According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 12 Biology textbook.
Reproduction in Organisms Class 12 NCERT Notes in Detail
Reproduction is a biological process wherein younger ones produced are identical to their parents. This phenomenon is significant in the continuity of the species, generation after generation. Typically, reproduction is observed in all living organisms, from single-celled entities such as amoeba to multicellular entities of the most advanced forms, such as human beings. Reproduction is carried out in two modes, depending upon the participation of one or both parents.
Necessity of Reproduction
Reproduction is vital to the process of continuity of species, and as a result, sustains a balance in the ecosystem amongst different biotic components precisely. Without reproduction, a life that is thriving now would cease. Reproduction also facilitates evolution due to variations arising from the process of reproduction through the intermingling of species (as seen in sexual reproduction).
See Also: Important Questions for Class 12 Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organism
Types of Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
In this mode of reproduction, a new offspring is produced by the involvement or participation of single parents only. The produced offsprings are not only identical but are also the exact copies of their parent because, in this process, a single parent divides itself to reproduce its offspring.

The different types of asexual reproduction are as follows.
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Binary fission
- Vegetative propagation

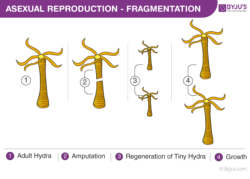
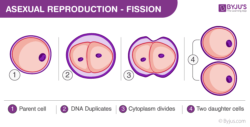
Examples of asexually reproducing organisms:
Asexual reproduction is common among:
- Single-celled organisms, such as amoeba, bacteria, hydras, yeast cells, etc. Amoeba and bacteria reproduce by binary fission; hydras and yeast cells reproduce by budding.
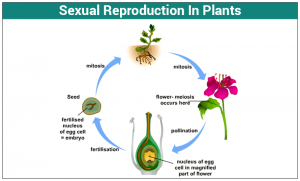
- A few plant species, including ginger, potatoes, sugarcane, agave, bryophyllum, etc., reproduce through vegetative propagation.
- A few animal species, including starfish, black worms, etc., reproduce using fragmentation.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction:
- It is carried out by a single individual, hence does not require finding a mate
- The process is faster compared to sexual reproduction
- Less energy is invested comparatively
- The whole process is less complicated as it involves only a single individual
- Can take place in varied environments
Sexual Reproduction
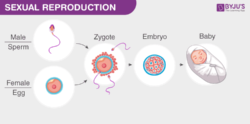
In this mode of reproduction, a new offspring is produced by the participation of two parents of the opposite sex. This type of reproduction is seen in all multicellular organisms, including birds, reptiles, dogs, cats, cattle, elephants, etc. The complete process of sexual reproduction consists of a set of events, including:
- Pre-fertilization
- Fertilization
- Post-fertilization
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction:
- The involvement of two parents results in the intermingling of genes resulting in the production of a new offspring.
- Genetically identical offspring are produced.
- Variations in species increase the chances of survival, hence the evolutionary advancements.
For more information on Spermatogenesis, watch the below video

Important Questions
- What is a bisexual flower?
- What is vegetative propagation?
- Distinguish between asexual and sexual reproduction.
- Distinguish between gametogenesis and embryogenesis.
Learn more about reproduction and their types from the topics given below:
| Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| Modes of Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 12 Biology Notes Reproduction in Organisms
What is budding?
A form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops from some generative anatomical point of the parent organism.
What is a hydra?
The genus of invertebrate freshwater animals of the class Hydrozoa (phylum Cnidaria) is called a hydra.
What is an embryo?
An unborn human or animal in the earliest stages of growth, when its basic structures are being formed, is called an embryo.
Comments