What is Carbon Disulfide?
CS2 is an organosulfur compound and a volatile liquid with the chemical name carbon Disulfide. It is also called Carbon bisulfide or disulfidocarbon or methanedithione.
Table of Contents
- Carbon Disulfide Structure
- Properties of Carbon Disulfide – CS2
- CS2 Uses
- Carbon Disulfide Reactions
- Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon Disulfide is a solvent for sulfur, bromine, fats, rubber, phosphorus, asphalt, selenium, iodine, and resins. It has been widely used to purify single-walled carbon nanotubes and in the manufacturing of flotation agents.
Carbon disulfide is a flammable, colourless to light yellow, poisonous, volatile liquid which has a strong disagreeable smell. It has a flash point value of -22°F and is insoluble in water. It is denser than water, therefore, sinks in it.
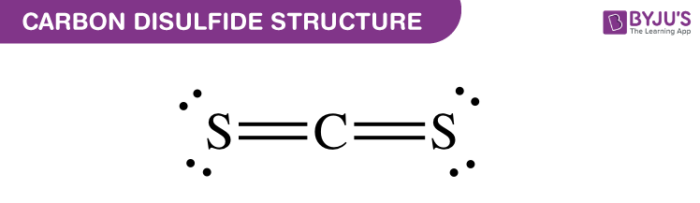
Carbon Disulfide Structure – CS2
Properties of Carbon Disulfide – CS2
| CS2 | Carbon Disulfide |
| Molecular weight of CS2 | 76.13 g/mol |
| Density of Carbon Disulfide | 1.539 g/cm3 |
| Melting point of Carbon Disulfide | −111.61 °C |
| Boiling point of Carbon Disulfide | 46.24 °C |
CS2 Uses (Carbon Disulfide)
- Carbon Disulfide is used in the production of carbon tetrachloride.
- Used as preparing soil disinfectants.
- Used in the manufacturing of rayon.
- Used as a solvent for iodine, phosphorous, etc.
- Used to manufacture electronic vacuum tubes.
- Used as a solvent in rubber-making industries.
- Used in camphor.
- Used in generating petroleum catalysts.
- Used as pesticide intermediate.
Carbon Disulfide Reactions
-
- Reacts with oxygen produce carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide.
CS2 + 3 O2 → CO2 + 2 SO2
-
- Sodium sulfide undergoes a reaction to produce trithiocarbonate:
Na2S + CS2 → [Na+]2[CS32−]
-
- Carbon disulfide is reduced with sodium to produce sodium 1,3-dithiole-2-thione-4,5-dithiolate and sodium trithiocarbonate.
4 Na + 4 CS2 → Na2C3S5 + Na2CS3
-
- Carbon tetrachloride is produced by chlorination of CS2
Health Hazards
It affects the CNS, eyes, liver, skin, cardiovascular system, and kidneys. It is absorbed through the skin in its liquid or vapour form, ingested or inhaled. The likely oral lethal dose for humans is between 0.5 to 5 grams kilogram per person. Also, it leads to disturbance of vision and sensory organs. The lowest lethal dose for a human is reported as 14 mg/kg per person.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is carbon disulfide an acid?
Carbon disulfide with the formula CS2 is a colourless volatile liquid. The compound is commonly used in organic chemistry as a building block, as well as a non-polar industrial and chemical solvent. This has an “ether-like” odour but usually, industrial samples are polluted with impurities that smell foul.
Where does carbon disulfide come from?
Limited quantities of carbon disulfide are present in nature in gasses emitted to the earth’s surface, e.g. in volcanic eruptions or over marshes. Microorganisms may also create carbon disulfide-containing gas in soil. Commercial carbon disulfide is produced at very high temperatures by adding carbon and sulphur.
Is carbon disulfide made of atoms or molecules?
Carbon disulphide is an organic compound or molecule made up of one carbon and two sulphur atoms. The smallest particles which have complete properties of carbon disulphide are molecules, not atoms.
What intermolecular forces does carbon disulfide have?
Due to the difference in electronegativities between C and S, the C-S bond is nonpolar. Carbon disulphide has a linear structure in which two bond dipoles are in opposite directions resulting in cancelling out the dipole moments. So carbon disulphide is non-polar.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of CS2 from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments