What are Mineral Resources?
A mineral is a naturally occurring substance, representable by a chemical formula, that is usually solid and inorganic, and has a crystal structure.
Table of Contents
- Recommended Videos
- Categories of Mineral Resources
- Uses of Minerals
- Examples of Minerals
- Conservation of Mineral Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Mineral resources are the key material basis for socio-economic development. Statistical results show that more than 95% of energy used by mankind, 80% of industrial raw materials and 70% of raw materials for agricultural production are from mineral resources.

A mineral is a pure inorganic substance that occurs naturally in the earth’s crust. More than two-thousand minerals have been identified and most of these are inorganic, which are formed by the various combination of elements. However, a small proportion of the earth’s crust contains organic materials, consisting of single elements such as gold, silver, diamond, and sulfur.
Recommended Videos

Also, Read ⇒ Geochemistry
Categories of Mineral Resources
Mineral resources can be divided into two major categories.
- Metallic Mineral Resources
- Non-metallic Mineral Resources
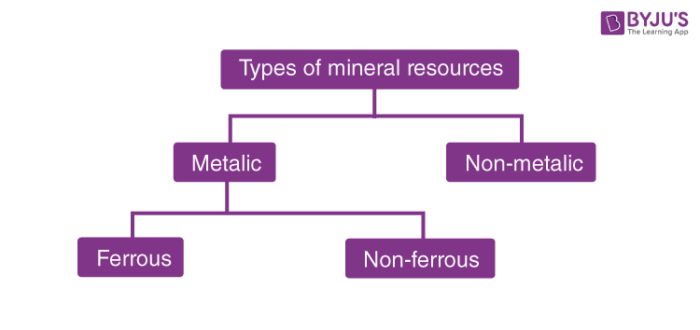
There are metals that are hard and conduct electricity and heat with characteristics of lustre or shine. Such metals are called metallic minerals. For example Silver, Chromium, Tin, Nickel, Copper, Iron, Lead, Aluminum, Gold, and Zinc.
1. Characteristics of Metallic Minerals
- Metallic Minerals show a metallic shine in their appearance.
- The potential source of the metal can be got through mining.
- Contains metals in their chemical composition.
- Metallic minerals contain metal in raw form.
Classification of metallic minerals:
- Ferrous metallic minerals
- Nonferrous metallic minerals
Minerals that contain iron are called ferrous minerals. Example of ferrous minerals is Chromites, Iron ore, and manganese.
Minerals that do not contain iron are called non-ferrous minerals. Examples of nonferrous minerals are lead, silver, gold, and copper.
There is a group of chemical elements that when melted do not generate a new product. Such special groups are called Nonmetallic minerals. Example: Dimension stone, halite, sand, gypsum, uranium metal, gravel.
2. Characteristics of Nonmetallic Mineral Resources
- Minerals appear with a non-metallic shine or lustre
- Do not contain extractable metals in their chemical composition
Uses of Minerals
The use of minerals depends upon their deposits. Some countries are rich in mineral deposits, while others have no deposits. The greatest use of minerals depends on their properties. For instance, Aluminum is light, strong and durable in nature, so it is used for aircraft, shipping, and car industries.
Minerals are used in almost all industries. Gold, silver, and platinum metal are used in the jewellery industry. Copper is used in the coin industry and for making pipes and wires. Silicon obtained from quartz is used in the computer industry.
Mineral elements give fireworks colour. Barium produces glossy greens; strontium yields dark reds; copper yields blues; and zinc yields sodium. Mixing elements can make many colours: strontium and sodium create bright orange; titanium, zirconium, and magnesium alloys create silvery white; copper and strontium make lavender blue.
Examples of Minerals
Minerals are compounds naturally produced on Earth. They have a clear structure and chemical composition. There are more than 3000 known minerals. Some, like gold and diamond, are rare and precious, while others, like quartz, are more ordinary.
Minerals are composed of atoms as are all compounds. There are just only a hundred components around us, and they are the fundamental building blocks in everything of us. They can be found in their pure form, or chemically combined with other compound-making elements. A compound is composed of two or more chemically united elements.
Over 99 per cent of the minerals that make up the surface of the Earth consists of only eight elements. Some of such elements are found as complexes in conjunction with other elements. Minerals are naturally occurring elements or compounds in the Earth’s crust. Rocks are minerally shaped mixtures. Much as the building blocks of rocks are elements, the rocks form the rock building blocks.
The mineral biotite has basal cleavage which means that it has a complete cleavage. The cleavage plane on top of this sample is visible on the smooth, reflective surface. The flat surface at the bottom, in line with the top of the bowl, is similar to the rim and thus reflects the same cleavage axis.
Conservation of Mineral Resources
The total volume of consumable mineral resources is just 1% of all the minerals present in the earth’s crust. However, the consumption rate is so high that these mineral resources which are non-renewable will get exhausted very soon. Here are some measures to conserve minerals:
- Use of minerals in a planned and sustainable manner.
- Recycling of metals
- Use of alternative renewable substitutes.
- Technology should be improved to use the low-grade ores profitably.
Any minerals usually occur as well-developed crystals and are treated in their crystal types. A detailed nomenclature has emerged to classify crystal types and may be familiar with some common names. Different properties aid in the detection of other minerals. For certain minerals, these properties may not be distinguishable enough to aid in their detection. And, they can only be found in some minerals
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the importance of mineral resources?
Mineral resources are among the most important natural resources that determine a country’s industrial and economic growth by supplying raw materials to the economy’s primary, secondary and tertiary sectors.
What are the uses of minerals?
Calcium provides bones and teeth with stability and endurance. It also aids in blood coagulation, enzyme regulation, nervous system processing of signals, etc. In transporting oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body, iron is needed.
How minerals are found?
Minerals can be found all over the world in the crust of the earth, but generally in such small quantities that they are not worth extracting. Minerals are found in economically viable deposits only with the aid of certain geological processes. Just where they are located will mineral deposits be collected.
What defines a mineral?
A mineral is an inorganic solid which occurs naturally, with certain chemical composition and an ordered atomic arrangement. This may sound a bit mouthful, but it becomes clearer if you break it down. There are minerals that occur naturally. They’re not made by people.
What are the characteristics of minerals?
Minerals are identified with eight main properties: crystal habit, lustre, hardness, cleavage, break, colour, line, and specific gravity. There is usually no specific diagnostic property that can be used to classify a mineral sample on its own.


Comments