Dinitrogen trioxide is a deep blue chemical compound with a chemical formula N2O3 that is formed upon mixing equal parts of nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide and cooling the mixture below −21 °C. It is a powerful oxidizer that is highly toxic and corrosive. In this article, learn in detail about the dinitrogen trioxide formula along with its chemical structure and properties.
Dinitrogen Trioxide Properties
| Properties of Dinitrogen Trioxide | |
| Name | Dinitrogen trioxide |
| Appearance | Deep Blue tinted gas |
| Chemical Formula | N2O3 |
| Boiling Point | 3.5 °C |
| Melting Point | −100.7 °C |
| Density | 1.4 g/cm³ (liquid)
1.783 g/cm3 (gas) |
| Molar mass | 76.01 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble |
Dinitrogen Trioxide Chemical Structure
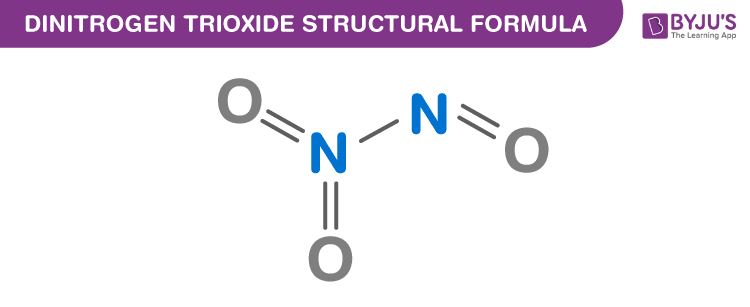
Dinitrogen Trioxide Uses
Dinitrogen trioxide is used as a special purpose fuels due to its highly combustible nature. The chemical only supports combustion and doesn’t actually burn. It is more often used as an oxidizing agent in combination with other chemical compounds.
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments