According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 10.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Heron’s Formula Notes – Download PDF Here
In geometry, a triangle is a closed three-dimensional figure. In this article, you are going to learn Heron’s formula for class 9, which is used to find the area of triangles. You will also learn how Heron’s formula is used to find the area of other polygons in detail.
Triangle
The plane closed figure, with three sides and three angles is called as a triangle.
Types of triangles:
Based on sides – a) Equilateral b) Isosceles c) Scalene
Based on angles – a) Acute-angled triangle b) Right-angled triangle c) Obtuse-angled triangle
For more information on Triangles, watch the below video

To know more about Triangles and Its Type, visit here.
Area of a Triangle
Area = (1/2) × base × height
In the case of equilateral and isosceles triangles, if the lengths of the sides of triangles are given, we use Pythagoras’ theorem in order to find the height of a triangle.
To know more about the Area of a triangle, visit here.
Area of an Equilateral Triangle
Consider an equilateral ΔABC, with each side as a unit. Let AO be the perpendicular bisector of BC. In order to derive the formula for the area of an equilateral triangle, we need to find height AO.

Using Pythagoras’ theorem,
AC2 = OA2 + OC2
OA2 = AC2 − OC2
Substitute AC = a,OC = a/2 in the above equation.
OA2 = a2 − a2/4
OA = √3a/2
We know that the area of the triangle is:
A = (1/2) × base × height
A = (1/2) × a × (√3a/2)
∴ Area of Equilateral triangle = √3a2/4
Area of an Isosceles Triangle
Consider an isosceles ΔABC with equal sides as a units and base as b units.
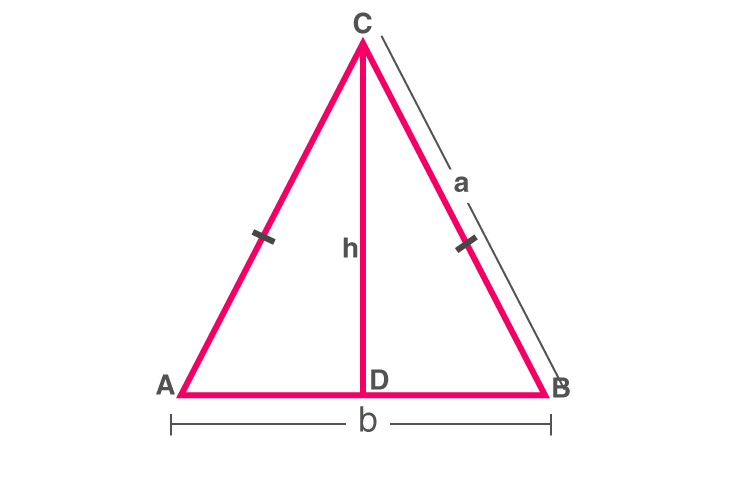
Isosceles triangle ABC
The height of the triangle can be found by Pythagoras’ Theorem :
CD2 = AC2 − AD2
⇒h2 = a2− (b2/4) = (4a2 – b2)/4
⇒h =(1/2) √(4a2 – b2)
Area of triangle is A = (1/2)bh
∴ A = (1/2) × b × (1/2)√(4a2 – b2)
∴ A = (1/4) × b × √(4a2 – b2)
Area of a Triangle – By Heron’s formula
Area of a ΔABC, given sides a, b, c by Heron’s formula (also known as Hero’s Formula) is:
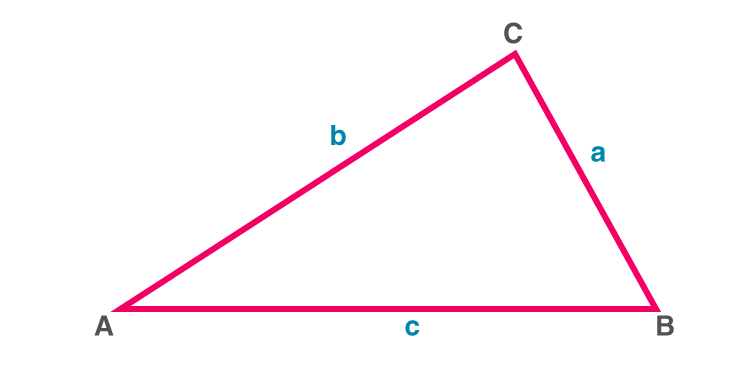
Triangle ABC
Find semi perimeter (s) = (a + b + c)/2
Area = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
This formula is helpful in finding the area of a scalene triangle, given the lengths of all its sides.
To know more about Heron’s Formula, visit here.
Area of Any Polygon – By Heron’s formula
For a quadrilateral, when one of its diagonal values and the sides are given, the area can be calculated by splitting the given quadrilateral into two triangles and using Heron’s formula.
Example: A park, in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has ∠C=90∘, AB = 9 cm, BC = 12 cm, CD = 5 cm and AD = 8 cm. How much area does it occupy?
⇒We draw the figure according to the information given.

The figure can be split into 2 triangles ΔBCD and ΔABD
From ΔBCD, we can find BD (Using Pythagoras’ Theorem)
BD2 = 122 + 52 = 169
BD = 13cm
Semi-perimeter for ΔBCD S1 = (12 + 5 + 13)/2 = 15
Semi-perimeter ΔABD S2 = (9 + 8 + 13)/2 = 15
Using Heron’s formula A1 and A2 will be:
A1 = √[15(15 – 12)(15 – 5)(15 – 13)]
A1 = √(15 × 3 × 10 × 2 )
A1 =√900 = 30 cm2
Similarly,
A2 will be 35.49 cm2.
The area of the quadrilateral ABCD = A1 + A2 = 65.49 cm2

superb byju’s
thanks for all this
Thanks for all this,it helps me a lot to understand this topic