What is Lead (IV) oxide?
PbO2 is an oxide where the oxidation state of lead is +4 with the chemical name Lead (IV) oxide. It is also called lead dioxide, anhydrous Plumbic acid, or Plumbic oxide. It is a powerful oxidising agent.
Plumbic oxide is a dark-brown crystalline powder which is insoluble in water and alcohol. It dissolves in dilute nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, oxalic acid, etc. It is widely used in explosives, matches, and electrodes.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Lead (IV) oxide
- Lead (IV) oxide structure
- Uses
- Production of Lead (IV) oxide
- Chemical reactions
- Health hazards
Properties of Lead (IV) oxide – PbO2
| PbO2 | Lead (IV) oxide |
| Molecular weight of PbO2 | 239.1988 g/mol |
| Density of Lead (IV) oxide | 9.38 g/cm3 |
| Flash point of Lead (IV) oxide | Non-flammable |
| Melting point of Lead (IV) oxide | 290 °C |
Lead (IV) oxide structure – PbO2
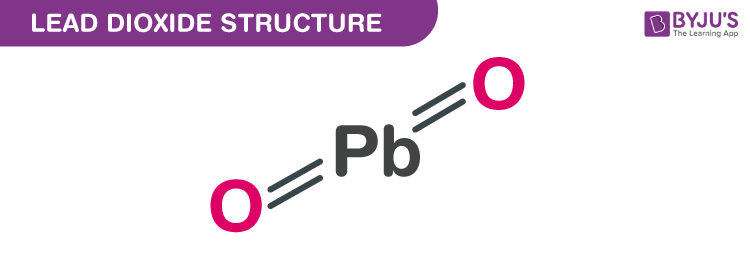
The exact mass and the monoisotopic mass of Lead dioxide is 239.966 g/mol. The number of hydrogen bond acceptors equals two and the number of hydrogen bond donors equals zero. This compound is canonicalized and has one covalently bonded unit.
PbO2 Uses (Lead (IV) oxide)
- Lead (IV) oxide is used to manufacture rubber substitutes.
- Used in making explosives.
- Used as a curing agent for polysulfide.
- Used as an oxidising agent in the manufacturing of dyes.
- Used as an analytical reagent.
- Used in making lightning arresters.
- Used as an anode material in electrochemistry.
- Used in electroplating copper.
- Used in lead-acid storage batteries.
- Used in textiles.
Production of Lead (IV) oxide
Commercially it is produced by methods of reacting lead dioxide with dilute nitric acid:
Pb3O4 + 4 HNO3 → PbO2 + 2 Pb(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
When lead chloride is treated with sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) solution it produces Plumbic oxide.
Chemical reactions:
Lead (IV) oxide decomposes when heated. The reaction is as follows:
PbO2 → Pb12O19 → Pb12O17 → Pb3O4 → PbO
Health hazards:
Plumbic oxide when swallowed and inhaled is toxic. When this compound is heated it produces corrosive, toxic, irritating gases. Contact with the substance may cause severe burns to the skin and eyes. It is considered to be a carcinogen.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of PbO2 from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments