Flashcards for NEET Chemistry are designed to boost your NEET preparation. Find below flashcards for the chapter “Thermodynamics”. These flashcards are prepared as per the NEET syllabus. These are helpful for aspirants of NEET and other exams during last-minute revision. It covers all the important points that are frequently asked in the exam. Check BYJU’S for the full set of Flashcards and Study material for NEET Chemistry.
Download PDF of NEET Chemistry Flashcards for Thermodynamics
|
Name of the NEET Sub-section |
Topic |
Flashcards Helpful for |
|
Chemistry |
Thermodynamics |
NEET Exams |
|
Thermodynamics |
|
|
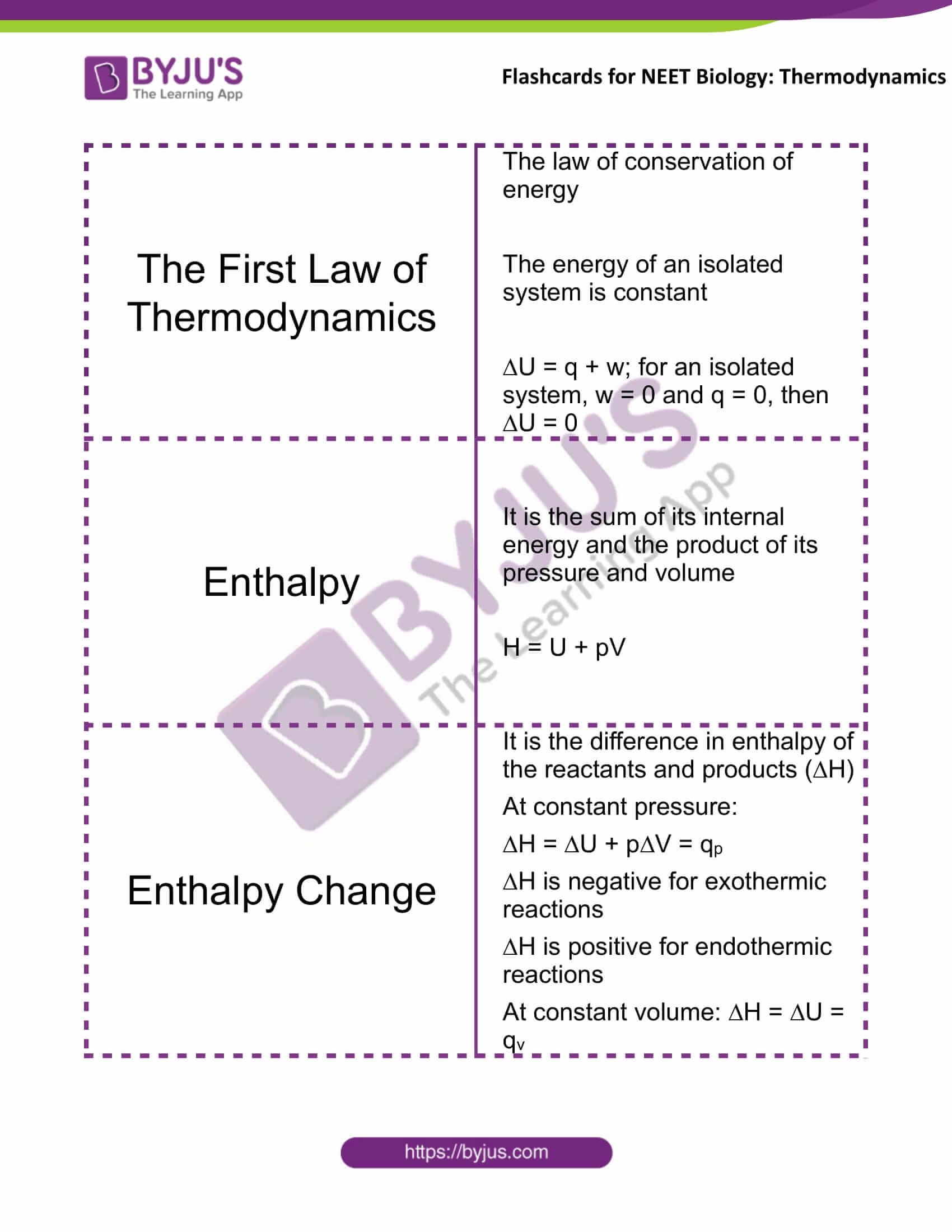
The First Law of Thermodynamics |
The law of conservation of energy The energy of an isolated system is constant ∆U = q + w; for an isolated system, w = 0 and q = 0, then ∆U = 0 |
|
Enthalpy |
It is the sum of its internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume H = U + pV |
|
Enthalpy Change |
It is the difference in enthalpy of the reactants and products (∆H) At constant pressure: ∆H = ∆U + p∆V = qp ∆H is negative for exothermic reactions ∆H is positive for endothermic reactions At constant volume: ∆H = ∆U = qv |
|
Extensive Property |
Its value depends on the quantity or size of matter present in the system E.g. mass, volume, internal energy, enthalpy, heat capacity, etc. |
|
Intensive Property |
Its value does not depend on the quantity or size of matter present in the system E.g. temperature, density, pressure, etc. |
|
Specific Heat Capacity |
The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of a substance by one degree celsius or one kelvin |
|
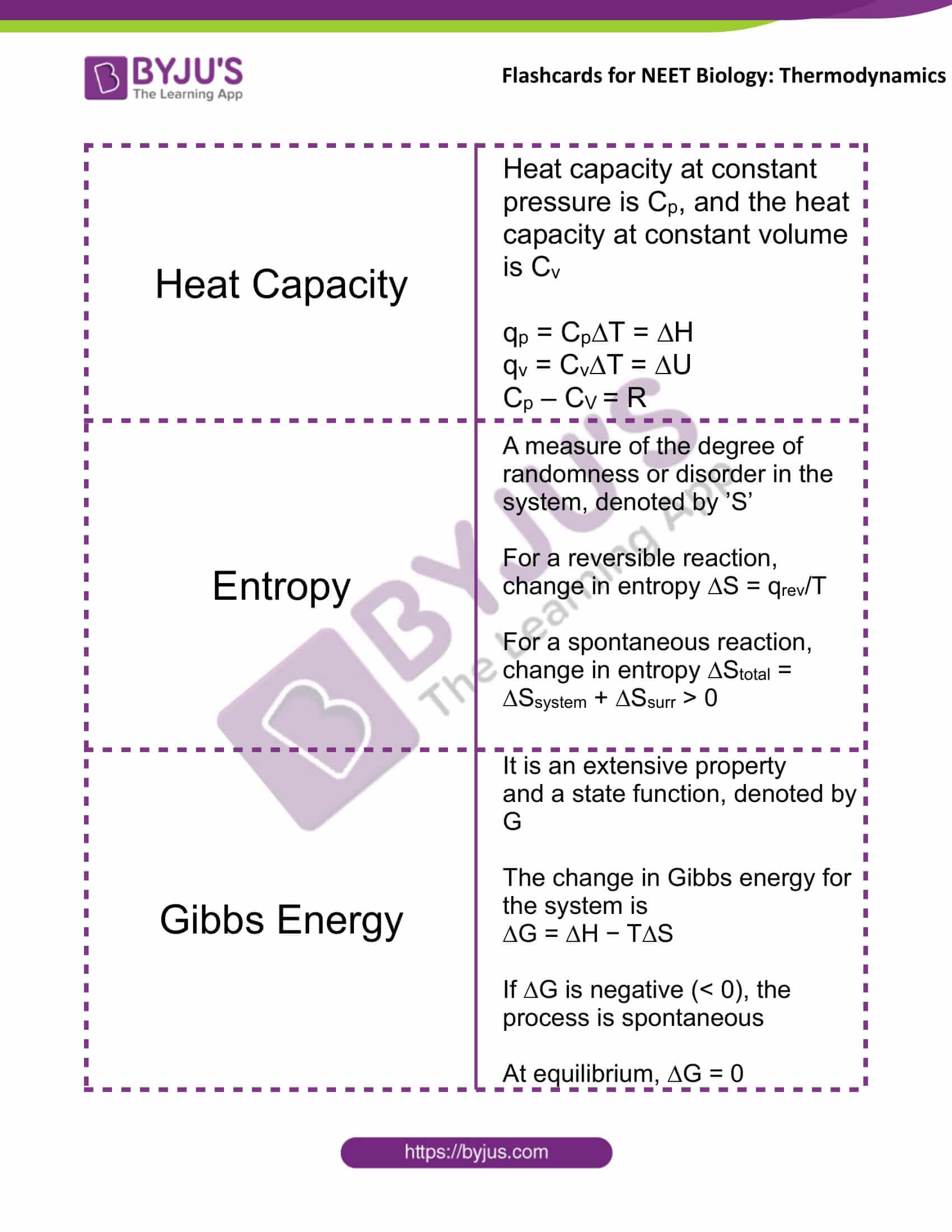
Heat Capacity |
Heat capacity at constant pressure is Cp, and the heat capacity at constant volume is Cv qp = Cp∆T = ∆H qv = Cv∆T = ∆U Cp – CV = R |
|
Entropy |
A measure of the degree of randomness or disorder in the system, denoted by ’S’ For a reversible reaction, change in entropy ∆S = qrev/T For a spontaneous reaction, change in entropy ∆Stotal = ∆Ssystem + ∆Ssurr > 0 |
|
Gibbs Energy |
It is an extensive property and a state function, denoted by G The change in Gibbs energy for the system is ∆G = ∆H − T∆S If ∆G is negative (< 0), the process is spontaneous At equilibrium, ∆G = 0 |
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
The entropy of an isolated system increases in the course of a spontaneous change ∆Stotal > 0 |
Get access to the full set of flashcards for NEET Chemistry, only at BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:

|
Also Check: |


Comments