What Are Esters?
The group of chemical compounds which are formed by bonding an alcohol group with a group of organic acids by losing water molecules is called Esters. Esters are polar in nature but not more than alcohols. These chemical compounds participate in the formation of hydrogen bonds as the acceptors of hydrogen bonds, but they cannot act as hydrogen-bond donors. This ability to participate in hydrogen bonding benefits some water solubility.
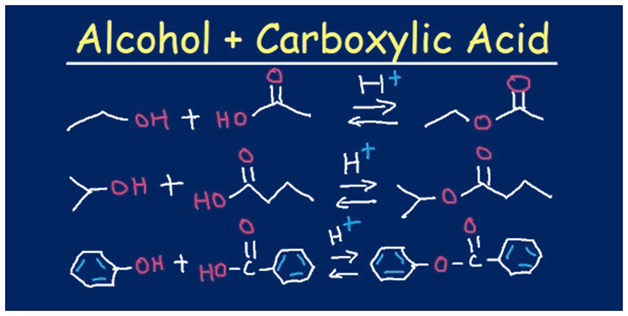
These esters are made from carboxylic acids and alcohols. The alcohol and carboxylic acid are heated in the presence of some catalyst, generally concentrated sulphuric acid. This is a form of condensation reaction in which two or more molecules join together, forming one larger molecule called the ester, and a smaller kind of molecule, usually water.
Esters are also produced by using acid chlorides or acyl chlorides, acid anhydrides, etc.
Mechanism of Formation of Esters from Carboxylic Acids
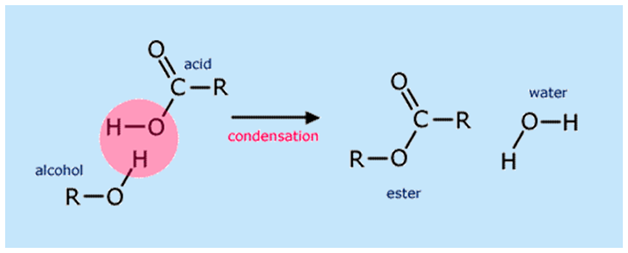
Esters are formed when the carboxylic acid is heated with the alcohol in the presence of a catalyst. In this reaction, concentrated sulphuric acid is used as a catalyst; a dry form of hydrogen chloride gas is used in some cases. This method of reaction is used to convert alcohol into an ester. It does not work for the compounds containing the OH- Group directly attached to the benzene ring. This method of reaction is called the esterification reaction.
This is a reversible and slow reaction. When the carboxylic acid is added to the catalyst and an alcohol, an ester is formed along with the water. This is called Fischer esterification.
The equation of the reaction between the alcohol ROH and the acid RCOOH (R’ and R might be the same or different) is given below:
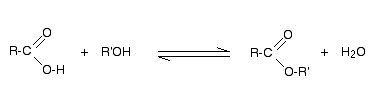
The reaction can also be written as:
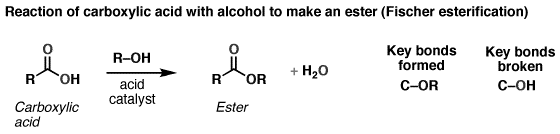
The reaction is said to be in equilibrium. The alcohol is usually used as the solvent, so it is present in large quantities. Many of the different acids can also be used; the commonly used ones are the H2SO4 (sulphuric acid) and the TsOH (toxic acid).
Carboxylic acids and alcohols are warmed together in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid to observe a smell of formed esters. The acid catalyst in the reaction is known to serve for two reasons: It makes the carbon atom of the carbonyl group a good electrophile, and allows the loss of water as a part of the leaving group.

Comments