What are Carbonyl Compounds?
The compounds containing a carbonyl group (the -C=O group) are called carbonyl compounds.
The carbonyl group, C=O, is probably the most important functional group in organic chemistry. These compounds are an integral part of organic chemistry and their primary members are called aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids.
In other words, A carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula C=O that is formed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and is divalent at the carbon atom.
Table of Contents
- Carbonyl Group
- Examples of Organic Carbonyl Compounds
- Recommended Videos
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Properties of Carbonyl Compounds
- Chemical Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
- Applications of Carbonyl Compounds
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
| Explore more about Carbonyl Compounds Questions |
Carbonyl Group
A carbonyl group is a functional group featuring a double bond between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom (illustrated below). However, the term ‘Carbonyl’ can also refer to carbon monoxide as the ligand within an organometallic or inorganic compound (say a metal carbonyl, such as nickel carbonyl).
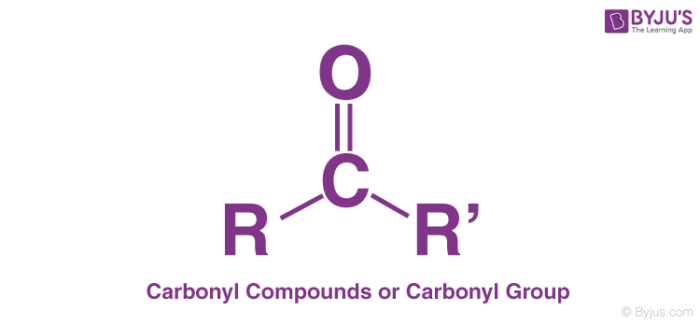
Carbonyl compounds can be further divided into organic and inorganic carbonyl compounds. This article details the carbonyl compounds that are organic in nature.
Examples of Organic Carbonyl Compounds
These include carbamates, urea, and also the derivatives of phosgene, acyl chlorides chloroformates, carbonate esters, lactones, thioesters, lactams, isocyanates, and hydroxamates.
Recommended Videos
Carbonyl Compounds

Functional Groups and Types and Formula

Carbonyl Compounds – Important and JEE PYQs

Carbonyl Compounds – Important Topics for JEE

Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
When the carbonyl group is linked to one alkyl or aryl group and one hydrogen atom, the resulting carbonyl compound is called an aldehyde. The general formula of an aldehyde is R-CHO. Ketones are carbonyl compounds in which the carbonyl carbon is linked to two alkyl or aryl groups. Their chemical formulae can be generalized to R-(C=O)-R’. When the carbonyl carbon is bonded to one alkyl/aryl group and one OH group, the resulting carbonyl compound can be classified as carboxylic acid and its chemical formula can be generalized to R-COOH.
In general, we come across the names aldehydes and ketones when we speak about Carbonyl compounds. What is the role of these in the lists of carbonyl compounds? The main difference between aldehydes and ketones is the position of the carbonyl group. In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is placed at the ending of the carbon chain whereas, in ketones, it is located in the middle of the carbon chain. Examples of aldehydes include propanol, butanol, 4-chlorobutanol, etc. and some examples of ketones are propanone, acetone, 2-methyl-3-pentanone, etc.
Properties of Carbonyl Compounds
Some properties of carbonyl compounds are given below:
- These are to be polar in nature. They exhibit both positive and negative charges in slight form. Hence, these are said to be polar molecules.
- These compounds are reported to be insoluble in water but sometimes they dissolve other forms of polar molecules.
- These are known to be chemically reactive compounds. These undergo nucleophilic addition and substitution reactions.
Chemical Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
The carbon atom of the carbonyl group is said to be electrophilic in nature as they tend to attract electron-rich compounds. Aldehydes and ketones undergo a variety of reactions which leads to the formation of different products. The most common reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions, which lead to the formation of alcohols, alkenes, diols and cyanohydrins. These also undergo nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Carbonyl Reduction: This reaction is a process in which the carbonyl groups are reduced by the hydride reagents such as the LiAlH4 and NaBH4 with baker’s yeast, or by the process of catalytic hydrogenation.
- Carbonyl alkylation: This is a process in which the carbonyl compounds are alkylated with the use of organometallic compounds like Grignard reagents, organolithium reagents, acetylides, etc.
- Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reaction: This kind of substitution reaction involves the substitution of the atom of α hydrogen by an electrophile.
Applications of Carbonyl Compounds
- The carbonyl compound propanone is used as a solvent since it gets dissolved in water as well as other organic solutions.
- Formaldehyde is used in the manufacture of plastics and also it is used in the biological laboratories for preservation purposes.
- Butanol is used to provide fragrance for keeping the bread fresh.
- Acetaldehyde is used as a Synthesizer in many organic reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is a carbonyl compound?
Carbonyl compounds are the class of organic compounds which possess a carbonyl group in which C is doubly bonded to O.
What is the role of carbonyl compounds?
The carbonyl group serves the functional role of destabilizing the bonds within the carbon chain. The electronegative oxygen atom tends to attract more electrons than the carbon it is bonded to within the carbonyl group.
What is the formula of the carbonyl group?
The carbonyl group is C=O. with the carbon atom bonded to two other atoms. Carbonyl compounds with only hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon atom are aldehydes or ketones.
Is ether a carbonyl group?
Ethers are compounds with an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups. Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl functional group. So ether is not a carbonyl compound but another class of organic compound.
Do esters have a carbonyl group?
Both carboxylic acids and esters contain a carbonyl group with a second oxygen atom bonded to the carbon atom in the carbonyl group by a single bond. In a carboxylic acid, the second oxygen atom also bonds to a hydrogen atom.

Comments