A dielectric material is a non-metallic substance having a high specific resistance, a negative temperature coefficient of resistance and a high insulating resistance. Another definition of dielectric material is a non-conducting substance that holds electrical charges.
Dielectric characteristics
When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, the electric charges do not flow through the material. Electric charges slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation.
Dielectric polarisation causes positive charges to flow in the direction of the field and negative charges to shift in the opposite direction of the field. This phenomenon yields an internal electric field, which in turn reduces the overall electric field within the dielectric material.
Electric susceptibility gives the measure of how easily a dielectric material can be polarized when placed in an electric field.
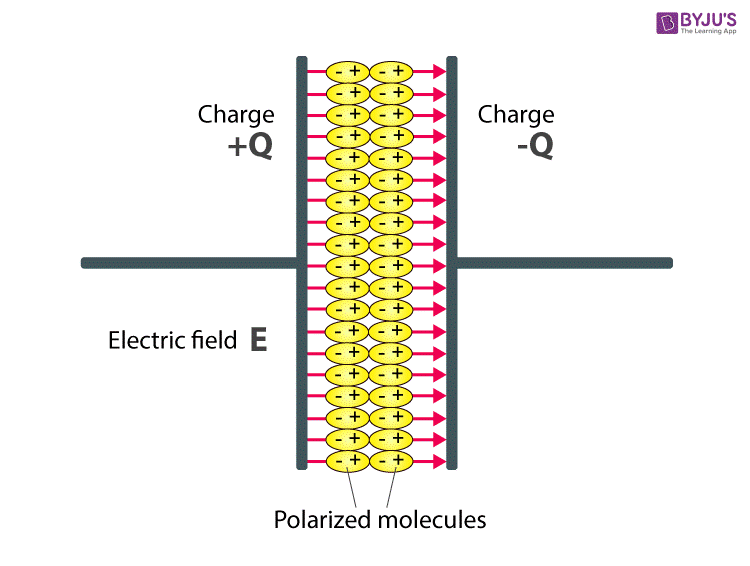
Above figure explains the polarisation of dielectric molecules when the electric field is applied.
Dielectric materials are mostly solids. The dielectrics are mostly solids. Some of the dielectrics are composed of weakly bonded molecules. In such scenarios, along with polarisation, we can also observe that molecules reorient themselves to align their symmetry axes with the field.
Dielectric materials are used to store energy. These materials exist in solid, liquid and gaseous forms. Some examples of dielectric materials are:
- Solid Dielectrics – Ceramic, Plastic, Mica, and Glass.
- Dielectric Liquid – Distilled Water.
- Dielectric Gas – Dry Air, vacuum, nitrogen and helium.
The Following Video Is an Explanation of Series and Parallel Combinations of Dielectrics along with the Formula

Properties of Dielectric Material
Following are the exhibits of dielectric materials:
- The energy gap in the dielectric materials is very large.
- The temperature coefficient of resistance is negative and the insulation resistance is high.
- The dielectric materials have high resistivity.
- The attraction between the electrons and the parent nucleus is very strong.
- The electrical conductivity of these materials is very low as there are no free electrons to carry current.
What are Dielectric Properties?
Dielectric properties of materials are defined as a molecular property that is fundamental in all the materials that are capable of impending electron movement, resulting in polarisation within the material on exposure to an external electric field.
What Are Dielectric Properties of Insulation?
Following are the dielectric properties of insulation:
- Breakdown voltage
- Dielectric parameters such as:
- Conductivity
- Power factor
- Loss angle
- Permittivity
What Are Dielectric Properties of Solids?
Following are the dielectric properties of solids:
- Piezoelectricity
- Pyroelectricity
- Ferroelectricity
- Anti ferroelectricity
What Are Dielectric Properties of Food?
Following are the dielectric properties that influence the food:
- Frequency of microwave or the radio frequencies
- Amount of water present in food
- Temperature
- The density of the material
- Composition and structure of the material
Accelerate Your JEE Main & Advanced Exam Preparation by
Watching this Video about Magnetism and Force on Dielectric in Charged Capacitor

Difference between Dielectric and Insulators
Dielectrics are often confused with insulators. The term “insulator” typically implies low electrical conductivity. However, the term dielectric is typically used to denote the material with superior polarisability. It is expressed numerically using relative permittivity. Insulator indicates electrical obstruction whereas dielectric indicates the ability of a material to store energy(by means of polarisation). The common example is a capacitor. Here, a dielectric insulating plate is sandwiched between metallic plates. For a given electric field strength, the capacitor’s surface charge is raised by polarising the dielectric plate. Let us learn more differences between dielectrics and insulators in the table given below:
Dielectric vs Insulators
| Dielectrics | Insulators |
| Material that can develop an electric field with minimal loss of energy is known as a dielectric. | A substance that has low conductivity and that which obstructs the flow of current is known as an insulator. |
| Weakly bonded as compared to insulators. | Covalently bonded. |
| Store charges. | Obstructs charges. |
| Their application lies in power cables, capacitors and more. | They are used in high voltage systems and conducting wires. |
Application of Dielectric Properties
- Dielectrics are used as a capacitor for storing energy.
- The dielectric material in a transformer is used as an insulator and as a cooling agent.
- To enhance the performance of a semiconductor device, high permittivity dielectric materials are used.
- Electrets are a processed dielectric material that acts as an electrostatic equivalent to magnets.
Physics-related topics:
| Dielectric Polarisation in Polar and Nonpolar Material and Dielectric Constant |
| Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance |
| Polar And Non-Polar Material: Dielectric Material And Dipole Moment |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
State true or false: All insulators are dielectric materials?
False.
Name the dielectric material widely used in capacitors?
The following are the types of light interference:
Ceramic, glass, paper and mica.
Name the non-polar dielectric.
H2, N2, and O2.
Why are dielectric materials used in capacitors?
Is vacuum a perfect dielectric?
Yes, vacuum is a perfect dielectric medium.
Hope you understood about dielectric materials. To know more about dielectric polarisation and dielectric constant, visit BYJU’S – The Learning App.

Comments