What Is Paper Chromatography?
Chromatography technique that uses paper sheets or strips as the adsorbent being the stationary phase through which a solution is made to pass is called paper chromatography. It is an inexpensive method of separating dissolved chemical substances by their different migration rates across the sheets of paper. It is a powerful analytical tool that uses very small quantities of material. Paper chromatography was discovered by Synge and Martin in the year 1943.
Table of Contents
- Paper Chromatography Principle
- Paper Chromatography Diagram
- Paper Chromatography Procedure
- Paper Chromatography Applications
- Types of Paper Chromatography
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Paper Chromatography Principle
The principle involved can be partition chromatography or adsorption chromatography. Partition chromatography because the substances are partitioned or distributed between liquid phases. The two phases are water held in pores of the filter paper and the other phase is a mobile phase which passes through the paper. When the mobile phase moves, the separation of the mixture takes place. The compounds in the mixture separate themselves based on the differences in their affinity towards stationary and mobile phase solvents under the capillary action of pores in the paper. Adsorption chromatography between solid and liquid phases, wherein the solid surface of the paper is the stationary phase and the liquid phase is the mobile phase.
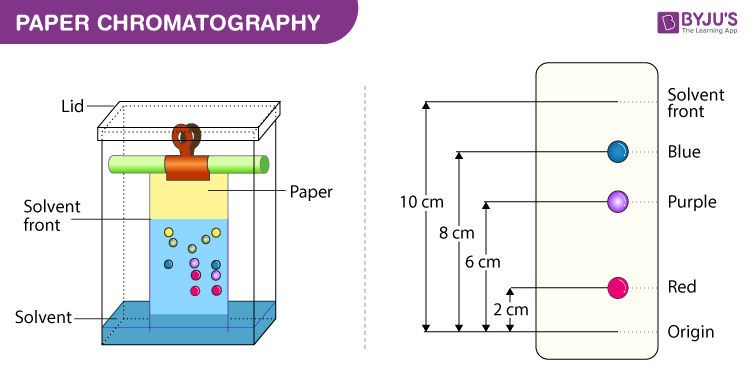
Paper Chromatography Diagram
Paper Chromatography Procedure
Below we have explained the procedure to conduct Paper Chromatography Experiment for easy understanding of students.
- Selecting a suitable type of development: It is decided based on the complexity of the solvent, paper, mixture, etc. Usually ascending type or radial paper chromatography is used as they are easy to perform. Also, it is easy to handle, the chromatogram obtained is faster and the process is less time-consuming.
- Selecting a suitable filter paper: Selection of filter paper is done based on the size of the pores and the sample quality.
- Prepare the sample: Sample preparation includes the dissolution of the sample in a suitable solvent (inert with the sample under analysis) used in making the mobile phase.
- Spot the sample on the paper: Samples should be spotted at a proper position on the paper by using a capillary tube.
- Chromatogram development: Chromatogram development is spotted by immersing the paper in the mobile phase. Due to the capillary action of paper, the mobile phase moves over the sample on the paper.
- Paper drying and compound detection: Once the chromatogram is developed, the paper is dried using an air drier. Also, detecting solution can be sprayed on the chromatogram developed paper and dried to identify the sample chromatogram spots.
Paper Chromatography Applications
There are various applications of paper chromatography. Some of the uses of Paper Chromatography in different fields are discussed below:
- To study the process of fermentation and ripening.
- To check the purity of pharmaceuticals.
- To inspect cosmetics.
- To detect the adulterants.
- To detect the contaminants in drinks and foods.
- To examine the reaction mixtures in biochemical laboratories.
- To determine dopes and drugs in humans and animals.
Types of paper chromatography:
- Ascending Paper Chromatography – The techniques goes with its name as the solvent moves in an upward direction.
- Descending Paper Chromatography – The movement of the flow of solvent due to gravitational pull and capillary action is downwards, hence the name descending paper chromatography.
- Ascending – Descending Paper Chromatography – In this version of paper chromatography, movement of solvent occurs in two directions after a particular point. Initially, the solvent travels upwards on the paper which is folded over a rod and after crossing the rod it continues with its travel in the downward direction.
- Radial or Circular Paper Chromatography – The sample is deposited at the centre of the circular filter paper. Once the spot is dried, the filter paper is tied horizontally on a Petri dish which contains the solvent.
- Two Dimensional Paper Chromatography – Substances which have the same rf values can be resolved with the help of two-dimensional paper chromatography.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are the advantages of Paper Chromatography?
Paper Chromatography Has Many Benefits
Simple and rapid
Paper chromatography necessitates a minimal amount of quantitative material.
Paper chromatography is less expensive than other chromatography methods.
The paper chromatography method can identify both unknown inorganic and organic compounds.
Paper chromatography takes up little space when compared to other analytical methods or equipment.
Outstanding resolving power
Why water is not used in paper chromatography?
It is preferable to use a less polar solvent, such as ethanol, so that the non-polar compounds will travel up the paper while the polar compounds will stick to the paper, separating them.
What are the limitations of Paper Chromatography?
Limitations of Paper Chromatography are as follows-
Paper chromatography cannot handle large amounts of sample.
Paper chromatography is ineffective in quantitative analysis.
Paper chromatography cannot separate complex mixtures.
Less Accurate than HPLC or HPTLC
What is the importance of paper chromatography?
Paper chromatography has traditionally been used to analyse food colours in ice creams, sweets, drinks and beverages, jams and jellies. Only edible colours are permitted for use to ensure that no non-permitted colouring agents are added to the foods. This is where quantification and identification come into play.
Is paper chromatography partition or adsorption?
A type of partition chromatography is paper chromatography.
To learn more about the different types of paper chromatography from the experts, register with BYJU’S now!
Other important links:
| Differential Extraction Chromatography | Difference between Adsorption and Absorption |

It is so easy to understand by students
Explained with applications also.