Chemical reactions tell us about the formation of matter, how the new substances formed and the results of these reactions. Chemical reactions help us understand matter and its chemical properties. Benzoin Condensation is one such chemical reaction that explains the formation of Benzoin from aldehydes. In 1832, Justus von Liebig and Friederich Woehler discovered this reaction.
Table of Contents
Definition and Meaning of Benzoin Condensation
Definition– Benzoin condensation reaction can be defined as the reaction between two kinds of aromatic aldehydes especially benzaldehyde, in the presence of some catalyst (either nucleophile or heterocyclic) to form an aromatic parent compound.
Condensation reactions are mainly used to create carbon to carbon bonds, polymers, new monomers, production of polypeptides, etc.
The benzoin condensation reaction is nothing but the coupling reaction that occurs between aldehydes for the formation of parent benzoin. In this case, the benzaldehyde is involved in this homocoupling process.
Mechanism of Benzoin Condensation Reaction
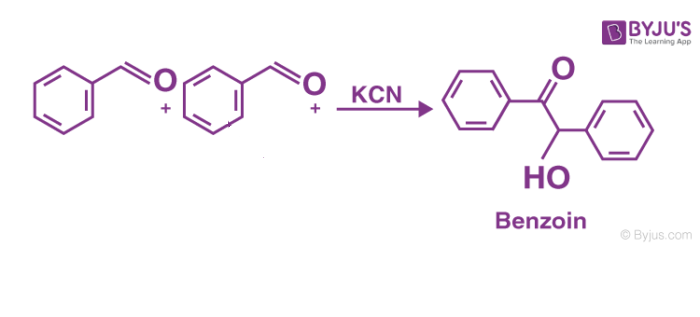
The general form of this condensation reaction is below-
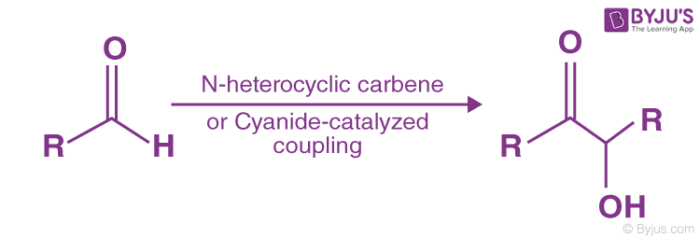
The mechanism of Benzoin condensation reaction is as in the steps below-
-
-
-
- The first phase of the process includes the reaction of cyanide ions with the benzaldehyde to form the product called cyanohydrin. In this step, the cyanide ion or sodium cyanide takes part in the nucleophilic addition reaction, and it is a reversible reaction. The cyanide ion helps the reaction to occur by acting as a nucleophile and facilitating the abstraction of protons, thus forming cyanohydrin. The cyanide ions serve as a catalyst in the reaction.
- The second step is the condensation reaction that occurs between the cyanohydrin and the benzaldehyde.
- In the third phase, rearrangement occurs and also the removal of the cyanide ions occurs resulting in the formation of benzoin. The Rearrangement process results in the reversal of polarity of the carbonyl group, later adding to the second group of carbonyl atom in the second nucleophilic addition.
-
-
In the reaction, a strong base deprotonates the former carbonyl C-atom and the second kind of an equivalent aldehyde reacts with the carbanion, thus eliminating the catalyst and regenerating the carbonyl compound at the end of the condensation reaction.
In this Benzoin Condensation reaction, the two different aldehydes serve two purposes. One aldehyde in the reaction donates the protons and whereas the other aldehyde accepts the protons.
Application of Benzoin and Benzoin Condensation Reaction
-
-
- The benzoin condensation reactions find uses in various organic synthesis and reactions.
-
- The product benzoin is made use in hardening of different polymers by making use of microemulsion.
-
- The reaction is helpful in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds and also extends to the aliphatic form of aldehydes.
-
- These reactions also find its applications in the poly chemistry, for the production of polymers as well in the condensation of new monomers.
-

Good