What is Potassium Iodide (KI)?
Potassium iodide is an inorganic chemical compound which is denoted by the chemical formula KI.
Potassium iodide is a metal-halide salt featuring an ionic bond between the potassium cation (K+) and the iodide anion (I–). It is colourless to white, it appears as cubical crystals, or powder or white granules. It has a highly bitter, saline taste.

This compound is prepared by iodine and mixing potassium hydroxide. It is one of the most effective and safe medicines required in a health system and is in the list of the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Properties of Potassium Iodide
1. Physical Properties
| KI | Potassium Iodide |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 166.0028 g/mol |
| Density | 3.12 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 1,330 °C |
| Melting Point | 681 °C |
2. Chemical Properties
Potassium iodide can be oxidized into an I2 molecule by introducing an oxidizing agent to it. An example of such a reaction is provided below.
2KI + Cl2 → 2 KCl + I2
This compound is used as an iodide source in several organic synthesis reactions. One such example is the synthesis of aryl iodides from the diazonium salts of arenes.
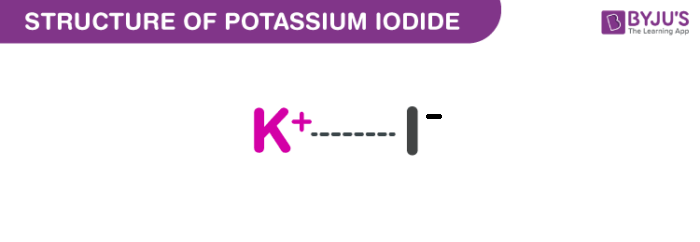
Potassium Iodide Structure (KI Structure)
A molecule of potassium iodide consists of one potassium cation and one iodide anion, which are held together by an ionic bond. The structure of a KI molecule is illustrated below.
Uses of Potassium Iodide
- It is used as a nutritional supplement in the human diet as well as in animal feeds.
- It is used in table salt as the most common additive.
- It is used to avoid the loss of iodine due to oxidation from salts.
- It is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism.
- It helps in promoting hormonal balance.
- It helps to filter out chlorides, bromides, fluorides, and mercury from cells and tissues.
- It is used as an expectorant to break up the mucus so the patient can breathe easily.
- It can help in shrinking the size of the thyroid gland and also decreases the number of thyroid hormones produced.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is potassium iodide used for?
Potassium iodide and anti-thyroid medications are also used to prepare the thyroid gland for surgical removal, to treat other overactive thyroid disorders (hyperthyroidism), and to protect the thyroid in an emergency of radiation exposure.
How do you make potassium iodide?
Potassium iodide (KI) is prepared by reacting potassium hydroxide to iodine with a hot solution. It is used mainly in the form of a saturated solution, 100 g potassium iodide to 100 ml water. That equates to around 50 mg/drop. Until drinking, the solution is normally applied to the tea, fruit juice or milk.
What does potassium iodide do for the body?
KI (potassium iodide) is a stable (not radioactive) iodine salt that can help prevent the absorption of radioactive iodine by the thyroid gland, thus shielding this gland from radiation injury. The thyroid gland is the most sensitive component of the body to radioactive iodine.
What happens if you eat potassium iodide?
If potassium iodide upsets your stomach, take it after meals or with food or milk, unless your doctor has suggested otherwise. If your stomach starts to get upset (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or diarrhea), consult with your doctor.
What are the side effects of potassium iodide?
Serious side effects of Potassium Iodide include: allergic reactions (skin rashes such as hives; swelling of various parts of the body, such as the face, lips, tongue, neck, hands or feet; fever with joint pain, difficulty breathing, speaking or swallowing, wheezing or shortness of breath)
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of KI from the experts at BYJU’S.
Other related links:
| Potassium | Potassium Permanganate |

Comments