Before we talk about the position, path length, and displacement and how they are different from one another, let us know what motion is. Everywhere you see objects moving around. Birds fly, animals go from one place to another in search of food, shelter, etc. People walk, run, and travel. Rivers flow, earth completes revolutions around the sun one after the other. Basically, motion is everywhere in the universe. But what is motion? Before that, what is common to all the instances discussed above? They all change places when they move from one place to another. So the motion is nothing but the change in position of an object with time. In this article, we will learn about the position and the difference between path length and displacement.
| Table of Contents: |
What is Motion?
Motion is the change in position of an object with respect to its surroundings in a given interval of time. The motion of an object with some mass can be described in terms of distance, displacement, speed, velocity, time, and acceleration. The motion refers to the change in the position of an object with reference to time. The branch of physics that describes the motion of objects without reference to their cause is known as kinematics. The branch of physics that deals with forces and their effect on motion is known as dynamics.
Watch the below to understand what is motion?.

Position
Let us say you moved from point A to B. This implies that your position was previously at A which shifted to B. How exactly would you represent your initial position? In physics, we specify a position with the help of a reference point and a set of three mutually perpendicular axes or the rectangular coordinate system. They are X-, Y- and Z-axes. The reference point is taken as the intersection point of the above three axes, called the origin. So we take point A as the reference point or origin with coordinates (0, 0, 0) and B is represented by a set of coordinates on the three axes (x, y, z).
But as we know that motion is the change in position with time, we install a clock in this system. The coordinate system along with the clock is called a frame of reference. Thus, if one or more coordinates of a body change with time, the body is said to be in motion.
Path Length and Displacement
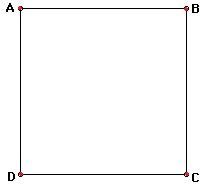
Let us take three examples here. In the first one, Amit starts travelling from point A of the square path ABCD with AB = 1 km. He travels through B, C, D, and comes back to A in 20 minutes. The distance traveled by him is 4 x 1 km = 4 km. But if you see the change in his position from the start to the end of the journey, it is nil. Amit started at A and came back at A.
In the third instance, Amit travels from A to B along the straight line in 60 minutes. The distance traveled by him is 5 km. In fact, the distance from the start to the endpoint is also 5 km.
![]()
Now Amit travels through the triangular path. He starts from A and reaches C through B in 120 minutes. The distance traveled by him is 3 km + 4 km = 7 km. But if we see how far he is from the point where he started his journey, it is 5 km.

You might notice that the distance traveled and the change in position may or may not be the same. The distance traveled by the body is known as the path length. Whereas the change in position, that is the difference between the initial and final positions of the body is called its displacement.
Thus, in the first case, the path length is 4 km but the displacement is 0. In the second case, the path length is the same as the displacement – 5 km. In the third example, the path length is 7 km but the displacement is 5 km.
Hope you learned the difference between path length and displacement. To learn more about position, displacement, and path length, download BYJU’S The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is motion?
What are the types of motion?
The following are the types of motion:
- Translational
- Rotational motion
- Linear motion
- Periodic motion
- Simple Harmonic motion
- Projectile motion
- Oscillatory motion

Comments