What Is Solenoid?
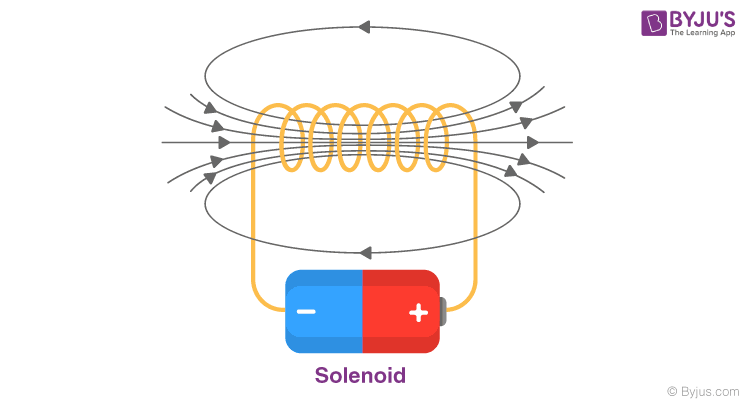
We can see from the figure that the magnetic field inside the solenoid is uniform in nature and is along the axis of the solenoid. The field at the exterior at any point immediately to the solenoid is very weak and the field lines cannot be seen near the close vicinity. It is important to note that the field inside it is parallel to its axis at every position.
From the Ampere’s Law, the magnetic force produced by a solenoid can be given as,
Where n is the number of turns of the wire per unit length, I is the current flowing through the wire and the direction is given using the right-hand thumb rule.
Read More: Ampere’s Law
To know more about solenoids, click on the video below
What Is Toroid?
A toroid is shaped like a solenoid bent into a circular shape such as to close itself into a loop-like structure. The toroid is a hollow circular ring, as can be seen in the image shown below, with many turns of enameled wire, closely wound with negligible spacing between any two turns.
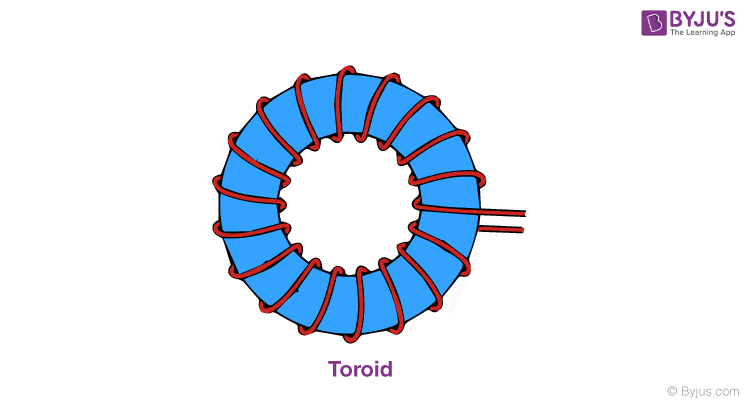
The magnetic field inside and outside the toroid is zero. The magnetic field inside the toroid, along with the circular turn, is constant in magnitude and its direction inside the toroid is clockwise as per the right-hand thumb rule for circular loops.
The magnetic field due to a toroid can be given as,
Where N is the number of turns of the toroid coil, I is the amount of current flowing and r is the radius of the toroid.
Accelerate your JEE Main & Advanced Exam preparation by
watching this video about magnetism and force on dielectric in charged capacitor

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is a solenoid?
What is a toroid?
What is a magnetic field?
What is the value of the magnetic field inside a toroid?
Who invented the toroid?
Watch the Video and Learn about Magnetic Field Due to Solenoid and Properties of Magnetic Field Lines

To learn more about solenoids, toroids, and how to make a solenoid engine visit BYJU’S.

Comments