Practising the previous year’s question papers is the best way of revising the Chemistry subject. By solving the last year’s questions, students get well versed with the change in the exam pattern and difficulty level of the exam. So, to help them, we have provided the ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solutions 2020 in pdf format. Students will also find a separate Chemistry paper pdf. Practising these 2020 Chemistry questions will boost students’ confidence level and fill them with positive energy for the exam.
Download ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solutions 2020 PDF
The ISC Class 12 Chemistry 2020 exam was conducted on 5th February 2020. The exam started at 9 am, and students were allotted 3 hours of time to complete the paper. They can download the ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2020 PDF from the link below.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2020
Download ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2020 PDF
In Chemistry, practicals also play a major role in increasing the scores for the ISC board exam. So, to give students an idea of the Chemistry practical exam, we have provided the ISC Class 12 practical question paper below for downloading.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Practical Question Paper 2020 PDF
Students can go through the ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Solution 2020 below. They can also access the year wise Solved ISC Class 12 Chemistry Solved Previous Year Question Papers for more practice.
Difficult Topics of ISC Class 12 Chemistry 2020 Question Paper
Below we have listed down the topics which students found confusing and difficult while appearing for the ISC Chemistry exam 2020.
- Numerical problems based on molar conductivity, Nernst equation, degree of association, calculation of activation energy, calculation of molality and lowering of vapour pressure.
- IUPAC nomenclature, isomerism, and hybridisation of coordination compounds.
- Reasoning questions of transition elements and colloidal state.
- Named organic reactions, conversion of organic compounds.
- Extraction of silver. • Outer orbital complex and its hybridisation.
- Antiseptics and disinfectants and their examples.
- Transition elements and their properties.
- Test to distinguish between organic compounds.
- Colloidal solutions and their properties.
- Nomenclature and isomerism of coordination compounds.
- Kohlrausch’s law and its application.
ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2020 With Solutions
Question 1:
(a) Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(iodoform, volume, mass, haloform, gram equivalent, chloroform, carbylamine, sp3d2, high, coke, d2sp3, low, gram mole, carbon monoxide)
(i) Equivalent conductivity is the conducting power of all the ions furnished by one ___________ of an electrolyte present in a definite ________ of the solution.
(ii) Bleaching powder, on treatment with ethanol or acetone gives _______. This is an example of _________ reaction.
(iii) Outer orbital complexes involve ________ hybridization and are _______ spin complexes.
(iv) Zinc oxide is reduced by _________ at 1673K to form zinc and __________.
(b) Select the correct alternative from the choices given:
(i) The packing efficiency of simple cubic structure, body centered cubic structure and face centered cubic structure respectively is:
(1) 52·4%, 74%, 68%
(2) 74%, 68%, 52·4%
(3) 52·4%, 68%, 74%
(4) 68%, 74%, 52·4%
(ii) When acetone is treated with Grignard’s reagent, followed by hydrolysis, the product formed is:
(1) Secondary alcohol
(2) Tertiary alcohol
(3) Primary alcohol
(4) Aldehyde
(iii) Which of the following electrolytes is least effective in causing flocculation of
positively charged ferric hydroxide sol?
(1) K3[Fe(CN)6]
(2) K2CrO4
(3) K4[Fe(CN)6]
(4) KBr
(iv) On heating an aliphatic primary amine with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide, the organic compound formed is an:
(1) Alkyl isocyanide
(2) Alkanol
(3) Alkanal
(4) Alkyl cyanide
(c) Match the following:
|
(i) Silicon and phosphorus |
(a) Acetaldehyde |
|
(ii) Iodoform test |
(b) Xenon hexafluoride |
|
(iii) Arrhenius equation |
(c) n-type of semiconductors |
|
(iv) Distorted octahedral structure |
(d) Frequency factor |
(d) Answer the following questions:
(i) What is the common name of the polymer obtained by the polymerization of caprolactam? Is it an additional polymer or condensation polymer?
(ii) Why Zn2+ ions colourless while Ni2+ ions are green and Cu2+ ions are blue in colour?
(iii) The molar conductivity of NaCl, CH3COONa and HCl at infinite dilution is 126·45, 91·0 and 426·16 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate the molar conductivity (λ∞m) for CH3COOH at infinite dilution.
(iv) Identify the compounds A, B, C and D.
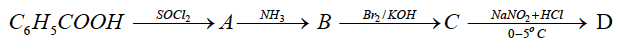
Answer:
(a) (i) gram equivalent, volume
(ii) chloroform, haloform
(iii) sp3d2, high
(iv) coke, carbon monoxide
(b) (i) (3) OR 52·4%, 68% ,74%
(ii) (2) OR Tertiary alcohol
(iii) (4) OR KBr
(iv) (1) OR Alkyl isocyanide
(c)
|
(i) Silicon and phosphorus |
(c) n-type of semiconductors |
|
(ii) Iodoform test |
(a) Acetaldehyde |
|
(iii) Arrhenius equation |
(d) Frequency factor |
|
(iv) Distorted octahedral structure |
(b) Xenon hexafluoride |
(d) (i) Nylon-6 or perlon
Condensation polymer
(ii) Zn2+ ions have completely filled d-orbitals (3d10) and are colourless.
Ni2+ ions and Cu2+ ions have incompletely filled d-orbitals (3d8 and 3d9). These ions are coloured due to d-d-transition.
(iii)
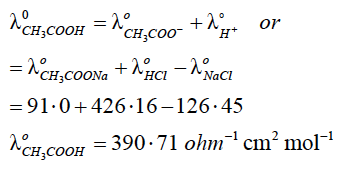
(iv) A → C6H5COCl
B → C6H5CONH2
C → C6H5NH2
D → C6H5N2Cl (Name or Formula)
Question 2:
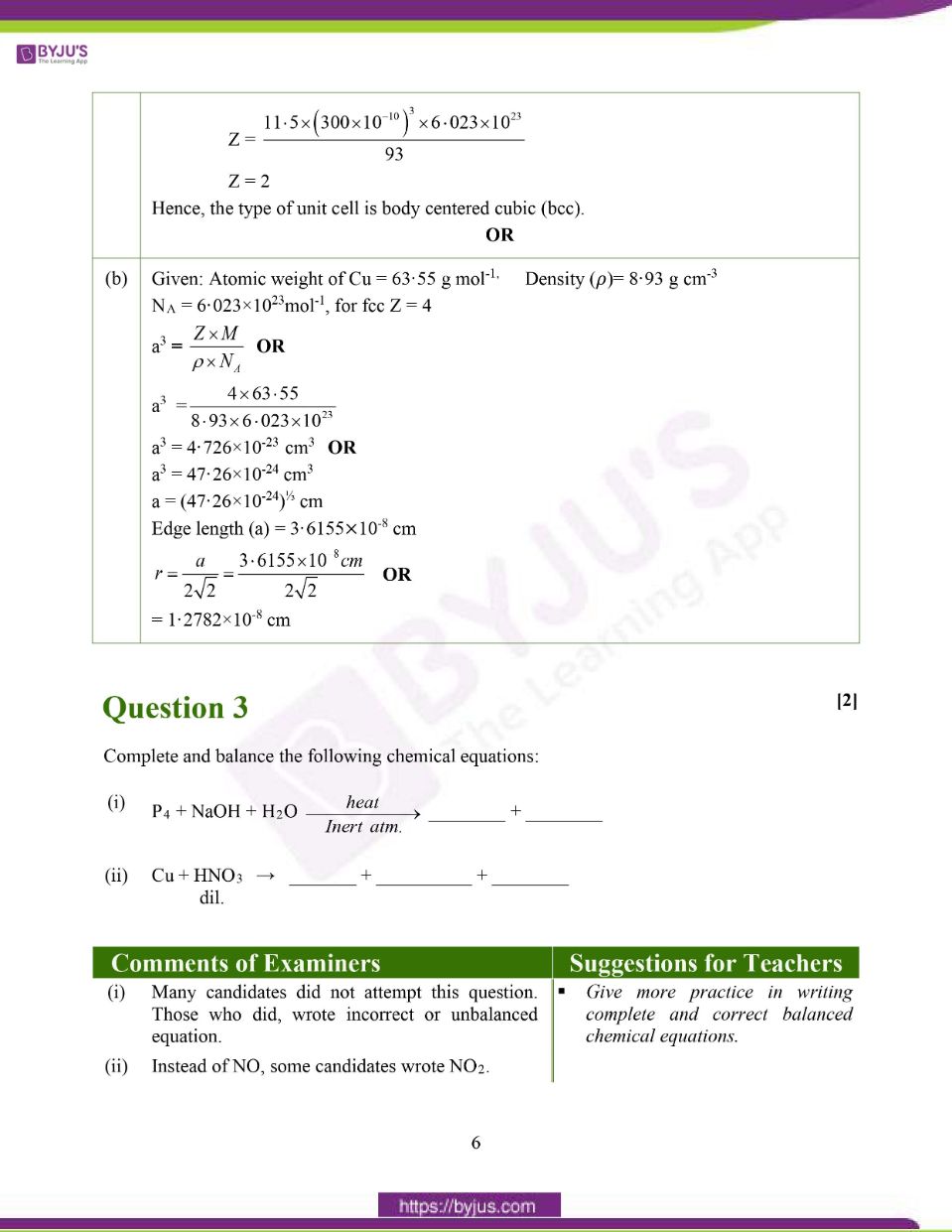
(a) An element has atomic weight 93 g mol-1 and density 11·5 g cm-3. If the edge length of its unit cell is 300 pm, identify the type of unit cell.
(NA = 6·023×1023 mol-1)
OR
(b) Calculate the radius of the copper atom. The atomic weight of copper is 63·55 g mol-1. It crystallises in face centered cubic lattice and has a density of 8.93 g cm-3 at 298K.
(NA = 6·023×1023 mol-1)
Answer:
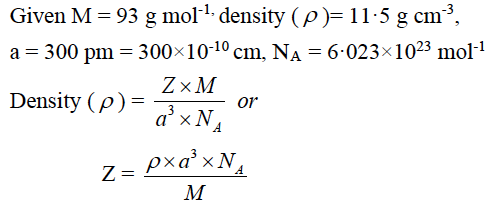
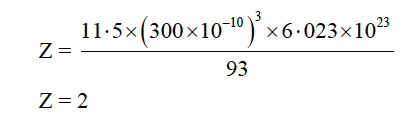
Hence, the type of unit cell is body centered cubic (bcc).
OR
(b) Given: Atomic weight of Cu = 63.55 g mol-1, Density (𝜌)= 8.93 g cm-3
NA = 6·023×1023mol-1, for fcc Z = 4
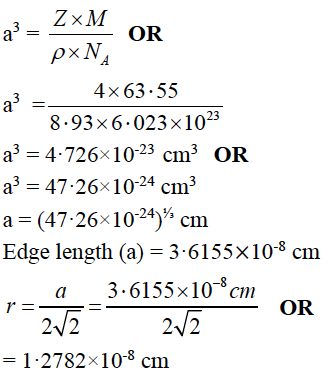
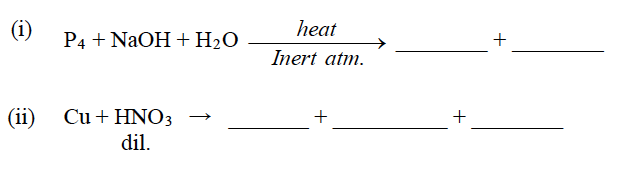
Question 3: Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
Answer:
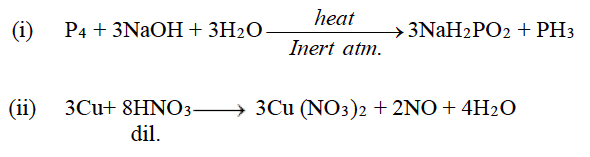
Question 4:
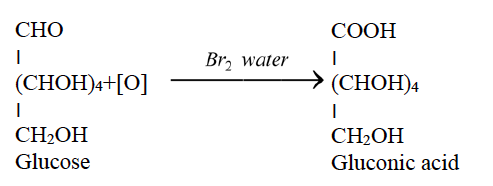
(i) Write the chemical equation for the reaction of glucose with bromine water.
(ii) Write the zwitter ion structure of glycine.
Answer: (i)
(ii)
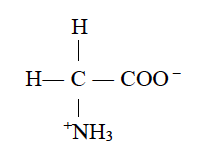
Zwitter ion structure of glycine
Question 5:
(i) How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants?
(ii) Name a substance that can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant.
Answer: (i)
|
Antiseptics |
Disinfectants |
|
The chemicals which prevent or kill the growth of microorganisms are called antiseptics. They can be applied to wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin. |
The chemicals which are capable of killing microorganism but are not safe to be applied to living tissues. They are applied to objects such as floors, instruments, etc. |
(ii) Phenol is used as an antiseptic (0·2% phenol) as well as disinfectant (1% phenol) or H2O2 (6%) H2O2(30%).
Question 6: An alloy of gold (Au) and cadmium (Cd) crystallises with a cubic structure in which gold atoms occupy the corners and cadmium atoms fit into the face centres. What is the formula of this alloy?
Answer:
In fcc arrangement:
The number of gold (Au) atoms (corner atoms)
8 corners x 1/8 atoms per corner
8×1/8 = 1 atom
The number of cadmium (Cd) atoms (face centred atoms)
6 face centres x1/2 atoms per face centre
6×1/2 = 3 atoms
Formula of the given alloy = AuCd3 or Cd3Au
Question 7:
(a) State reasons for the following:
(i) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is insoluble in water.
(ii) Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines.
OR
(b) Complete and balance the following equations:
(i) C6H5NH2 + CH3COCl → ________+ ___________
(ii) C2H5NH2 + HNO2 →________+ ___________ + ___________
Answer:
(a) (i) Ethylamine is soluble in water because ethylamine forms intermolecular hydrogen bonds with water. While, in aniline the aryl group possess steric hindrance and do not form hydrogen bonds.
(ii) In Aliphatic amines, the lone pair is easily available for donation (due to +I effect). Hence, aliphatic amines are stronger bases. While, in aromatic amines the lone pair of electrons present on nitrogen takes part in resonance (M effect) and hence, not available for donation and are weaker bases.
OR
(b) (i) C6H5NH2 + CH3COCl → CH3CONHC6 H5 + HCl
(ii) C2H5NH2 + HNO2 → RC2H5OH + N2 + H2O
Question 8: Draw the structure of xenon tetrafluoride molecule. State the hybridisation of the central atom and the geometry of the molecule.
Answer:
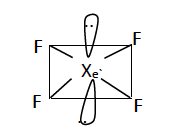
Hybridisation of the central atom = sp3d2
Geometry of the molecule = square planar geometry or Octahedral geometry.
Question 9:
(a) Calculate the emf and ΔG for the given cell at 25oC:
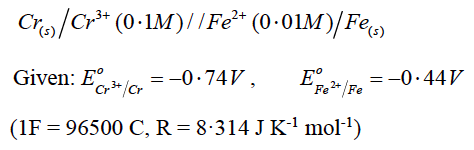
OR
(b) Calculate the degree of dissociation (∝) of acetic acid, if its molar conductivity (Ʌm) is 39·05 S cm2 mol-1.
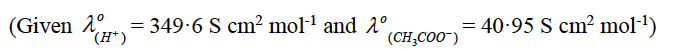
Answer: (a)
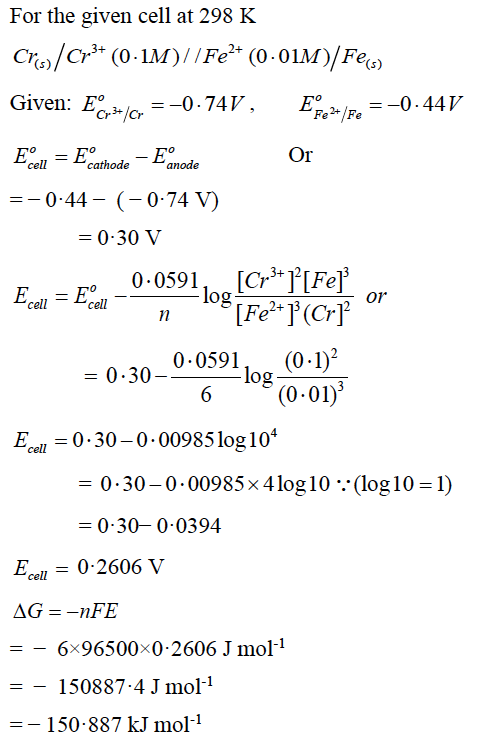
OR
(b) Given Ʌm = 39·05 S cm2 mol-1
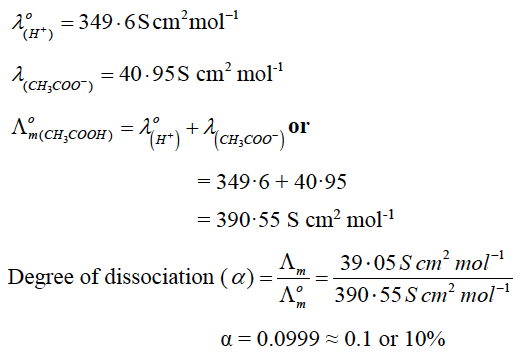
Question 10: Name an important ore of silver. How is silver extracted from its sulphide ore? Give balanced chemical equations involved in the extraction of pure silver.
Answer: Argentite (Ag2S) OR Horn Silver (AgCl)
• Concentration by – Froth floatation process
• Treatment with sodium cyanide (Leaching)
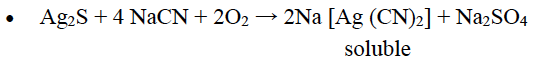
• Precipitation of Silver with zinc
• 2Na [Ag (CN)2]+ Zn → Na2 [Zn(CN)4 ]+2Ag
• Electrolytic refining
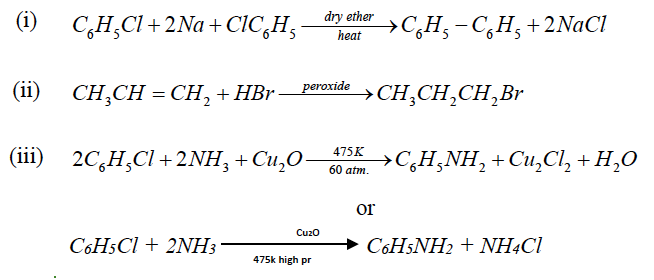
Question 11: How will you convert the following:
(i) Chlorobenzene to biphenyl.
(ii) Propene to 1- bromopropane.
(iii) Chlorobenzene to aniline.
Answer:
Question 12: Explain what is observed when:
(i) A beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution.
(ii) An electric current is passed through a colloidal solution.
(iii) An electrolyte (AlCl3) is added to a colloidal solution of arsenious sulphide (As2S3).
Answer:
(i) The path of the beam is illuminated in all the directions. It is called the Tyndall effect. This effect is due to scattering of light by the colloidal particles present in colloidal solution.
(ii) The colloidal charged particles move towards the cathode or anode depending upon the charges on the colloidal particle (Electrophoresis/ coagulation/ precipitation).
(iii) The colloidal solution of arsenious sulphide is negatively charged, when AlCl3 is added the Al3+ ions (effective ion) coagulates the negatively charged arsenious sulphide sol. Or
coagulation / precipitation takes place.
Question 13:
(a) How will you convert the following: (Give balanced equation)
(i) Benzoyl chloride to benzaldehyde.
(ii) Methyl chloride to acetic acid.
(iii) Acetic acid to methane.
OR
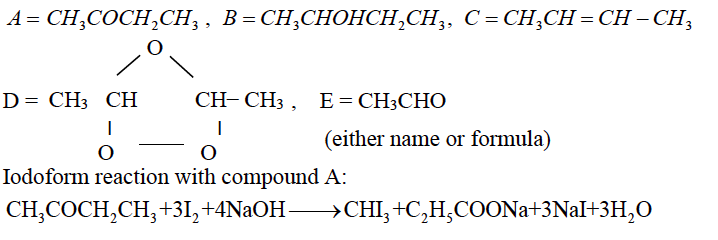
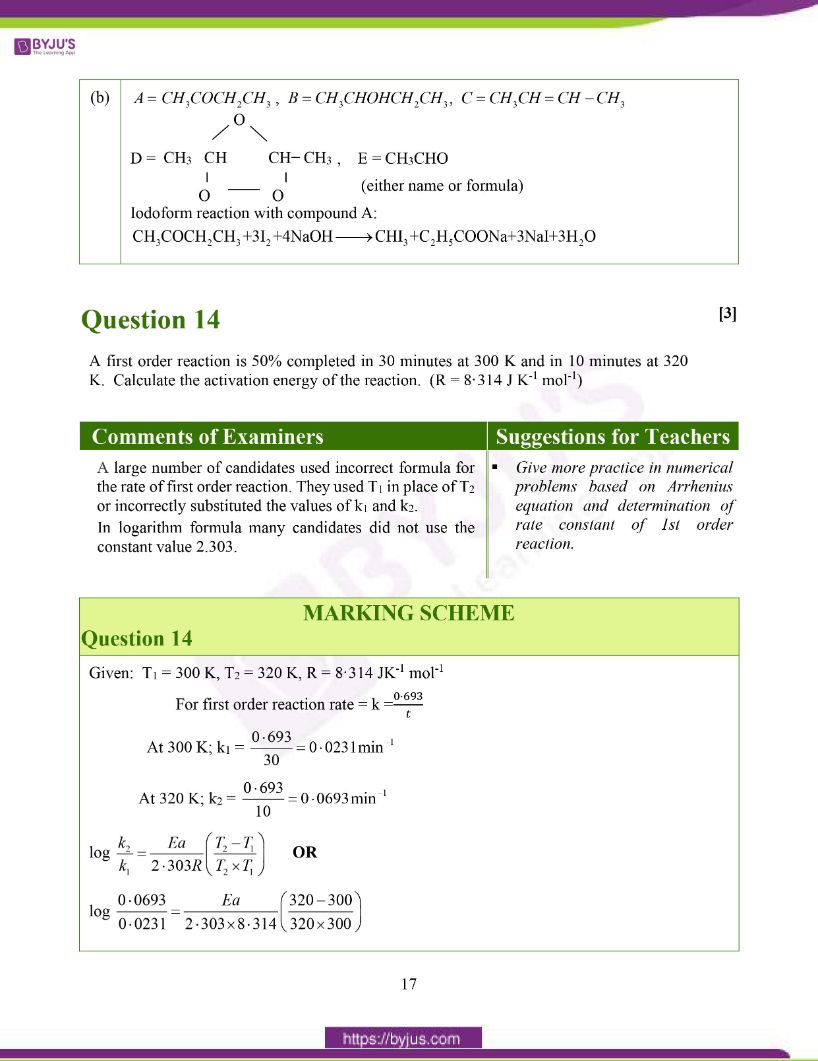
(b) A ketone A (C4H8O) which undergoes Iodoform reaction gives compound B on reduction. B on heating with conc.H2SO4 at 443 K gives a compound C which forms ozonide D. D on hydrolysis with Zn dust gives only E. Identify the compounds A to E. Write the Iodoform reaction with compound A.
Answer: (a)
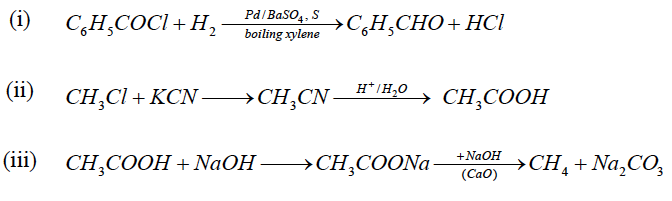
OR
(b)
Question 14: A first order reaction is 50% completed in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction. (R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1)
Answer:
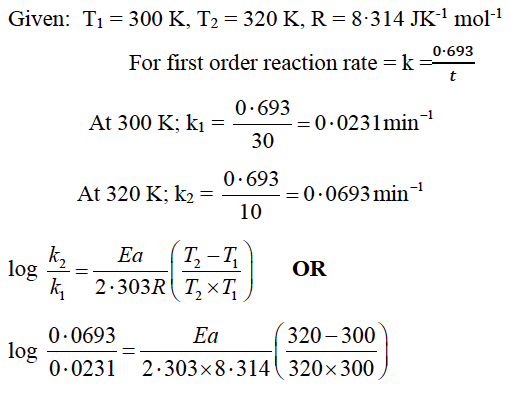
Ea = 43,839·29 J mol-1 OR
Ea = 43.839kJ mol-1
Question 15:Explain the following:
(i) Transition metals and their compounds generally exhibit a paramagnetic behaviour.
(ii) There is an increase in density of elements from titanium (Z=22) to copper (Z = 29) in the 3d series of transition elements.
(iii) K2Cr2O7 acts as a powerful oxidising agent in acidic medium.
Answer:
(i) Transition metal ions have unpaired electrons in d-orbitals (d1 – d9). They exhibit paramagnetic behaviour.
(ii) As we move from left to right along the 3d transition series (from Ti to Cu) the atomic radii decrease due to increase in nuclear charge. Therefore, atomic volume decreases with increase in atomic mass. Hence, density of transition metal increases from Ti to Cu.
(iii) In acidic medium K2Cr2O7 liberates nascent oxygen which oxidises the other substances hence, it acts as a strong oxidising agent.
OR
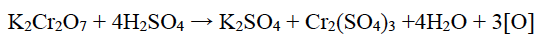
Question 16:
(a) (i) The elevation in boiling point when 0·30 g of acetic acid is dissolved in 100 g of benzene is 0·0633 oC. Calculate the molecular weight of acetic acid from this data. What conclusion can you draw about the molecular state of the solute in the solution?
(Given Kb for benzene = 2·53 K kg mol-1, at. wt. of C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
(ii) Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 0·025 g of K2SO4 in 2 litres of water at 25oC, assuming that K2SO4 is completely dissociated.
(R = 0.0821 Lit-atm K-1 mol-1 , mol. wt. of K2SO4 = 174 g mol-1)
OR
(b) (i) An aqueous solution of a non-volatile solute freezes at 272·4 K, while pure water freezes at 273·0 K. Determine the following:
(Given Kf = 1·86 K kg mol-1 , Kb = 0·512 K kg mol-1 and vapour pressure of water at 298 K = 23·756 mm of Hg)
(1) The molality of solution
(2) Boiling point of solution
(3) The lowering of vapour pressure of water at 298 K
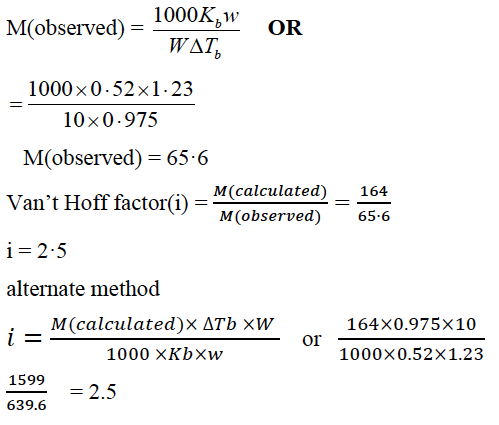
(ii) A solution containing 1·23 g of calcium nitrate in 10 g of water, boils at 100·975ºC at 760 mm of Hg. Calculate the van’t Hoff factor for the salt at this concentration.
(Kb for water = 0·52 K kg mol-1, mol. wt. of calcium nitrate = 164 g mol-1)
Answer: (a) (i) Given w = 0.30 g of acetic acid, W = 100 g of benzene
ΔTb = 0·0633K, Kb = 2·53 K kg mol-1 (for benzene)
Normal molecular weight of CH3COOH = 60

(ii) Given: w = 0·025 g of K2SO4, Volume (V = 2 litres)
T = 273 + 25 oC= 298 K, m = 174 g mol-1
R = 0.0821 Lit-atm K-1 mol-1 π = ?
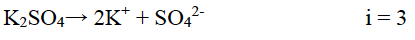
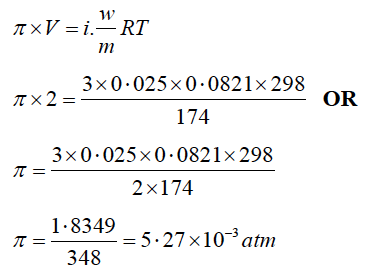
(b) (i) (1) The molality of solution:
ΔTf = Kf m
ΔTf = T0 −Ts
= 273·0 – 272·4
= 0 ·6 K
∴ m=0.6/1.86 = 0.3225m
⋅
(2) Boiling point of solution:
ΔTb = Kb m
= 0·512×0·3225
ΔTb = 0.165 K
Ts = To + ΔTb
= 373+0·165
= 373·165 K or 100·165oC
(3) The lowering of vapour pressure of water at 298 K:
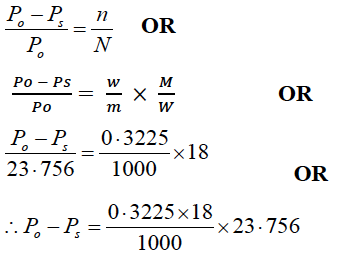
(Po − Ps )or ΔP = 0⋅1379 mm of Hg
(ii) Given: w =1.23g W =10g
ΔTb = 100.975 – 100 = 0.975
Kb = 0·52 K kg mol-1
Question 17:
(a) (i) Write the IUPAC names of the following complexes:
(1) [Cu (NH3)4]SO4
(2) [Co(en)2Cl2]
(3) K3[Al(C2O4)3]
(ii) With reference to the coordination complex ion [Fe (H2O)6]2+ answer the following:
(at. no. of Fe = 26)
(1) Give the IUPAC name of the complex ion.
(2) What is the oxidation number of the central metal atom?
(3) How many unpaired electrons are there in the complex ion?
(4) State the type of hybridisation of the complex ion.
(b) (i) Name of the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pairs of compounds:
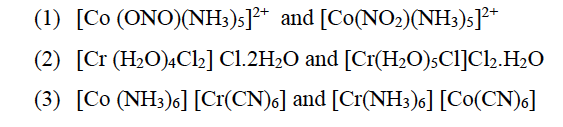
(ii) Using the valence bond approach, predict the shape, hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of [Ni (CO)4]. (at. no. of Ni = 28)
Answer: (a) (i) (1) tetraamminecopper(II) sulphate.
(2) dichloridobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt (II)
(3) Potassium trioxalatoaluminate(III)
(ii) (1) hexaaquairon (II) ion
(2) +2
(3) Four unpaired electrons
(4) sp3d2
OR
(b) (i) (1) Linkage isomerism
(2) Hydrate isomerism or Solvate Isomerism
(3) Coordination isomerism
(ii) [Ni(CO)4]
Shape – tetrahedral
Hybridisation –sp3
Magnetic behaviour – diamagnetic
Question 18:
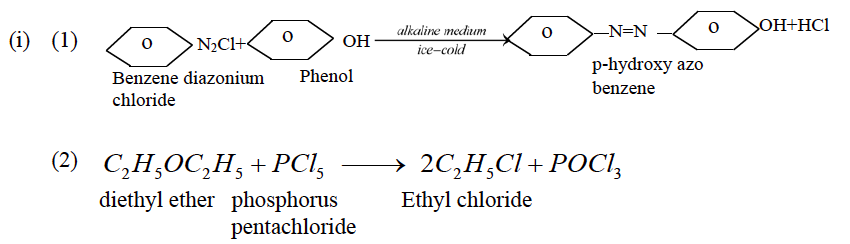
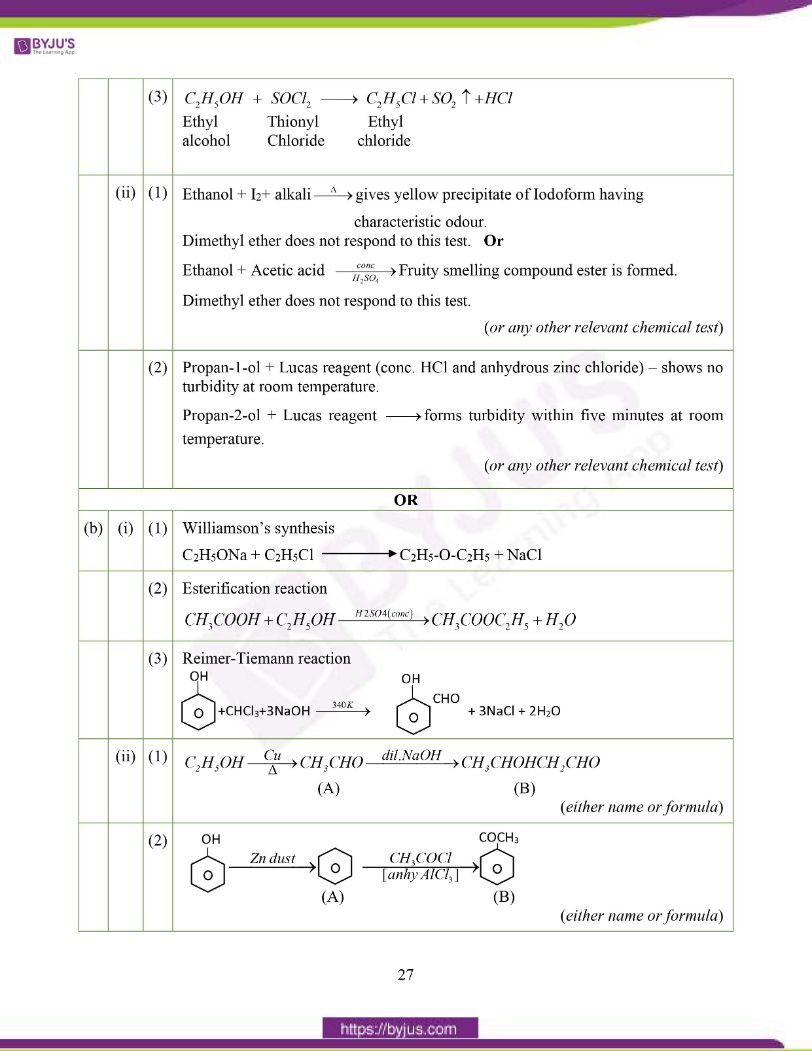
(a) (i) Give balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(1) Phenol is treated with an ice cold alkaline solution of benzene diazonium chloride.
(2) Diethyl ether is treated with phosphorus pentachloride.
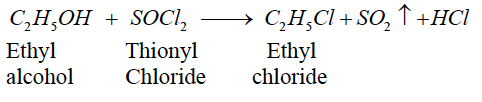
(3) Ethyl alcohol is treated with thionyl chloride.
(ii) Give one chemical test each to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(1) Ethanol and dimethyl ether
(2) Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol
OR
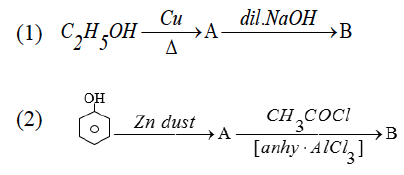
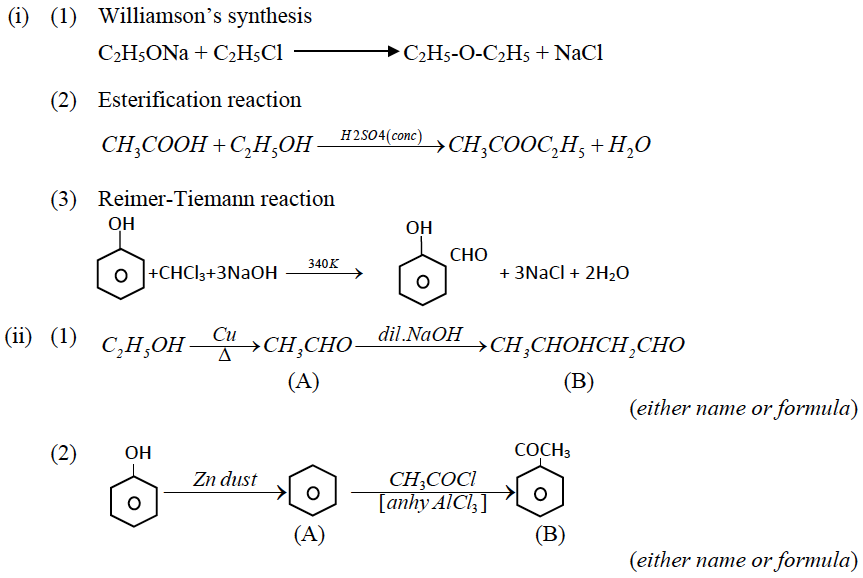
(b) (i) Write chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions:
(1) Williamson’s synthesis.
(2) Esterification reaction
(3) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
(ii) Identify the compounds A and B in the given reactions:
Answer: (a)
(3)
(ii) (1)
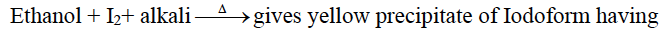
characteristic odour. Dimethyl ether does not respond to this test. Or
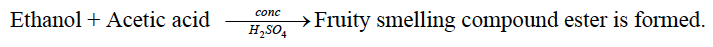
Dimethyl ether does not respond to this test.
(or any other relevant chemical test)
(2) Propan-1-ol + Lucas reagent (conc. HCl and anhydrous zinc chloride) – shows no turbidity at room temperature.
Propan-2-ol + Lucas reagent → forms turbidity within five minutes at room temperature.
(or any other relevant chemical test)
OR
(b)
NOTE: For questions having more than one correct answer/solution, alternative correct answers / solutions, apart from those given in the marking scheme, have also been accepted.
We hope students must have found this information on “ISC Class 12 Chemistry Question Papers Solutions 2020” helpful for their studies. To get the year-wise ISC Class 12 Previous Years Question papers along with solutions for other subjects, click here. Keep learning and download the BYJU’S App to access interactive study videos.
























Comments