Flashcards for NEET Chemistry are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for the chapter “States of Matter”. These flashcards are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. These are helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. It covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Chemistry.
Download PDF of NEET Chemistry Flashcards for States of Matter
|
Name of the NEET Sub-section |
Topic |
Flashcards Helpful for |
|
Chemistry |
States of Matter |
NEET Exams |
|
States of Matter |
|
|
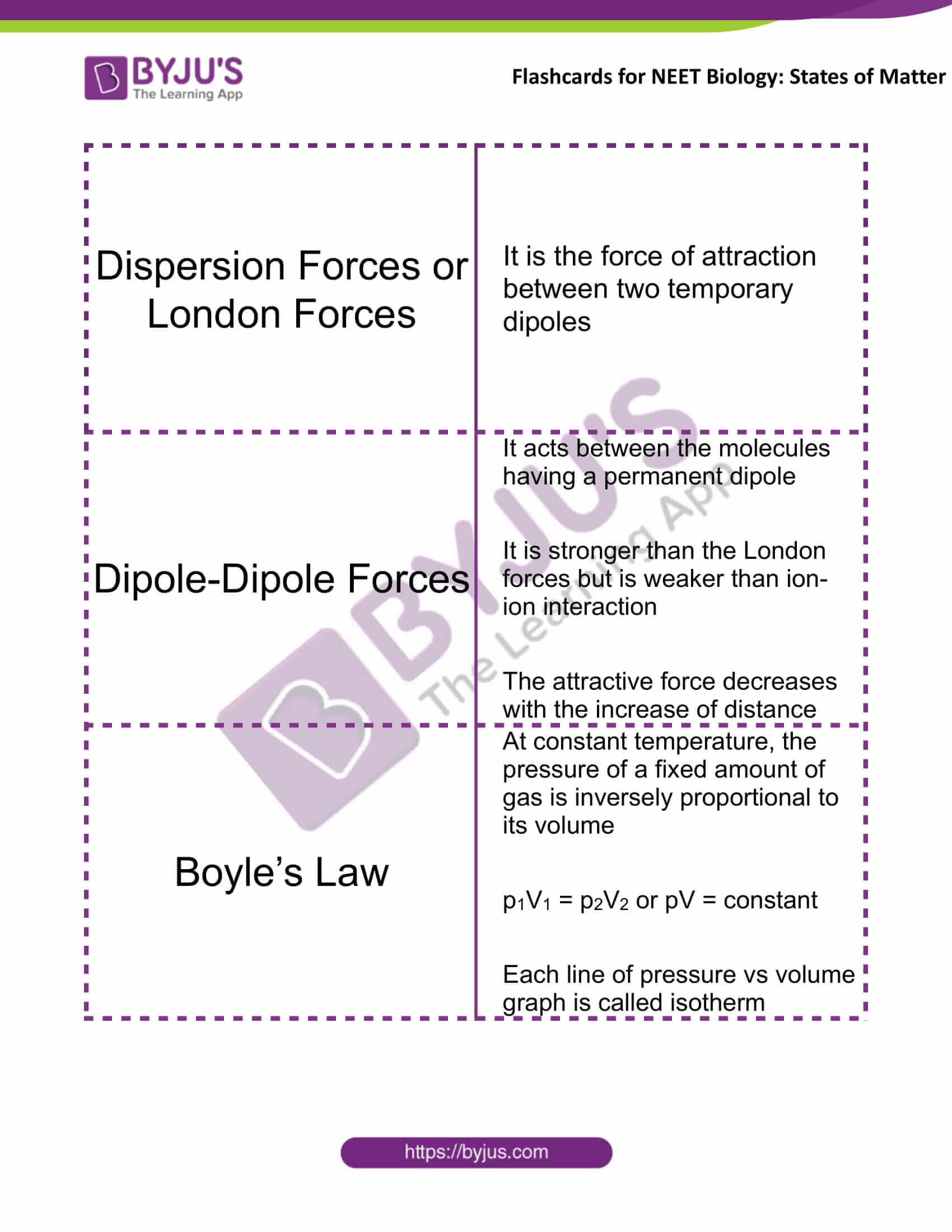
Dispersion Forces or London Forces |
It is the force of attraction between two temporary dipoles |
|
Dipole-Dipole Forces |
It acts between the molecules having a permanent dipole It is stronger than the London forces but is weaker than ion-ion interaction The attractive force decreases with the increase of distance |
|
Boyle’s Law |
At constant temperature, the pressure of a fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to its volume p1V1 = p2V2 or pV = constant Each line of pressure vs volume graph is called isotherm |
|
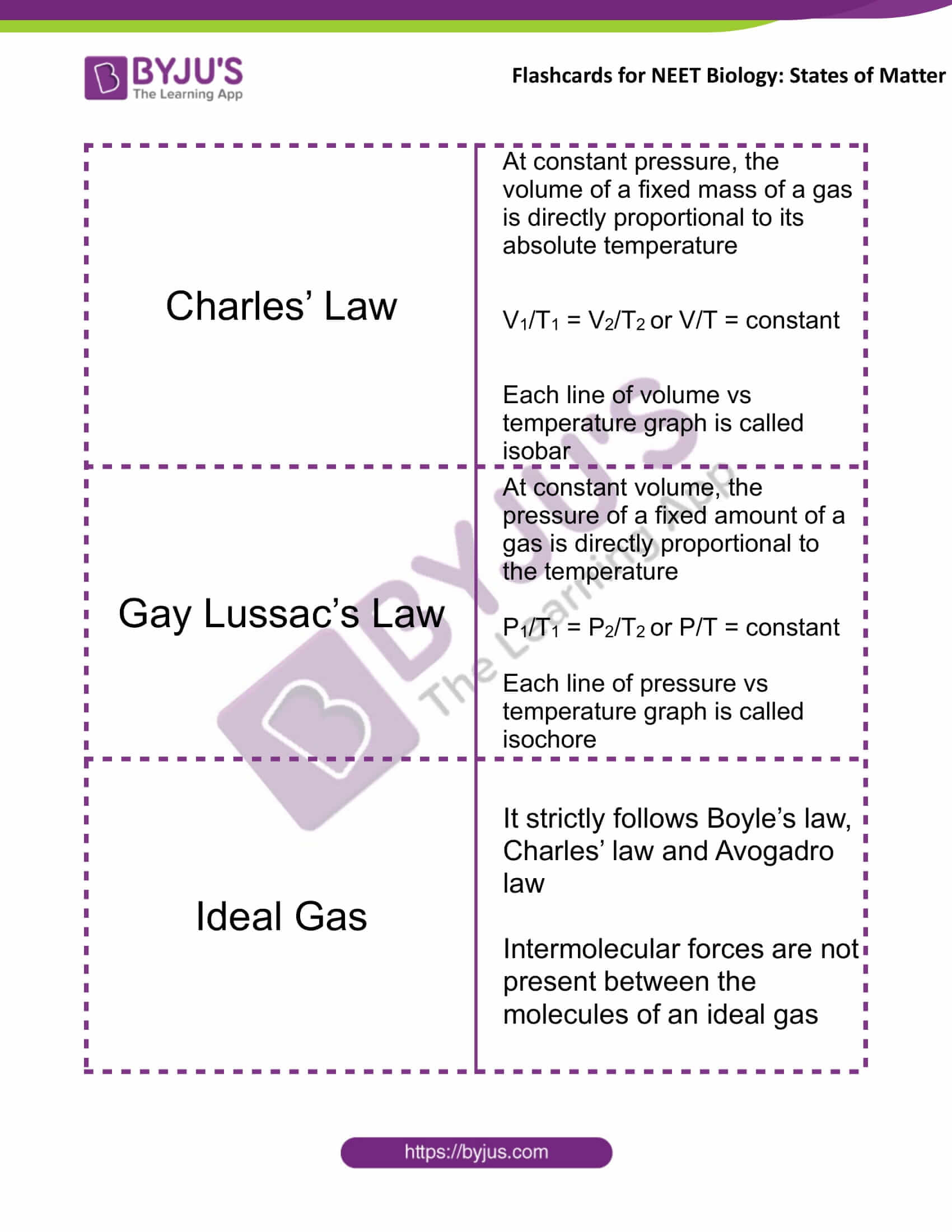
Charles’ Law |
At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature V1/T1 = V2/T2 or V/T = constant Each line of volume vs. temperature graph is called isobar |
|
Gay Lussac’s Law |
At constant volume, the pressure of a fixed amount of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature P1/T1 = P2/T2 or P/T = constant Each line of pressure vs temperature graph is called isochore |
|
Ideal Gas |
It strictly follows Boyle’s law, Charles’ law and Avogadro law Intermolecular forces are not present between the molecules of an ideal gas |
|
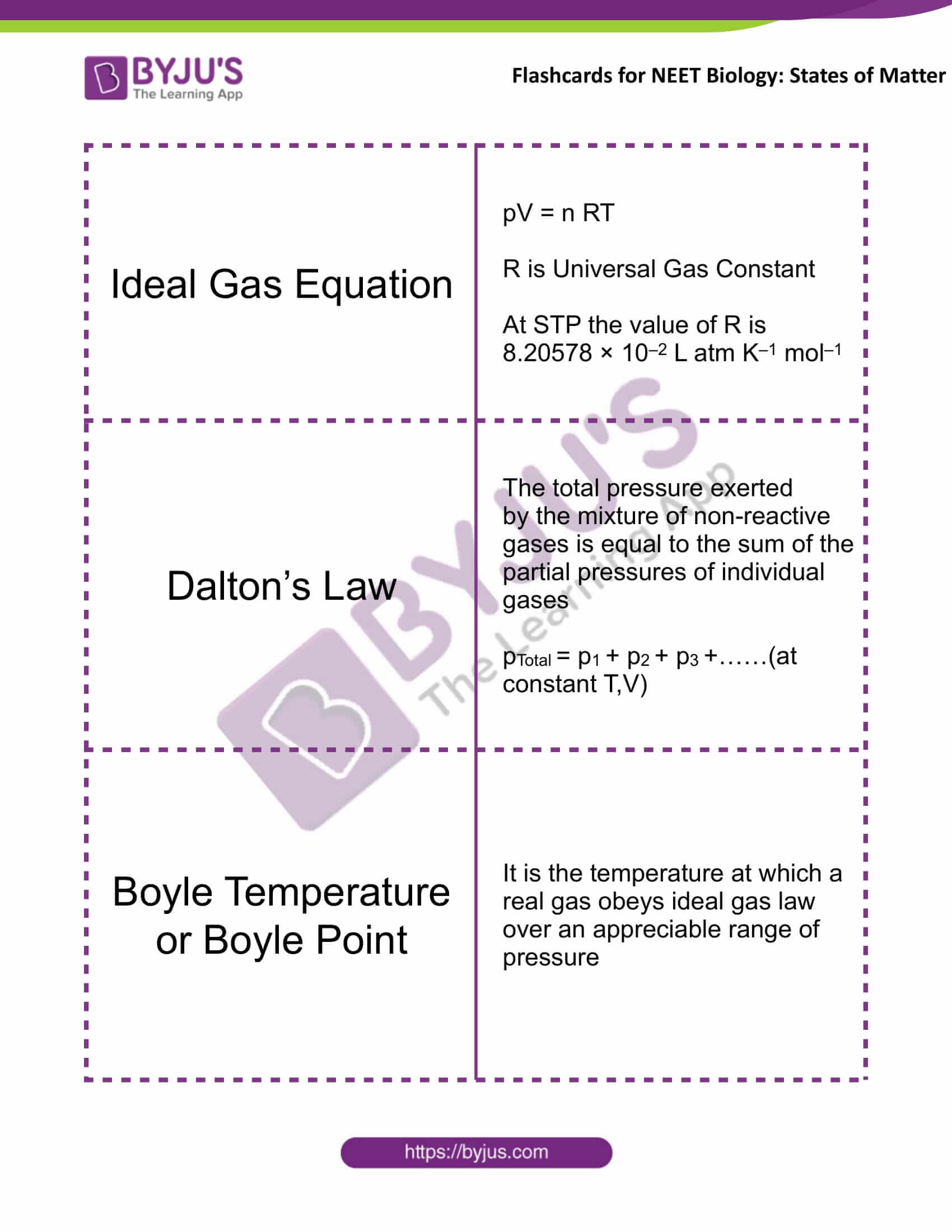
Ideal Gas Equation |
pV = nRT R is Universal Gas Constant At STP the value of R is 8.20578 × 10–2 L atm K–1 mol–1 |
|
Dalton’s Law |
The total pressure exerted by the mixture of non-reactive gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of individual gases pTotal = p1 + p2 + p3 +……(at constant T,V) |
|
Boyle Temperature or Boyle Point |
It is the temperature at which a real gas obeys ideal gas law over an appreciable range of pressure |
|
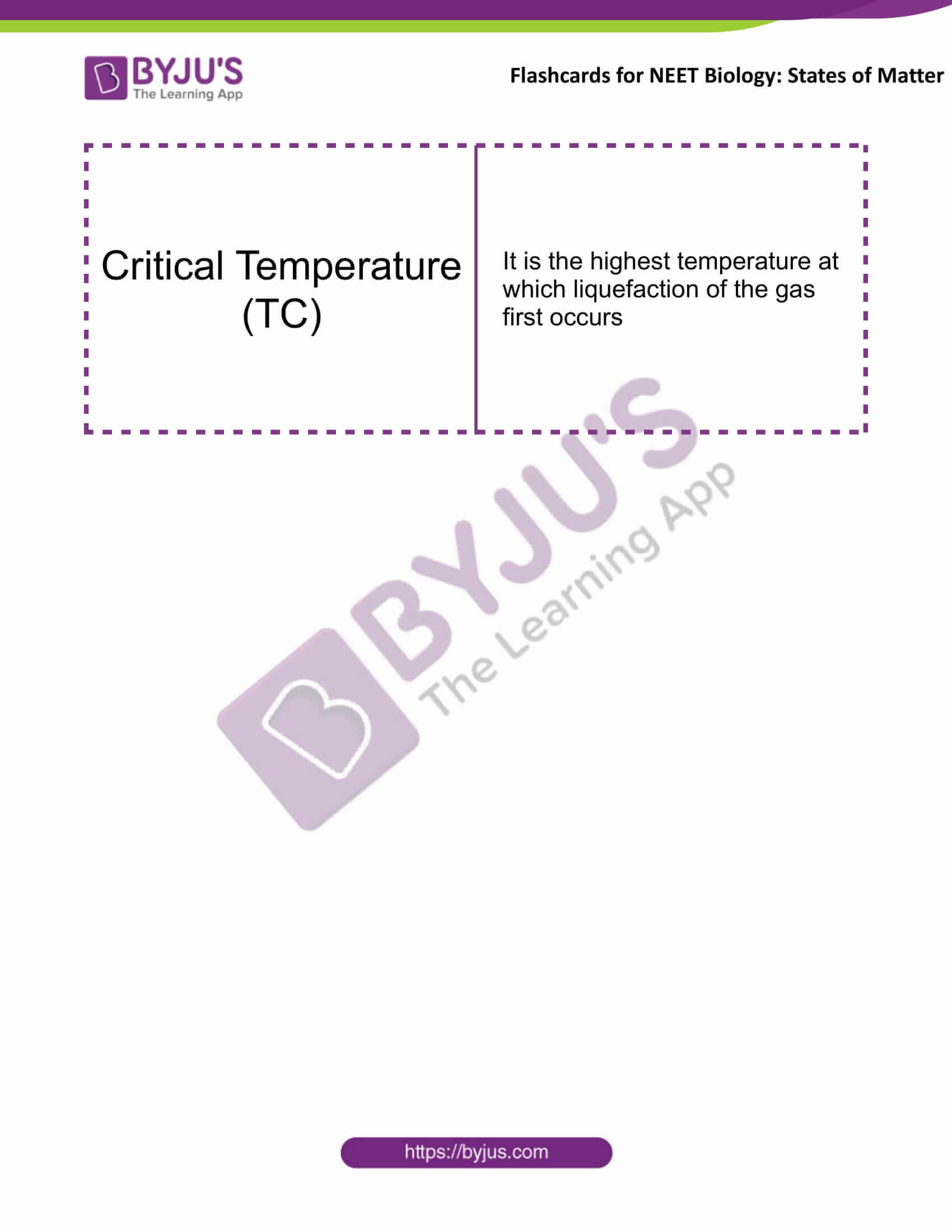
Critical Temperature (TC) |
It is the highest temperature at which liquefaction of the gas first occurs |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Chemistry, only at BYJU’S.
|
Also Check: |
Comments