What is Chloroacetic acid?
C2H3O2Cl is an organochlorine compound with chemical name Chloroacetic acid. It is also called monochloroacetic acid (MCA) or 2-Chloroacetic acid or Chloroethanoic acid. It is a Chlorocarboxylic acid that carries a 2-chloro substituent. It functions as an herbicide and an alkylating agent. It is derived from acetic acid.
Chloroethanoic acid was first prepared in the year 1843 by a French chemist named Felix LeBlanc. It was prepared by chlorinating acetic acid (CH3COOH) in the presence of sunlight. In the year 1857 it was prepared by a German chemist named Reinhold Hoffmann by a method of refluxing glacial acetic acid in the presence of sunlight and chlorine. A French chemist named Charles-Adolphe Wurtz also prepared Chloroethanoic acid in the same year (1857) by reacting chloroacetyl chloride with water.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Chloroacetic acid-C2H3O2Cl
- Chloroacetic acid structure-C2H3O2Cl
- C2H3O2Cl Uses (Chloroacetic acid)
- Production of Chloroacetic acid
- Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Properties of Chloroacetic acid – C2H3O2Cl
| C2H3O2Cl | Chloroacetic acid |
| Molecular weight of C2H3O2Cl | 94.49 g/mol |
| Density of Chloroacetic acid | 1.58 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point of Chloroacetic acid | 189.3 °C |
| Melting point of Chloroacetic acid | 63 °C |
Chloroacetic acid structure – C2H3O2Cl
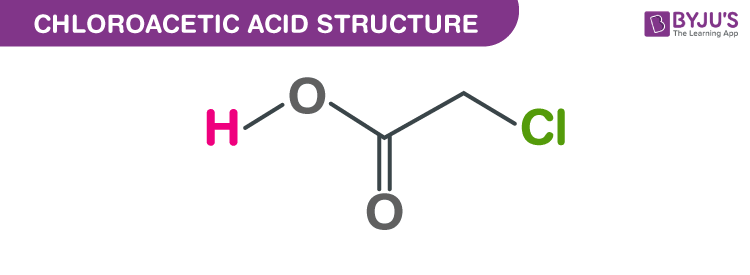
In its solid form it is a colourless or light-brown crystalline solid. It dissolves and sinks in water. It causes thermal burns when transported in its molten liquid form. It is toxic when ingested, inhaled or absorbed through skin. It is combustible and corrosive.
C2H3O2Cl Uses (Chloroacetic acid)
- Chloroacetic acid is used as an intermediate in the production of ethyl chloroacetate.
- Used as a bacteriostat.
- Used as a herbicide.
- Used as a preservative.
- Used as a chemical intermediate.
Production of Chloroacetic acid
Industrially monochloroacetic acid is prepared in two methods. The primary method is chlorinating acetic acid with the help of a catalyst such as acetic anhydride.
CH3CO2H + Cl2 → ClCH2CO2H + HCl
The other method to obtain chloroacetic acid is by hydrolysing trichloroethylene with the help of catalyst such as sulfuric acid.
CCl2=CHCl + 2H2O → ClCH2CO2H + 2HCl
Health Hazards
This material is very toxic. The lethal dose is 50-500 mg/kg of body weight. When 2-Chloroacetic acid comes in contact with the skin and eyes it causes irritation and burning sensation. When inhaled it severely damages mucous membranes. Swallowing can cause peritonitis. Other issues related to health include CNS depression, and respiratory system depression.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How do you make chloroacetic acid?
Industrially, chloroacetic acid is prepared through two routes. The prevalent procedure involves acetic acid chlorination, with acetic anhydride as a catalyst. This route suffers from the processing, as impurities, of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid that are difficult to isolate by distillation.
Which is the strongest acid?
In a laboratory in California, the world’s strongest acid, at least a million times more potent than condensed sulphuric acid, was developed. It is, maybe confusingly, one of the least corrosive, too. The compound, known as carborane acid, is, according to its makers, the first ‘super acid’ that can be contained in a container.
How do you make chloroacetic acid?
Industrially, chloroacetic acid is prepared through two routes. The prevalent procedure involves acetic acid chlorination, with acetic anhydride as a catalyst. This route suffers from the processing, as impurities, of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid that are difficult to isolate by distillation.
Is benzoic acid a white crystalline solid?
As a white crystalline solid, benzoic acid occurs. Slightly water-soluble. A compound containing a benzene ring core bearing a carboxylic acid substituent is benzoic acid.
Which is the most harmful acid?
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is just a mild acid, meaning that in water it does not dissociate completely from its ions. And though, since it’s the one you’re most likely to find, it is potentially the most dangerous acid on this list. This acid, like Teflon and fluorine gas, is used to produce fluorine-containing medicines.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of C2H3O2Cl from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments