Table of Contents
Oxoacids Of Phosphorus
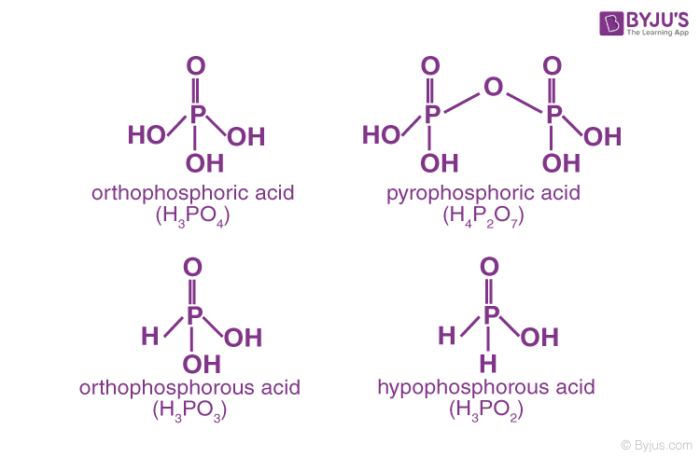
Acids that contain element oxygen are known as Oxoacids. Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids such as H3PO4, H3PO3,etc. The oxoacids of phosphorus contain phosphorus atoms- tetrahedrally surrounded by other atoms.In general, these acids show at least one P–OH bond and one P=O bond.
Along with P–OH and P=O, the oxoacids also contain P–P and P–H bonds hence, the oxidation state of oxygen is less than +5. Further, these acids can easily disproportionate to higher or lower oxidation state.For example, heating phosphorus acid (O.S. +3) results in the formation of phosphine (O.S. -3) and phosphoric acid (O.S. +5).
The P-H bonds in oxoacids cannot undergo ionization to release H+ ions whereas the H atoms attached to oxygen in P-OH are ionizable.Therefore, we can conclude that only H atoms attached to oxygen can cause basicity. Consequently, phosphorus acid (H3PO3 )is dibasic as it contains two P-OH bonds whereas phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is tribasic as it contains three P-OH bonds. Oxoacids of phosphorus having P-H bonds have strong reducing properties.On these grounds, we may conclude that hypophosphorus acid containing two P-H bonds and thus acts as a good reducing agent.
Well Known Oxo-acids of Phosphorous
Phosphorus acid, H3PO3: Phosphorous acid is a diprotic acid which means that one molecule of it will release two protons. Its structural formula HPO(OH)2 explains it all.Acidic or aqueous(steam) hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride yields Phosphorous acid.
Phosphoric acid, H3PO4: Phosphoric acid is a triprotic acid which means that its one molecule will release three protons. It is non-toxic(in pure state) and is a solid at room temperature and pressure. Phosphoric acid is prepared by adding sulphuric acid to calcium hydroxyapatite or fluorapatite.
Ca5(PO4)3X+5H2SO4+10H2O→3H3PO4+5CaSO4.2H2O+HX
X can be F, Cl, Br and OH
Meta Phosphoric (HPO3)n
Meta Phosphoric acid is formed by warming orthophosphoric acid at around 850 K. It exists as a cyclic trimer, polymer or cyclic tetramer except as a monomer.
H3PO4 → HPO3 + H2O
Hypophosphoric Acid (H4P2O6)
Hypophosphoric acid is prepared by hydrolysis and oxidation of red phosphorus by NaOCl, or white phosphorus by water and air.
2 P + 4 NaClO2 + 2 H2O → H4P2O6 + 2 NaCl
There are no P-H bonds and so this acid is not a reducing agent.
It has four acidic hydrogens.
It contains P-P bond.
Pyrophosphoric Acid (H4P2O7)
Pyrophosphoric Acid is a medium-strong inorganic hygroscopic by nature and is a colourless as well as odourless chemical.It is is corrosive as well as toxic in nature.
2H3PO4 ———> H4P2O7 + H2O
Orthophosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
Orthophosphoric acid refers to phosphoric acid. Phosphoric Acid is a weak, tribasic acid with chemical formula H3PO4. It is present in teeth and bone and helps in metabolic processes.
It can be conveniently prepared by dissolving P2O5 in water followed by boiling the solution to form a thick syrup.
P2O5 + 3H2O → 2H2PO4
Red phosphorus when heated with conc.HNO3 yields orthophosphoric acid.
P + 5HNO3 → H3PO4 + H2O + 5NO2
On a large scale, it is prepared by treating phosphorite rock with dil.H2SO4.
Ca3(PO4)2 + 3H2SO4 → 3CaSO4 + 2H3PO4
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How do you explain the reducing nature of phosphinic acid(H3PO2)?
What happens when Phosphorus acid is heated?
What is the basicity of H3PO4 ?
Which of the following acids forms three series of salts?H3PO2, H3PO4,H3PO3
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of Phosphorus is treated with concentrated nitric acid.
Also Read:
For detailed discussion on other topics like Oxoacids of sulphur, halogens you can visit BYJU’S or download the app.

Comments