Tides are the up and down motion of water bodies created by the effects of forces of gravity applied by the Sun and Moon, and the Earth’s axial rotation.
Tidal force (in Earth) is generally the vector difference between the force of gravity exerted by the Moon and the Earth’s centre of mass. An object on Earth experiences both the forces, a tug of forces that create tidal waves.
The ocean’s surface is part of the entire Earth structure called a geoid, which includes the natural force of gravity applied by the Earth’s mass and rotational centrifugal force. Other main variables are the effects of massive celestial bodies, such as the Sun and Moon. These gigantic objects have intense gravitational force fields that decrease with distance and push the water bodies from the geoid. They create a new equilibrium on the ocean plane, which bulges towards the side of the Moon and another bulge away from the Moon on the other side. As mentioned earlier, the Earth’s axial rotation respective to this configuration generates the daily tidal series.

|
Table of Contents |
|---|
What is a spring tide?
Spring tides happen twice each month (lunar), most relevant on a full moon or new Moon. These are taller and larger tides, caused by the simultaneous gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon. In other words, water bodies are sandwiched between these massive gravitational force fields.
The term ‘spring tide’ is not related to any seasons. It was coined from the verb ‘springan’, which means ‘to spring, well, burst’. Here, it is used to describe the extraordinary strength of waves that occurs during the above planetary alignments.
How are spring tides formed?
Tides are waves that roll around the planet as the ocean is “pulled” back and forth by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, as these bodies interact with the Earth in their monthly and yearly orbits.
Average tidal ranges are slightly larger when the Earth, Sun, and Moon are nearly in alignment during a full or new moon. This occurs twice each month. The Moon appears new (dark) when it is directly between the Earth and the Sun. The Moon appears full when the Earth is between the Moon and the Sun. In both cases, the Sun’s gravitational pull is “added” to the gravitational pull of the Moon on Earth, causing the oceans to bulge a bit more than usual. This means that high tides are slightly higher, and low tides are slightly lower than average.
These are called spring tides.

A video about ‘Why does the moon change shape?’

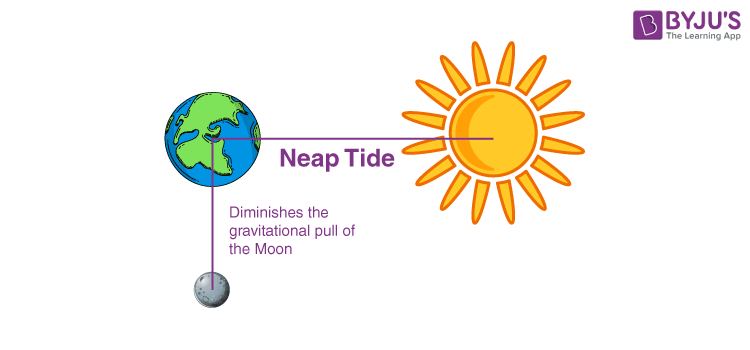
Neap Tides
Approximately seven days after following a spring tide, the Moon and Sun align at right angles. When this occurs, the upsurge of the ocean created by the sun partly nullifies the upsurge of the ocean generated by the Moon. This causes mediocre tides called neap tides. It means that high tides are shorter and low tides are higher than usual. Neap tides are developed in the first and third part of the moon cycle, when the Moon is half full.
Perigean Spring Tide
Perigean tides occur when the Moon is full or new, and the lunar distance is very short.
Usually, the full Moon or new Moon coincides with the perigee of the Moon about six to eight times a year. Tides are always higher and larger than the tides occurring during the rest of the year.
Perigean Spring Tide Relevances
When the Perigean Spring Tide merges with the weather changes in the ocean, it may create coastal flooding in a few areas near sea level. When strong Perigean Spring Tides coincide with ocean disturbances (like large winds or tsunamis), devastating coastal flooding might occur.
Perigee is the closest point at which the Moon stands relative to Earth. This is the period when the Moon’s gravitational force field reaches its peak. There will be a considerable increase in the average heights of tides during these times. During the next 14 days, the Moon slowly approaches ‘apogee’. It is the point where the distance between the Moon and the Earth becomes the longest. The Moon’s gravitational pull decreases, and therefore, the size of the tides also declines.
Unique Facts about Tides
- Very long waves can flow at about 450 mph.
- Tidal forces in the ocean can sometimes affect the shape of the Earth’s crust (altering the form by a few inches)
- Tides produce a lot of friction against the surface of the ocean floor. Other than dissipating it as heat, the enormous friction is transferred into tremendous kinetic energy that works as a counterforce to slow down the Earth’s axial rotation. The consequence is straightforward: days get longer, and the Earth’s rotation becomes relatively slower.
|
Related Links |
|---|
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are tides?
Tides are the up and down motion of water bodies created by the effects of forces of gravity applied by the Sun and Moon, and the Earth’s axial rotation.
What are Spring Tides?
Spring tides happen twice each month (lunar), most relevant on a full Moon or new Moon. These are taller and larger tides caused by the simultaneous gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon. In other words, water bodies are sandwiched between these massive gravitational force fields.
What are Neap Tides?
Approximately seven days after following a spring tide, the Moon and Sun will align at right angles. When this occurs, the upsurge of the ocean created by the sun partly nullifies the upsurge of the ocean generated by the Moon. This causes mediocre tides called neap tides.
What are Perigean Spring Tides?
Perigean tides occur when the Moon is full or new, and the lunar distance is very short.
Usually, the full Moon or new Moon coincides with the perigee of the Moon about six to eight times a year. Tides are always higher and larger than the tides occurring during the rest of the year.
How do tidal forces affect the Earth’s rotation?
Tides produce a lot of friction against the surface of the ocean floor. Other than dissipating it as heat, the enormous friction is transferred into tremendous kinetic energy that works as a counterforce to slow down the Earth’s axial rotation. The days get longer, and the Earth’s rotation becomes slower.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S and Fall in Love with Learning!
Comments