Polymer is a material which is built up together with a large number of small recurring molecules called monomers. The process of formation of polymers from respective monomers is called polymerization. As monomers join with other monomers through the covalent bond formation process, they form larger molecules , called polymers.
These substances also turn into a structure similar to a chain. Polymers have been around in the natural world since the very beginning of time. Starch, cellulose, and rubber all have polymeric qualities. Scientists have been researching man-made polymers since 1832. The polymer industry today has grown to be larger than the combined aluminum, copper, and steel industries.
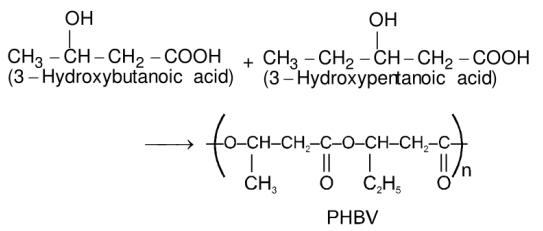
Poly beta hydroxybutyrate-co-beta-hydroxyvalerate – PHBV
Nylon 66
Nylon 66 and nylon 6 are synthetic polymers that are widely used in daily life, synthesized by adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine (HMDA) polymerization.
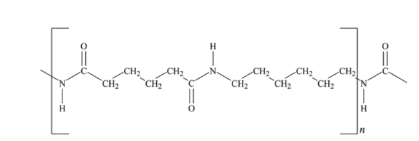
Nylon is the trade name for a form of thermoplastic polyamide. It was first developed in the mid-1930s by DuPont engineers, and has been used in almost every industry since then. Nylon polyamide has a wide range of uses, including rope, gears, and even storages. It is usually formed into fibers that can be used in microfilaments and yarns.
Polyethylene
One of the most common types of plastic is polyethylene, also known as polythene. There are several different polyethylene forms, most of which are defined by the chemical formula (C2H4)n.
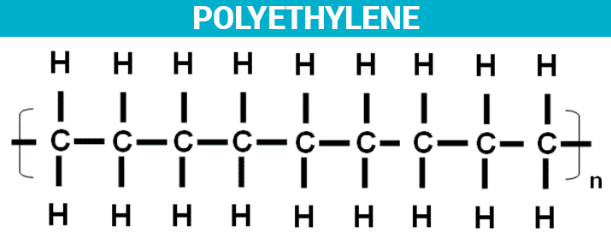
Polyethylene is produced from ethylene typically obtained from petroleum or natural gas, and from less common sources of renewable energy. Polyethylene is widely used, mainly as packaging in the form of bags, sacks, films, geomembranes, containers, pipes, etc.
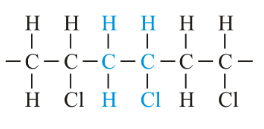
Polyvinyl Chloride – PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) after polyethylene and polypropylene, is one of the most commonly manufactured thermoplastic polymers in the world. PVC is a naturally thin, porous plastic, without the additives of plasticizers. Its most common use is in the construction industry, but it is also used as a fiber for clothing in signs manufacturing, healthcare applications.
Polystyrene
Polystyrene also known as PS is a high molecular weight polymer produced from styrene. This thermoplastic has an extremely wide range of applications, being therefore one of the most produced polymers.
Neoprene
Neoprene or polychloroprene is a synthetic rubber that is flexible at different temperatures, has good resistance to oil and substantial stability to the chemical. Neoprene is rapidly cross-linked by zinc oxide, so ZnO is typically the last ingredient added to a neoprene mix.
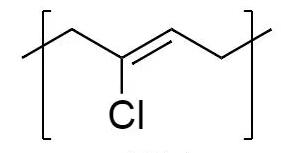
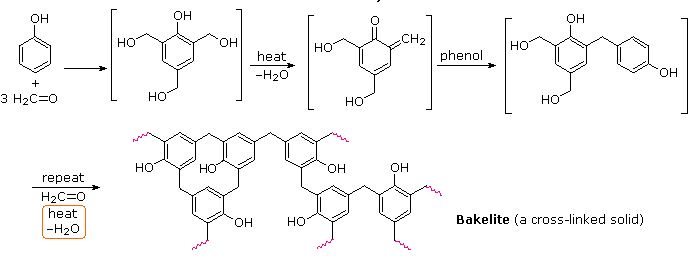
Bakelite
Bakelite is a trade name of the phenol-formaldehyde resin, which is one of the earliest synthetic polymers. Early plastic is bakelite, or polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride. It is a formaldehyde resin of thermosetting phenol, formed from a formaldehyde phenol condensation reaction.
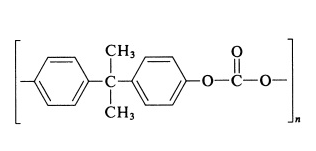
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates are groups of polymers, which also include groups of carbonates within their chemical structures. Their structure also allows them to be transparent at times and to transmit light to that of glass with precision of course.
Thermoforming polycarbonate is a manufacturing method that involves heating the plastic to a soft, flexible state, then fitting it around a custom mold or tool to create a desired shape.
Polymers are species of a high molecular weight, composed of numerous repeat units. The characteristics that polymers exhibit are one major difference between polymers and small molecules (monomers). Polymers typically have higher viscosities, higher boiling points, and greater mechanical strength over small molecules (monomers).
Recommended Video:

Frequently visited NEET Chemistry posts:
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Important Topics
- NEET Chemistry MCQs
- How to Score 160 Plus in NEET Chemistry
- NEET Chemistry Weightage
- Chemistry Formulas for NEET
Comments