Evaporation and Condensation:
In our daily life, we find different kinds of substances. Either they are mixtures or pure substances. Mixtures are made up of two or more two substances. Some mixtures are water-soluble while some of them are not. For example, the salt solution is a water-soluble mixture whereas a mixture of sand and iron nails is a water-insoluble mixture. The iron nails and sand mixture can be easily separated using magnetic separation methods. But in a salt solution, salt and water cannot be separated so easily. The separation techniques like condensation and evaporation are used to extract water and salt separately.
Table of Contents
- What is evaporation?
- Examples of evaporation
- What is condensation?
- Applications of condensation
- Water Cycle
- Recommended Videos
What is Evaporation?
Evaporation, is the process by which an element or compound transitions from its liquid state to its gaseous state below the boiling point.
Examples of evaporation
Some common examples of evaporation are discussed below:
- Evaporation of sprinkled water on rooftop or ground.
- The nail paint, when applied on nails, evaporates due to the presence of acetone.
- Lakes and rivers dry due through a process of evaporation.
- Cooling of hot tea or coffee over time is due to evaporation.
What is condensation?
Condensation is the process where the vapour or gaseous state of water is changed to a liquid state.
The formation of clouds takes place as a result of condensation. This process is measured by Psychrometry. It measures condensation rate by evaporating into the air moisture at different atmospheric temperatures and pressures.
Applications of condensation
- Condensation is a significant component of distillation.
- It occurs naturally and is used to produce water in large quantities.
- In the areas where active desertification is taking place, it is used to retain soil moisture.
- Used to generate power
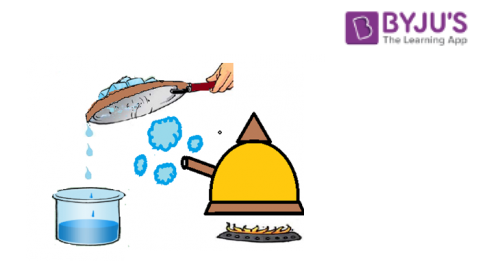
Let us find how evaporation and condensation help in separating salt and water from salt solution with the help of an experiment.
Let us take a beaker full of salt solution. Heat it at a high temperature so that water present in the solution evaporates and forms vapours leaving the salt crystals behind. This process of conversion of water into water vapour is known as evaporation. At the top of the beaker at some distance keep a plate so that water condenses. Make the surface of the plate inclined such that condensed water falls on the other beaker kept below. This process of conversion of water vapour into water is known as condensation.
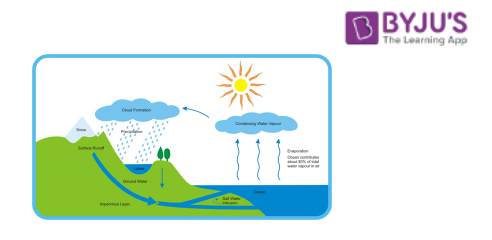
Water Cycle:
Let us understand the concept of evaporation and condensation in detail with another example of the water cycle process in the atmosphere. During the rainy season, we see that rainwater is collected on top of the roof and corners of the road. But after a few days, it disappears. Now the question is where does it go? Rainwater is heated with the help of sunlight. Water converts into vapour in the air by the process of evaporation. After some time, water vapour in the air gets cooler and converts into water droplets, like clouds. This process is known as the condensation of water vapour. When air cannot hold more amount of water i.e. clouds get heavy, the water falls back on the earth’s surface as rain. This is known as precipitation. The rainwater cycle is a continuous cycle.
To learn more about the separation techniques for water-soluble substances and the rainwater cycle, download BYJU’S – the learning app.
Recommended Videos
Corrosion of Metals

Handpicking Separation Technique

Sieving – Separation Of Mixture

Read more:

Comments