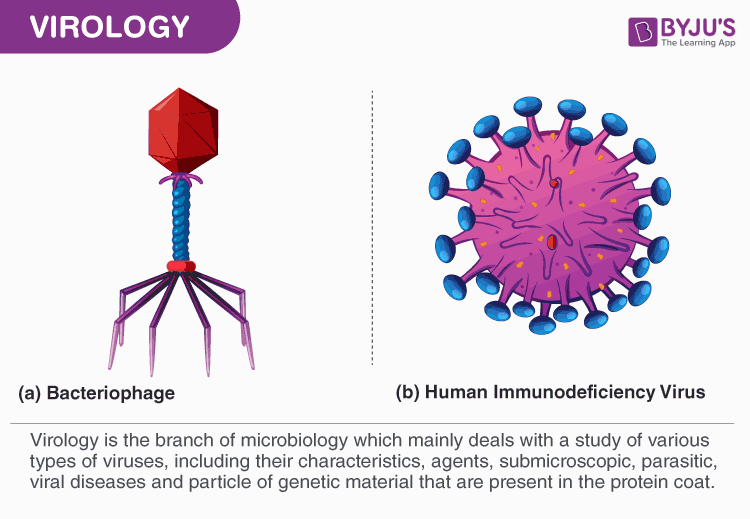
Virology is the branch of microbiology which mainly deals with a study of various types of viruses, including their characteristics, agents, submicroscopic, parasitic, viral diseases and particle of genetic material that are present in the protein coat.
Virology is a stream of science that mainly focuses on aspects such as their immunity, the ability to destroy or infect the host cells, their evolution, classification, structure, composition, several ways of infecting, different ways of culturing them, their use in laboratory, various methods to isolate them and their physiology.
Read on to explore what is virology and different aspects related to it.
Viruses
Viruses are non-cellular microscopic organisms, which are composed of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They belong to the family viridae and genus virus.
Characteristics of Viruses
- They have no cell nucleus.
- They do not have an organized cell structure.
- They typically have one or two strands of DNA or RNA.
- They are enclosed in a protective coat of protein called the capsid.
- They do not respire, do not metabolize and do not grow but they do reproduce.
- They are considered both as living and nonliving things, as they are inactive outside the host cell, and are active when present inside host cell.
Types of Viruses
Based on the type of nucleic acid, viruses are classified into the following types:
RNA Virus
The virus that possesses RNA as genetic material is called RNA virus. They can either be a single-stranded or a double-stranded RNA. Some of the diseases caused by the RNA virus to humans include common cold, hepatitis, polio, West Nile fever, influenza, SARS, and measles. All plant viruses are examples of the RNA virus.
Mutation rates are higher for the RNA virus. Therefore, it may be considered as a one of the main reason for lacking back in preventing effective vaccines to treat and prevent certain viral diseases.
Double-stranded RNA virus comprises of distinct virus that differs widely based on host-virus such as fungi, bacteria, genome, virion, and organization.
A single-stranded RNA are categorized based on senses that are positive sense or negative sense.
- Positive-sense RNA is similar to mRNA. They are usually translated into host cells.
- Negative-sense RNA must be converted into positive sense RNA before translation using RNA polymerase.
DNA Virus
The virus that possesses DNA as a genetic material is called DNA virus. They are DNA dependent and they replicate using DNA polymerase. They are usually double stranded DNA but in some cases, they can either be single-stranded DNA.
Bacteriophages, cyanophages and most of the animal virus are examples of DNA virus.
Based on the type of host and genetic material. There are three types of virus.
- Animal viruses –The viruses which infect and live inside the animal cell including humans are called animal viruses. They contain DNA or RNA as genetic material. Some examples of animal viruses are rabies virus, influenza virus, poliovirus, mumps virus, etc.
- Plant viruses – The viruses which infect plants are called as the plant viruses. They contain RNA as a genetic material, which remains enclosed in the protein coat. Some examples of plant viruses are potato virus, tobacco mosaic virus, beet yellow virus, turnip yellow virus etc.
- Bacteriophage – The viruses which invade and infects bacterial cells are called as the bacteriophage. They contain DNA as genetic material. There are varieties of bacteriophages. Usually, each kind of bacteriophage will attack only one species or only one strain of bacteria.
Viral Disease
There are many viruses that can infect people and make them sick. One of the most common viral infectious diseases is influenza which are the main causes of flu. Other diseases caused by virus include the common cold, measles, mumps, yellow fever, hepatitis, AIDS, etc.
Some virus called oncovirus also leads to a certain form of cancers. The most common among them is cervical cancer and liver cancer.
Clinical Virology and Veterinary Virology
Clinical virology is the field of virology concerned with the study of viruses that cause human pathologies. Veterinary virology, on the other hand, is the field of virology that deals with the prevention and treatment of animal viruses, viral agents and other diseases caused by viruses. For eg., prion diseases, artery virus, pestivirus, etc. Veterinary virology is also an important field in clinical virology.
To know more about what is virology, its definition and its various characteristics, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.
Related Links
| Virus | Microbes |
| Microbiology | Viral Diseases |

Comments