According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 10.
Carbohydrates are classified into three groups viz monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Glucose is obtained by the digestion of starch. Polysaccharides and disaccharides are formed by the monosaccharides connected with glycosidic linkages between them. Proteins are a chain of twenty different α-amino acids which are linked by peptide bonds. Around ten amino acids cannot be synthesized by our body and must be consumed through diet. These are called essential amino acids. Certain dynamic and structural functions are carried out by protein. Proteins are classified as simple proteins and secondary or tertiary. Simple proteins are proteins containing only α-amino acids. Whenever there is a change in PH or temperature, the secondary and tertiary proteins get disturbed and are unable to carry out their function. This is known as the denaturation of the protein. Enzymes increase the rate of a chemical reaction and are very selective and specific in their action. Chemically every enzyme is a protein.
Students can refer to the short notes and MCQ questions along with separate solution pdf of this chapter for quick revision from the links below:
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules – Related Links
For more information on Carbohydrates and Amino Acids, watch the below videos


Types of Nucleic Acids
The deficiency of vitamins leads to many diseases. Vitamins are food factors required for the body and are consumed through diet. They can be classified as fat-soluble and water-soluble. Polymers of nucleotides consisting of a phosphate moiety, base, and pentose sugar are called nucleic acids. The transfer of characters from parents to offspring is carried out y nucleic acids. Types of nucleic acids are RNA and DNA.
- DNA – It contains a five-carbon sugar molecule which is called 2-deoxyribose; it has adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine, a double-stranded structure, and it has coded messages for proteins to be synthesized.
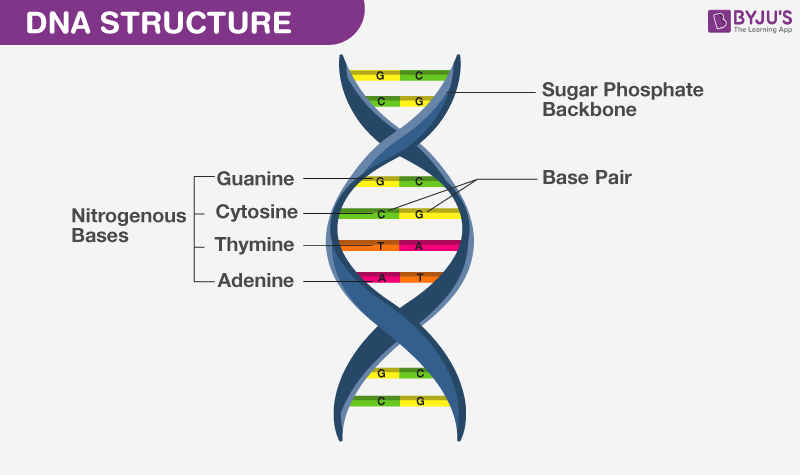
- RNA – It contains ribose. it has adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, single-stranded structure, protein synthesis is carried out by three types of RNA viz mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA.
Few Important Questions
- How are starch and cellulose structurally different??
- What is Peptide linkage?
- Define nucleic acids. List their important functions.
- Mention the different types of RNA present in the cell.
- What are monosaccharides? What are disaccharides? Write the difference between them.
Keep visiting us for the latest updates on CBSE class 12 chemistry notes.
For more questions on Biomolecules and Polymers, watch the below video

Other Important Links:
| Nucleic Acids Functions | Protein Structure And Levels Of Protein |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 Biomolecules
What are biomolecules?
Biomolecules are chemical compounds found in living organisms, for example, nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, carbon, hydrogen, etc.
What are some of the main uses of biomolecules?
Biomolecules have multiple roles to play in the human body. 1. Carbohydrates: Helps in sugar breakdown and glucose creation 2. Lipids: energy supply to cells 3. Proteins: Act as building blocks of life
What is the abbreviation of DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Comments