The organic molecules also exhibit the property of resonance or mesomerism. In organic chemistry, the factor called resonance or mesomerism describes the delocalised electrons within certain molecules where one single Lewis structure does not express the bonds. An ion or molecule with these delocalised electrons can be represented by contributing several structures, which are called resonance structures.
Resonance Effect or Mesomeric Effect in Chemistry
The withdrawal effect or releasing effect of electrons attributed to a particular substituent through the delocalisation of π or pi-electrons that can be seen by drawing various canonical structures is called a resonance effect or mesomeric effect. M or R symbols are used to represent the resonance effect.
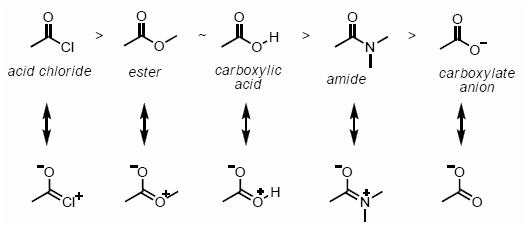
The concept of resonance effect tells about the polarity induced in a molecule by the reaction between a lone pair of electrons and a pi bond. It also occurs by the interaction of 2 pi bonds in the adjacent atoms. Resonance, in simple terms, is the molecules with multiple Lewis structures. Resonance in chemistry helps in understanding the stability of a compound, along with the energy states.
Definition – The resonance effect can be defined as a chemical phenomenon that is observed in the characteristic compounds having double bonds in the organic compounds. The organic compounds contain these double bonds in the structures and usually have the overlapping of the p-orbitals on the two adjacent sides of carbon atoms.
Types of Resonance Effects
There are two types of resonance effects, namely, positive resonance effect and negative resonance effect.
- Positive Resonance Effect – Positive resonance effect occurs when the groups release electrons to the other molecules by the process of delocalisation. The groups are usually denoted by +R or +M. In this process, the molecular electron density increases. For example, -OH, -SH, -OR and -SR.
- Negative Resonance Effect – Negative resonance effect occurs when the groups withdraw the electrons from other molecules by the process of delocalisation. The groups are usually denoted by -R or -M. In this process, the molecular electron density is said to decrease. For example, -NO2, C=O, -COOH and -C≡N.
Video Lesson on SIR Effect
Stability of Resonating Structures

Thanks for article