Flashcards for NEET Chemistry are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for the chapter “Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure”. These flashcards are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. These are helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. It covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Chemistry.
Download PDF of NEET Chemistry Flashcards for Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
|
Name of the NEET Sub-section |
Topic |
Flashcards Helpful for |
|
Chemistry |
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure |
NEET Exams |
| Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | |
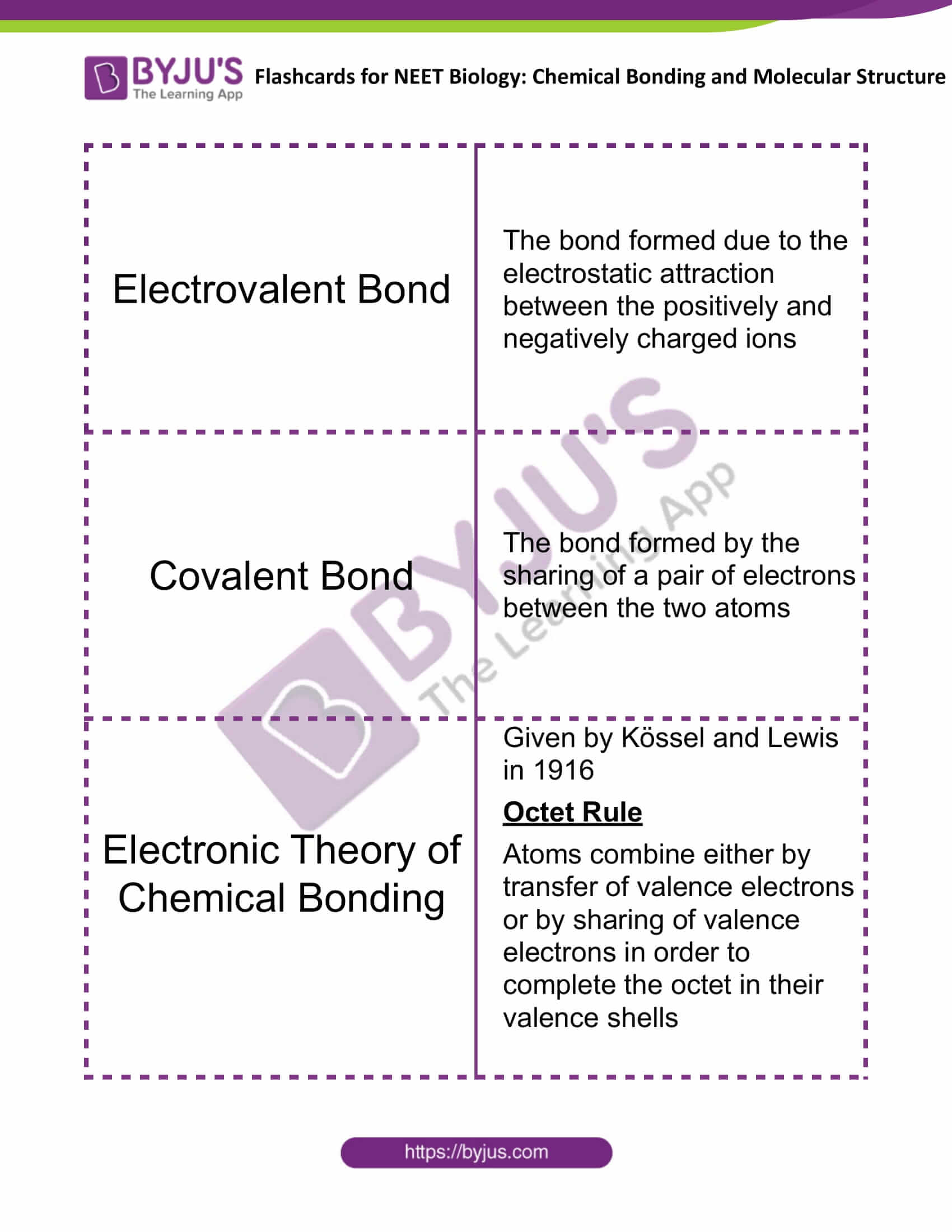
| Electrovalent Bond | The bond formed due to the electrostatic attraction between the positively and negatively charged ions |
| Covalent Bond | The bond, formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between the two atoms |
| Electronic Theory of Chemical Bonding | Given by Kössel and Lewis in 1916
Octet Rule Atoms combine either by transfer of valence electrons or by sharing of valence electrons in order to complete the octet in their valence shells |
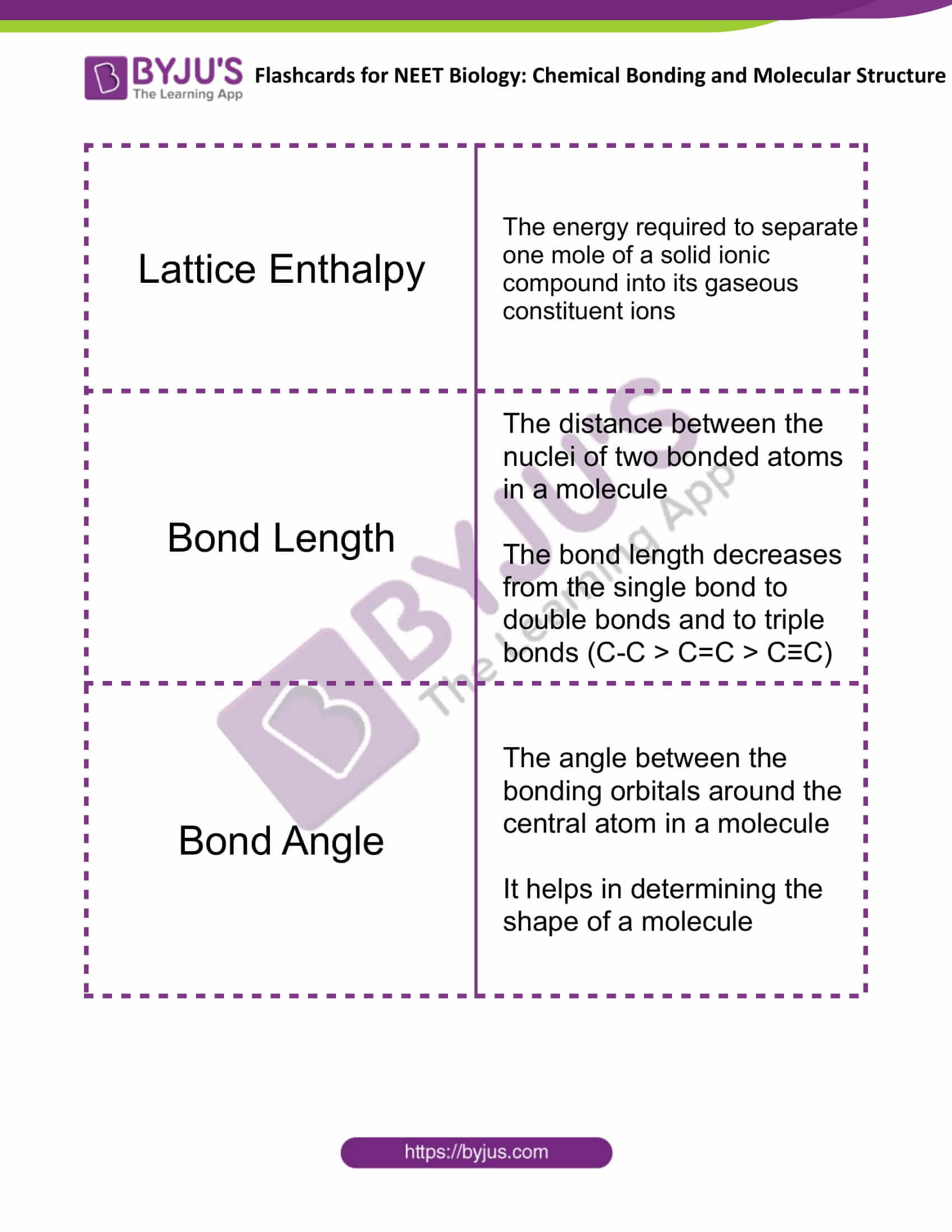
| Lattice Enthalpy | The energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous constituent ions |
| Bond Length | The distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule
The bond length decreases from the single bond to double bonds and to triple bonds (C-C > C=C > C≡C) |
| Bond Angle | The angle between the bonding orbitals around the central atom in a molecule
It helps in determining the shape of a molecule |
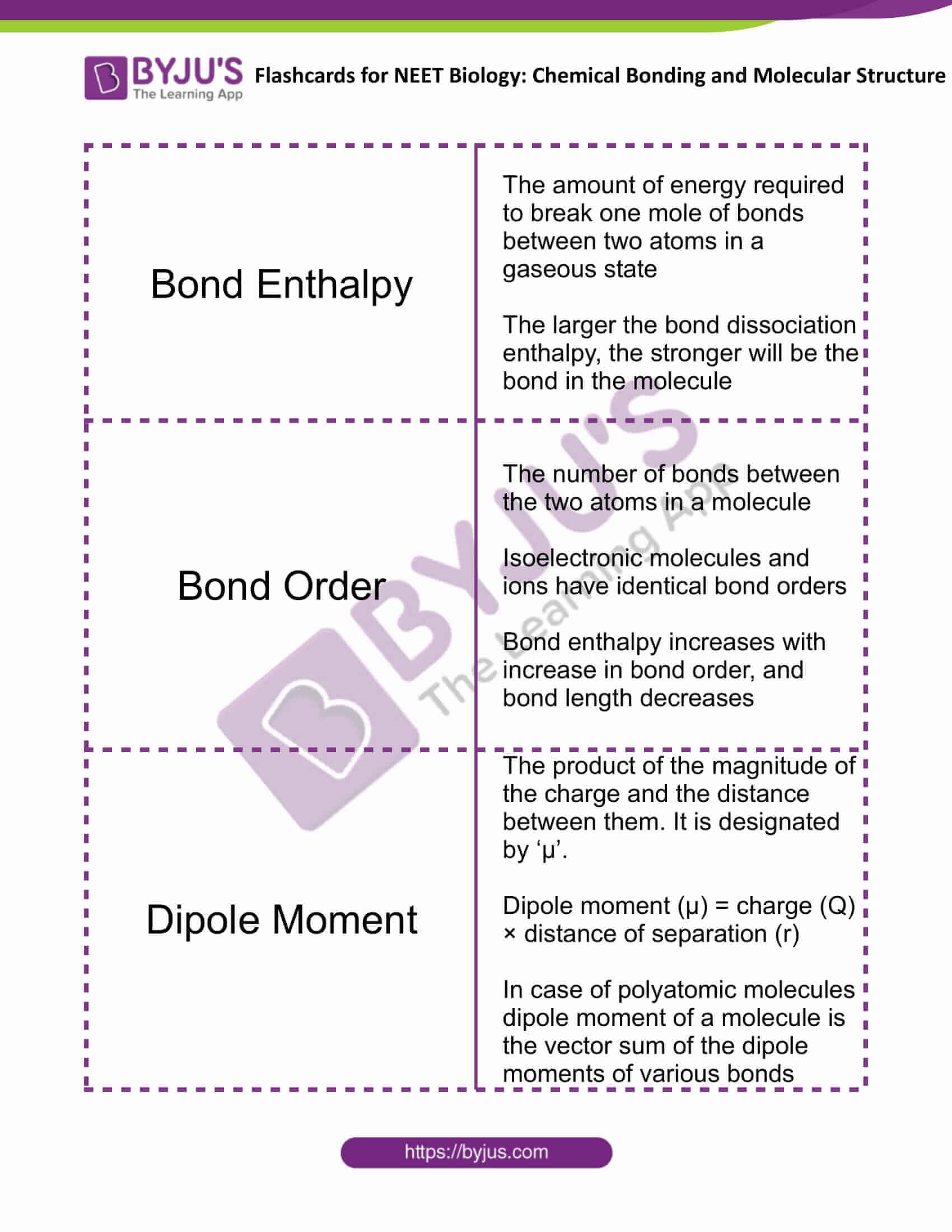
| Bond Enthalpy | The amount of energy required to break one mole of bonds between two atoms in a gaseous state
The larger the bond dissociation enthalpy, the stronger will be the bond in the molecule |
| Bond Order | The number of bonds between the two atoms in a molecule
Isoelectronic molecules and ions have identical bond orders Bond enthalpy increases with an increase in bond order, and bond length decreases |
| Dipole Moment | The product of the magnitude of the charge and the distance between them. It is designated by ‘μ’.
Dipole moment (μ) = charge (Q) × distance of separation (r) In the case of polyatomic molecules dipole moment of a molecule is the vector sum of the dipole moments of various bonds |
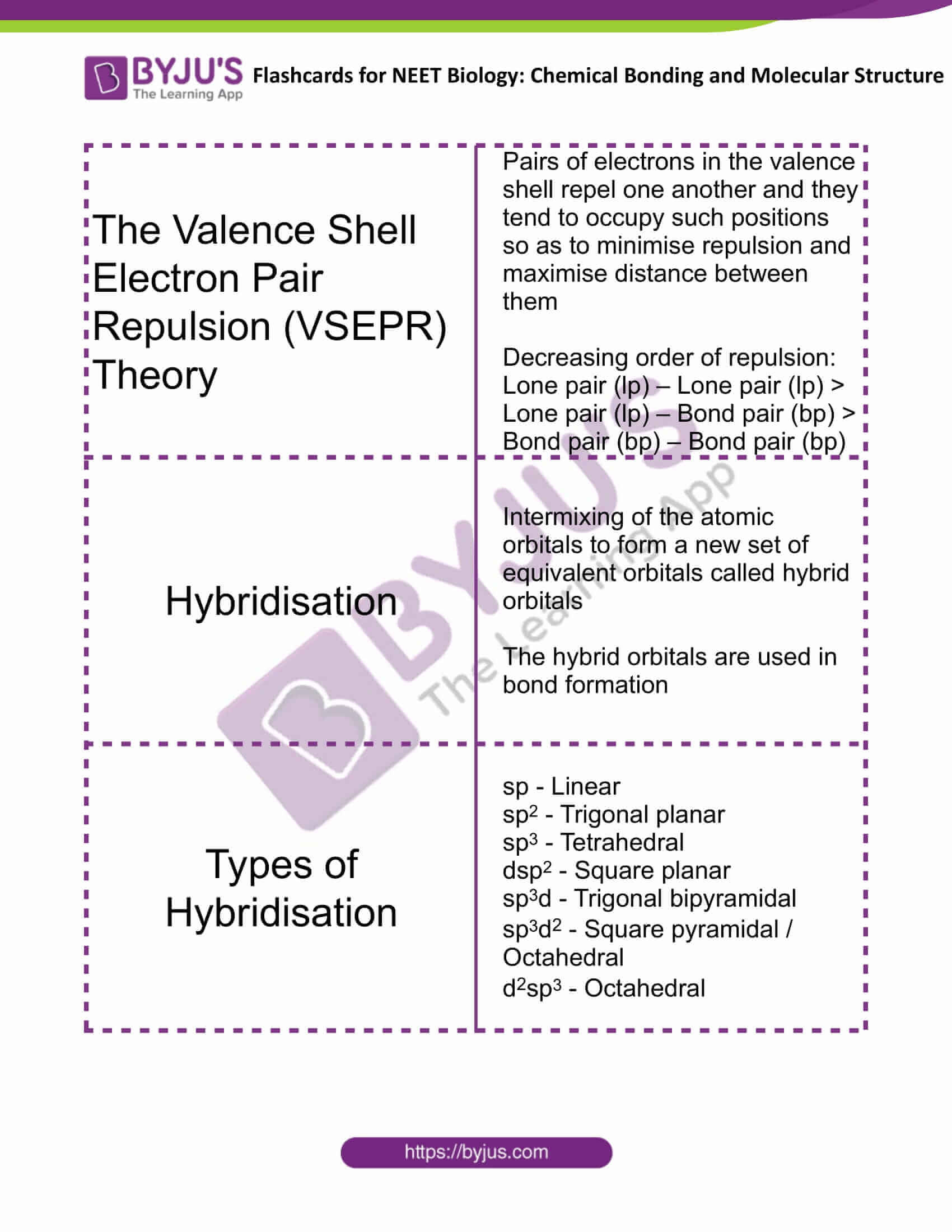
| The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory | Pairs of electrons in the valence shell repel one another and they tend to occupy such positions, so as to minimise repulsion and maximise the distance between them
Decreasing order of repulsion: Lone pair (lp) – Lone pair (lp) > Lone pair (lp) – Bond pair (bp) > Bond pair (bp) – Bond pair (bp) |
| Hybridisation | Intermixing of the atomic orbitals to form a new set of equivalent orbitals called hybrid orbitals
The hybrid orbitals are used in bond formation |
| Types of Hybridisation | sp – Linear
sp2 – Trigonal planar sp3 – Tetrahedral dsp2 – Square planar sp3d – Trigonal bipyramidal sp3d2 – Square pyramidal/Octahedral d2sp3 – Octahedral |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Chemistry, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:
| Also Check: |
Comments