What is Amylose?
Amylose is a polysaccharide used in various industries as a functional biomaterial. It is mainly a linear component consisting of about 100-10,000 glucose monomers linked by 1,4 alpha bindings.
Table of Contents
- Amylose Structure
- General Properties of Amylose
- Physical Properties of Amylose
- Chemical Properties of Amylose
- Uses of Amylose
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Amylose was discovered in 1940 by Meyer and his co-workers found that properties were different from those of native maize starch. It is found in algae and other lower forms of plants. It is a spread polymer of around 6000 glucose deposits with branches on 1 in each 24 glucose ring.
IUPAC name – (1→4)-α-D-Glucopyranan
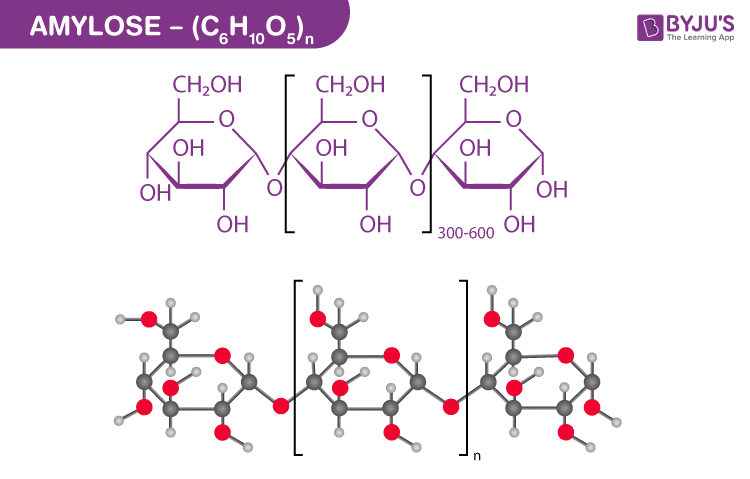
Amylose Structure – (C6H10O5)n
General Properties of Amylose –(C6H10O5)n
| (C6H10O5)n | Amylose |
| Density | 1.25 g/mL |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | Variable |
| Boiling Point | 627.7±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Bond Type | α glycosidic bonds |
| Chemical Formula | Variable because it’s a polymer |
Physical Properties of Amylose – (C6H10O5)n
| Odour | Unpleasant Odour |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Surface tension | 74.4±5.0 dyne/cm |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
Chemical Properties of Amylose – (C6H10O5)n
- Amylose forms a distinctive blue colour complex with iodine. The analysis is provided by high-performance size exclusion chromatography and other methods.
- Amylose molecules may form extensive hydrogen bonds that render the molecules less susceptible to enzymatic degradation.
Uses of Amylose – (C6H10O5)n
- Uses for amylose include permanent textile finishes, plastics, film making and paper pulp fibre bonding.
- High amylose starches have been used together with an instant starch or food gum as a binder to provide a crisp coating for french fries which also reduces oil absorption.
- Used as starches in the usage of sausage casings and food wrappers, incorporation into bread crusts and pasta for more uniform heating in the microwave.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is amylose used for?
The α-amylase digestive enzyme is responsible for breaking up the starch molecules into maltose and maltotriose, which can be used as energy sources. In both industrial and food-based contexts, amylose is also an effective thickener, water binder, emulsion stabiliser and gelling agent.
What is the difference between amylopectin and amylose?
Amylose and amylopectin are two different types of polysaccharides found in starch granules. They have similarities and differences both in structure and chemistry. The key difference between amylose and amylopectin is that amylose is a straight-chain polymer while amylopectin is a polymer with a branched-chain.
Which foods contain amylose?
Amylose can be found in:
Legumes and beans
Whole grains
Vegetables and starchy fruits
Rice and potatoes
What are the functions of amylose and amylopectin?
Energy storage and food reserve are the fundamental activities of Amylose, Amylopectin, Cellulose, and Glycogen. Starch is a good example of this, as it contains 10-20% amylose and 80-90% amylopectin. Starch is the most essential carbohydrate consumed by humans and is the main source of energy for green plants.
Where is amylose found?
Amylose is a polymer that can be found in starch. It is made up of hundreds to thousands of glucose molecules in a linear chain. It is a water-soluble component that accounts for 20 to 25% of starch.


Comments