Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues are provided in this article. Tissue is a group of cells that work together to perform a particular function. In the previous chapter, we studied the basic fundamental unit of life, that is, the cell. The next level is tissues. The types of tissue, permanent tissue and temporary tissue, are explained in a precise manner in this chapter. We will also learn about the tissues which help in building the different organs of the body.
Chapter 3, Tissues, highlights the types of tissue present in plants and animals and also the functions they perform. Topics such as how tissues play a major role in building up the muscles, multicellular organisms contain hundreds of tissues in the body, etc., are explained in this chapter.
Download PDF of Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues
Access Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Biology Chapter 3 Tissues
Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is the importance of tissues?
Answer
- Tissue provides structural strength and mechanical strength, and shows the division of labour.
- A collective number of tissues form organs in the multicellular organism.
2. Why do plants and animals possess different types of tissues?
Answer
Plants are autotrophic and stationary, whereas animals have to move from one place to another in search of food, mate, and shelter. Plant tissues are suited for the stationary habit of plants, whereas tissue organisation in animals is targeted at providing higher mobility. Plants and animals are different kinds of organisms; hence, they require different types of tissues to carry out their bodily functions.
3. Tabulate differences between plants and animal tissues.
Answer
| Plant Tissues | Animal Tissues |
| Dead supportive tissues are more abundant than living tissues in plants. | Living tissues are more than dead tissues. |
| Less energy maintenance is required. | More energy maintenance is required. |
4. Write a short note on intercalary meristem.
Answer
Intercalary meristems are located in the leaves and internodes at the intercalary position. They help to increase the length of the internode. It is found in grass, monocots, and pines. It is a part of the apical meristem and adds to the height of the plant.
5. Write one main function of
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Lateral meristem
Answer
(a) They are responsible for root and stem elongation, resulting in an increase in the height of the plant (primary growth).
(b): They cause an increase in the diameter and girth of stems or roots (secondary growth).
6. What are simple tissues? Explain their three different types.
Answer
Simple tissues consist of cells that are structurally and functionally similar. They are made up of only one type of cell. Simple tissues are of three types, namely parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma – they are living cells and walled, soft in nature due to the presence of thin-walled cells
Collenchyma – These are characterized by uneven thick-walled living cells.
Sclerenchyma – They have cells with thickened lignified walls, providing them strength and making them waterproof.
7. Draw a well-labelled diagram of parenchyma and collenchyma.
Answer


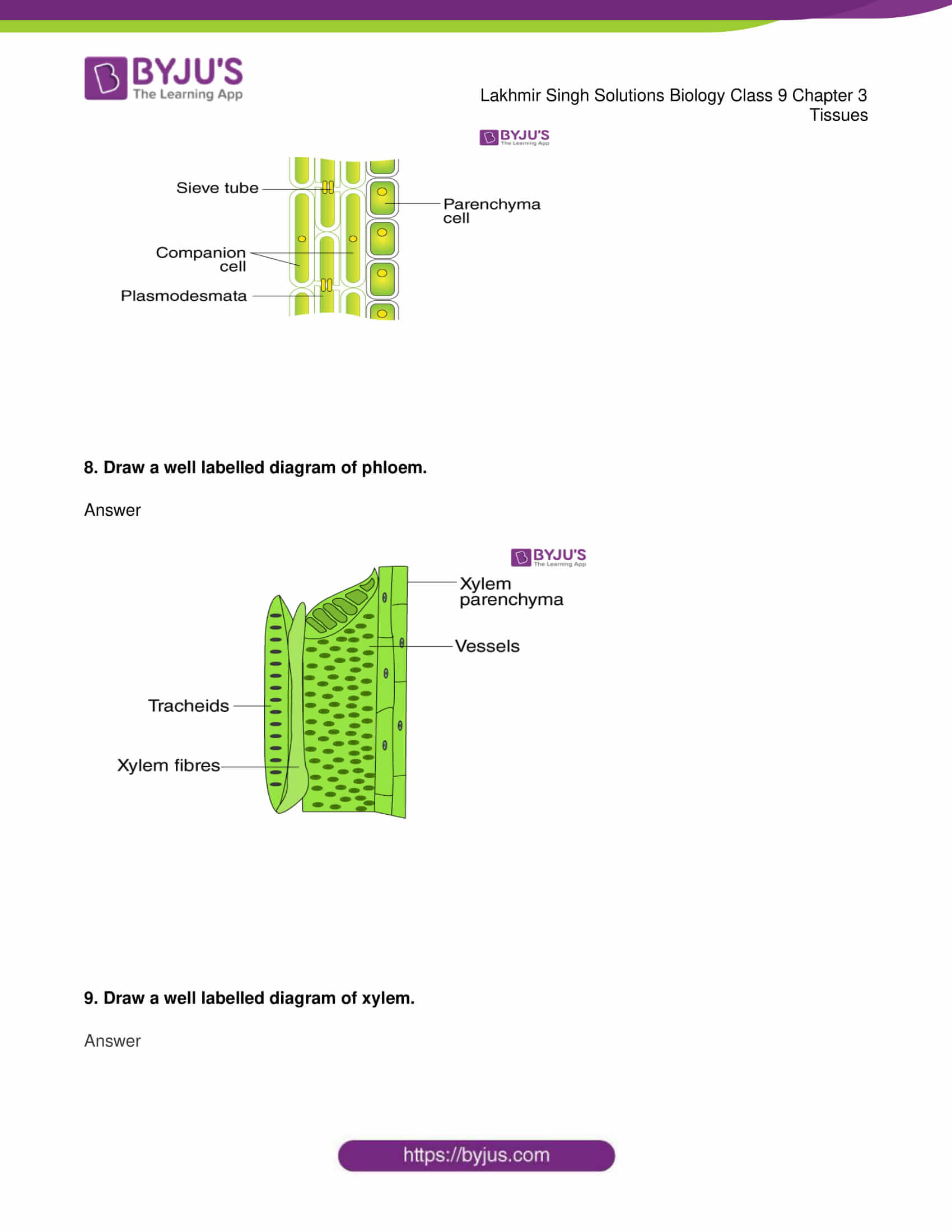
8. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the phloem.
Answer

9. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the xylem.
Answer

10. Give two functions of collenchyma.
Answer
Functions of collenchyma
- Provides mechanical support and elasticity in young dicotyledonous stems.
- Manufactures sugar and starch if their cells possess chloroplast.
11. Write a short note on sclerenchyma.
Answer
Sclerenchyma cells are elongated, dead cells with lignin deposits in their cell wall. They have no intercellular gaps. Sclerenchyma is found in the covering of seeds and nuts, around the vascular tissues in stems and in the veins of leaves. Sclerenchyma provides strength to the plant. The main function of sclerenchyma is to provide mechanical support and protection to the plant.
12. Distinguish between the xylem and phloem.
Answer
| Xylem | Phloem |
| Xylem tissue helps in the transport of water and minerals. | Phloem tissue helps in the transport of food. |
| Water is transported upwards from roots to all other plant parts. | Food is transported in both upward and downward directions. |
13. Distinguish between tracheids and vessels.
Answer
| Tracheids | Vessels |
| They are single-celled. | They are made up of a row of cells. |
| The end walls remain intact. | The end walls get dissolved and become perforated. |
14. Explain different types of elements present in the phloem.
Answer
Phloem is a living tissue in vascular plants which conducts the soluble organic compounds synthesized during photosynthesis downwards from the leaves.
The constituents of phloem are:
- Companion cells – It appears to check the activity of the adjacent sieve element and participates in loading and unloading of the sugar into the sieve element
- Sieve tubes – These elongated living cells convey carbohydrates, chiefly sucrose, from leaves to roots and fruits
- Phloem fibres – They are commercially useful as they possess great pliability and tensile strength
- Phloem parenchyma – They are also known as transfer cells, and are found near the finest branches, and ends of sieve tubes in leaf veinlets, functional here in conveying food
15. What are tracheary elements? Describe their functions.
Answer
Tracheary elements are dead, hollow cells with patterned cell walls comprising xylem vessels and tracheids, which function as conductive hollow tubes for water and nutrient transport throughout the plant body. Xylem fibre cells, with evenly thickened secondary cell walls, provide mechanical support to the plant body.
16. Write the functions of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Answer
Functions of parenchyma:
- The main function of parenchyma is to store and assimilate food. Hence, they are referred to as food storage tissues.
- It serves as a packing tissue to fill the spaces between other tissues and maintain the shape and firmness of the plant.
- Stores waste products of plants.
Functions of collenchyma:
- A mechanical tissue that provides mechanical support and elasticity to the stems of dicot plants.
- Cells possess chloroplast, then it is involved in manufacturing sugar and starch.
- Provides tensile strength and flexibility to the plant body.
Functions of sclerenchyma:
- Provides mechanical strength to the plant.
- Makes the plant body rigid, flexible, and elastic.
17. What is the difference between parenchyma and collenchyma?
Answer
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma |
| It consists of thin-walled living cells. | In collenchyma, cells are thickened at localised regions. |
| They are involved in food storage. | They are the chief mechanical tissue in young plants, particularly dicot stems. |
18. What are the differences between collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Answer
| Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| It consists of living cells. | It consists of dead cells. |
| Its cells possess cytoplasm. | Its cells lack cytoplasm. |
| It provides mechanical support and elasticity to the plant body. | It is mainly a mechanical tissue. |
19. Name the different types of elements found in the xylem.
Answer
Types of elements found in the xylem are:
tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibre.
20. What are the functions of the xylem?
Answer
Functions of xylem:
(i) To carry water and mineral salts upwards from the root to different parts of shoots.
(ii) To provide mechanical support to the plant as the walls of tracheids, vessels, and fibres of the xylem are lignified.
Also, visit Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 9 Biology to get complete solutions for all chapters.