In electromagnetism, the electric field is defined as the measure of the flow of electric current through a given area. It is a property of an electric field that may be thought of as electric field lines that intersect at a particular area. These field lines arise from +ve electric charges and cut off at -ve charges. Electric flux is the rate at which the electric field flows through a given area. The electric flux is directly proportional to the number of electric field lines going through the virtual surface. Electric field lines that are conducted out of a sealed (closed) surface are +ve, and the lines that are carried into on a sealed surface are considered -ve.
Suppose there is no net charge within a sealed surface; then, the field line that is conducted into the surface continues to travel inwards of the surface, and then it is led outwards somewhere on the surface. The net electric flux is ‘0’ when -ve flux is equal to +ve flux in magnitude. The unit of flux is Volt metres (V m)
Let E be the electric intensity at a point in an electric field. If the normal to the area A is along the direction of the electric field, then the flux through the small area A is given as
Φ = EA
If the normal to the area is at an angle θ to the direction of the field, then the flux through the area A is given as
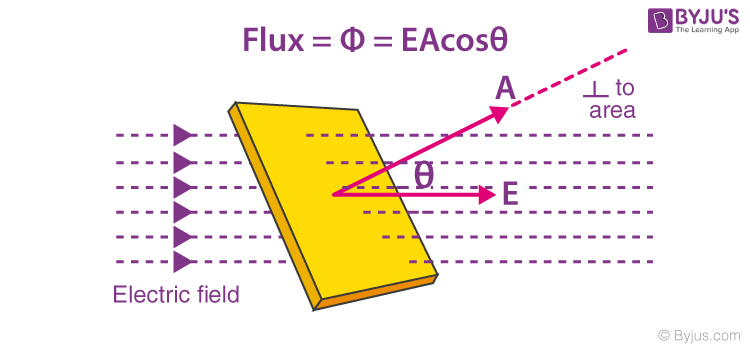
Φ = EACos θ
Zero Flux: No electric field lines will pass through a surface when it is placed parallel to the electric field.
Φ = EACos θ
= EA Cos 900
= EA (0) = 0
Maximum Flux: The maximum electric field lines of force passes through a surface when it is placed perpendicular to the electric field.
Φ = EACos θ
= EA Cos 00
= EA (1) = EA
Gauss’s Law
For an electric field, the mathematical relation between an enclosed charge and the electric field is given by Gauss’s law. It is one of the core laws of electromagnetism. The Gauss law states that the total electric flux through a hypothetical closed surface is always equal to (1/ε0) times the net charge enclosed by the surface.
Φ = EACos θ = q/ε0
It simplifies the calculation of the electric field for the geometry of sufficient symmetry. It is an important tool has it allows the appraisal of the volume of enclosed charges by mapping the field on a surface.
Electric Flux

Frequently Asked Questions on Flux of Electric Current
What is the difference between electric flux and electric current?
The electric flux is given by the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area taken perpendicular to the field. At the same time, electric current is the rate of flow of electric charges.
When is the electric flux maximum?
If the electric field is uniform, the electric flux passing through the surface of area A is given as
ΦE = EAcosθ
When θ = 0, cosθ = 1
Therefore, the electric flux of a surface is maximum when the area vector is parallel to the direction of the electric field.
What does Gauss’s law state?
According to Gauss’s law, the electric flux through the closed surface is proportional to the total electric charge enclosed by the surface.
What is electric current?
Charges in motion constitute an electric current.

Comments