Nomenclature rules published by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) are accepted by chemists of most of the countries and thus forms the international authority for organic and for inorganic chemistry.
The technical terms used in organic chemistry nomenclature are
- Systematic name – A name composed wholly of syllables specially coined or selected to describe structural features: hexane, thiazole.
- Trivial name – A name part of which is used in a systematic sense: Xanthophyll, furan.
- Semisystematic = semi trivial name
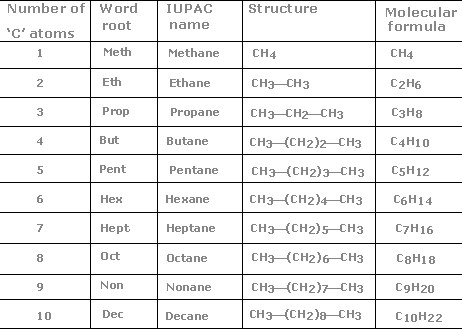
Nomenclature of Alkanes
The molecule’s parent name is determined by the number of carbons in the longest chain. The carbons in the chain are counted with the first substituent beginning from the nearest end. In the case where substituents from both ends have the same number of carbons, numeration begins from the nearest end of the next substituent.
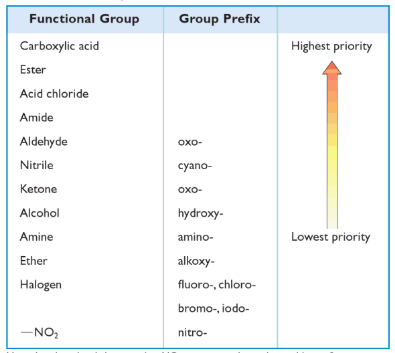
Nomenclature of Functional Groups
Most of the compounds in organic chemistry are fairly simple. In addition to any carbon-carbon double bond or triple bonds, they have contained only one functional group and could be named by using suffixes such as -ynol or -dienone. However, for a compound that contains more than one heteroatom functional group, only one of these functional groups can be designated in the suffix.
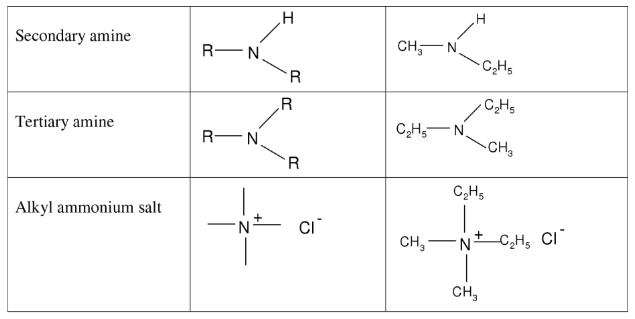
Nomenclature of Amine
IUPAC nomenclature for primary amines is similar to that for alcohols, except that the suffix is -amine rather than -ol. An -NH2 group, like an -OH group, has priority in numbering the parent carbon chain.
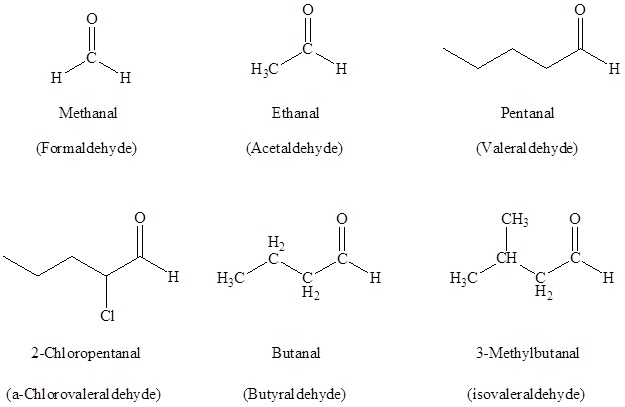
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
In the case of aldehydes, the suffix -al is used with taking the longest carbon chain into consideration. The numbering starts with the carbonyl carbon.
For ketones, the suffix -one is used and the numbering starts from the carbon which is nearest to the carbonyl carbon considering the longest carbon chain. Substituents are written in alphabetical order as a prefix.
Nomenclature of Esters
Esters are named after the name of the carboxylic acid portion of the parent chain. They end with a “-oate” suffix. They are produced by an acid and alcohol reaction with the removal of molecule water.
Esters of long-chain carboxylic acids are the primary constituents of fats. Among the most abundant fats in the animal tissues are the triglycerides, which actually contain three ester linkages.
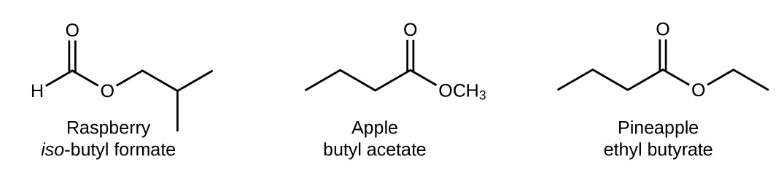
The naming of chemical compounds is often referred to as nomenclature. Before we can name a compound, which consists of multiple elements. Chemical nomenclature is used to identify a chemical species and allows for a common language of communication among chemists.
NEET Chemistry articles for you:
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- How to Score 160 Plus in NEET Chemistry
- NEET Chemistry Weightage
- Chemistry Formulas for NEET
- NEET Chemistry MCQs
- NEET Chemistry Important Topics
Comments