What is Dichloromethane?
Dichloromethane is a geminal organic compound and is also called Methylene chloride or Methylene dichloride. It can be obtained naturally from oceanic sources, macro algae, volcanoes, and wetlands. The majority of Methylene dichloride in the environment is due to industrial emissions. The chemical formula of Dichloromethane is CH2Cl2.
Methylene chloride is a colourless liquid which has a sweet, penetrating, ether-like smell. It is a volatile liquid chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is non-combustible but if exposed to high temperatures it may produce toxic chloride fumes. At higher concentrations vapours are narcotic. It is widely used as a paint remover and solvent.
Properties of Dichloromethane – CH2Cl2
| Dichloromethane | CH2Cl2 |
| Molecular Weight of Dichloromethane | 84.93 g/mol |
| Density of Dichloromethane | 1.3266 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point of Dichloromethane | −96.7 °C |
| Boiling Point of Dichloromethane | 39.6 °C |
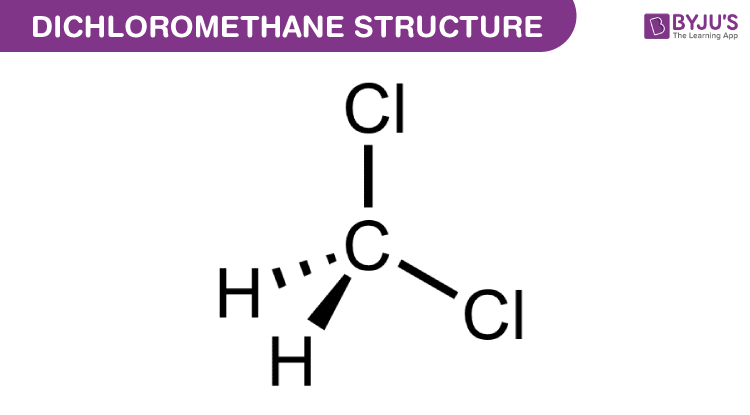
Structure of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
Uses of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
- Dichloromethane is used as a solvent in food technology.
- It is used in aerosol formulations.
- It is am ethane foam blowing agent.
- Used as a solvent in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products.
- CH2Cl2 is used as a degreasing agent.
- Used in the manufacturing of electronics.
Production of Dichloromethane (DCM)
It was first prepared by a French chemist Henri Victor Regnault in the year in 1839. He isolated it from a mixture of chlorine and chloromethane which was exposed to sunlight.
DCM can be synthesized by treating methane or chloromethane with chlorine gas at a temperature range of 400–500 °C. They undergo a series of reactions producing more chlorinated products. In the year 1993, approximately 4,00,000 tons was obtained in countries such as Europe, Japan, and the US.
This process produced a mixture of chloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and dichloromethane. Further, they were separated by the process of distillation.
Health hazards
Inhaling methylene chloride causes irritation in the nose and throat. It affects the central nervous system (CNS). It is a possible mutagen and anticipated to be a human carcinogen.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the uses of dichloromethane?
Dichloromethane (often abbreviated to DCM) is a volatile and non-flammable compound that is commonly used as an organic solvent in several applications on the industrial and laboratory scale. This compound is often referred to as methylene chloride due to its high volatility and ability to dissolve compounds.
What are the health hazards associated with dichloromethane?
Dichloromethane is considered by many to be a neurotoxin. It has been proven to cause brain damage and also damage to the central nervous system (abbreviated to CNS). The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has also classified this compound as a probable carcinogen towards humans. This is because high levels of exposure to dichloromethane has been proven to cause cancer of the lungs and liver in many animals.
How can dichloromethane be prepared?
Chlorinating methane is widely used to produce dichloromethane. The process also produces the other three C1 chlorohydrocarbons-chloromethane, trichloromethane (chloroform), and tetrachloromethane (carbon tetrachloride). Separating the four is achieved by distillation.
Learn more about the physical properties, chemical properties, and the uses of Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments