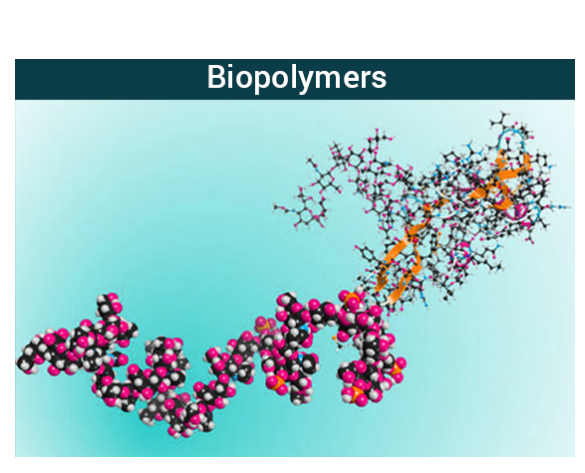
Biopolymers are polymers that are produced by living organisms. They are generally polymers of starch. These are composed of monomeric units. There are three main classes of biopolymers, classified according to the monomers used and the structure of the biopolymer formed: polynucleotides, polypeptides, and polysaccharides.
Difference between Biopolymers and Synthetic Polymers
A major difference can be identified by their structure. All polymers are composed of monomers, the repetitive units. Lignocellulose is a biopolymer with a finite structure. In proteins, primary structure consists of specific chemical composition, and all units are arranged in sequence. Numerous biopolymers naturally fold into compact shapes which defines biological functions.
Relatively synthetic polymers are simple and arbitrary structures. Their synthesis is regulated through template-directed process, this factor may point to the molecular mass distribution that is not found in biopolymers.
Conventions
Sugars
Polymers of sugar are either branched or linear and are attached with glycosidic bonds. Various chemical modifications can occur in many saccharide units. This type of biopolymer is often difficult in terms of conventions.
Polypeptides
Conventions regarding polypeptides are to ;list residues of amino acids occurring from amino terminus. Residues of amino acids are held together by peptide bonds. One of the prime examples for this type of polypeptide is protein. They can even be modified to add non- peptide components.
Nucleic acids
Conventions regarding nucleic acids are to list the nucleotides in a sequence occurring from the fifth end to the third end of the polymer chain. Where fifth and third represent the numbering of carbons that is present around the ribose ring participating in the formation of phosphodiester linkages of the chain.
Impacts on Environment
- Biopolymers are renewable. They are composed of plant material which can be grown endlessly. These polymers would create a viable industry as these plant materials are derived from non- food crops.
- These are compostable. They are used in industrial composting process.
- They are biodegradable. Microorganisms breakdowns biopolymers into water and carbon dioxide. Minute number of biodegradable biopolymers are compostable.
Recommended Videos
Natural Polymers

Comments