Polyhalogen Compounds – Dichloromethane, Trichloromethane, Tetrachloromethane, Iodoform, Freons, DDT
The hydrocarbons or any carbon compounds containing more than one halogen atom (group 17 elements of the modern periodic table) are known as polyhalogen compounds.
Many of these compounds are useful in industry and agriculture. Some notable polyhalogen compounds are described below:
1. Dichloromethane
- Dichloromethane is a geminal organic compound and is also called Methylene chloride or Methylene dichloride.
- It can be obtained naturally from oceanic sources, macroalgae, volcanoes, and wetlands.
- The majority of Methylene dichloride in the environment is due to industrial emissions.
- The chemical formula of Dichloromethane is CH2Cl2.
Uses of Dichloromethane
- Dichloromethane is used as a solvent in food technology.
- It is used in aerosol formulations.
- It is an ethane foam blowing agent.
- Used as a solvent in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products.
- CH2Cl2 is used as a degreasing agent.
- Used in the manufacturing of electronics.
2. Trichloromethane (Chloroform)
- Chloroform, also referred to as trichloromethane is an organic compound.
- Chloroform is an organic chemical compound initially employed as an ideal anesthetic.
- It was first prepared in 1831.
- The chemical formula is CHCl3.
- It is a colourless, sweet-smelling dense liquid produced on a large scale.
Uses of Chloroform – CHCl3
- Used as an anaesthetic and used in dentistry during root canal procedures.
- The spectrum of pure chloroform is used as the reference or background, and pure cholesterol powder or cholesterol extract from milk products is dissolved in chloroform and used for FTIR analysis.
- Chloroform was utilised in the past as an extraction dissolvable for fats, greases, oils, and different items; as a laundry spot.
- Used as an indirect food additive in food packaging materials for adhesive components and as a component of food contact materials.
3. Tetrachloromethane (Carbon Tetrachloride)
- It is a colourless liquid with a “sweet” smell that can be detected at low levels. The molecular formula of carbon tetrachloride is CCl4.
- It is used in the manufacturing of refrigerants, as a cleaning agent and was also used as a fire extinguisher.
- Medically, it is one of the most potent hepatotoxins (toxic to the liver) and is widely used in scientific research to evaluate hepatoprotective agents.
- When carbon tetrachloride is released into the air, it rises in the atmosphere and depletes the ozone layer. Depletion of the ozone layer is believed to increase human exposure to ultraviolet rays, leading to increased skin cancer, eye diseases and disorders, and possible disruption of the immune system
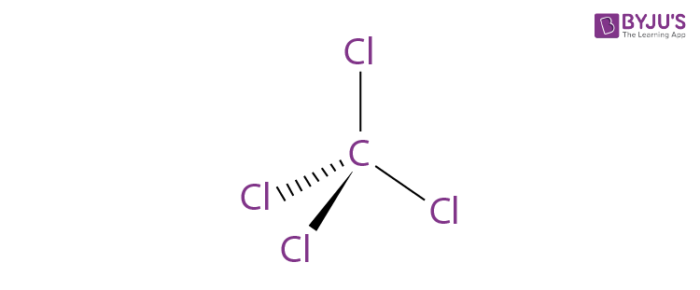
4. Iodoform
- Iodoform which is also called triiodomethane is a yellow crystalline solid.
- It is insoluble in water but soluble in solvents like ethanol, chloroform, and ether.
- It is hydrolyzed to give sodium methanoate (sodium formate) when treated with an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution.
- Iodoform was used earlier as an antiseptic but the antiseptic properties are due to the liberation of free iodine and not due to the iodoform itself.
- Due to its objectionable smell, it has been replaced by other formulations containing iodine.
5. Freons (CFCs)
- Freons are the chlorofluorocarbon compounds of methane and ethane. The chlorofluorocarbon compounds refer to the compounds having mainly carbon, fluorine, and chlorine. Freons is the brand name for this group of compounds coined by DuPont.
- They are extremely stable, unreactive, non-toxic, non-corrosive and easily liquefiable gases.
- Freon 12 or R-12 (CCl2F2) is one of the most common representatives of this group. It is manufactured from tetrachloromethane by Swarts reaction.
- These are usually produced for aerosol propellants, refrigeration and air conditioning purposes.
6. DDT (p, p’-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)
- It is a colourless, crystalline, tasteless and almost odourless organochloride known for its insecticidal
- It was the first chlorinated organic insecticide prepared in 1873. But in 1939, Paul Miller identified the different uses of DDT. Paul Muller was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine and Physiology in 1948 for this discovery.
- It became popular because of its effectiveness against the mosquito that spreads malaria and lice that carry typhus.
- But due to the ill effects of DDT such as chemical instability and fat solubility, it got banned in many countries
Recommended Videos
Polyhalogen Compound – Haloalkanes & Haloarenes

For a more detailed and interactive analysis of freons, DDT, Carbon tetrachloride, download BYJU’S – the learning app to Google Play Store and Apple app store.

Comments