We have observed that water flowing from is a tap has a smooth texture when the flow rate is low, but as the flow rate is increased, after reaching a certain value, voids and disturbances can be seen in. In such a situation, if we introduce a stream of ink when the flow is smooth, the ink flows without mixing with the other layers whereas if it is introduced in the case of turbulent flow, we can see the mixing of the layer of ink with the other layers of water as shown in the figure below. In this section, we will learn about the first kind, i.e., the streamline or the laminar flow.
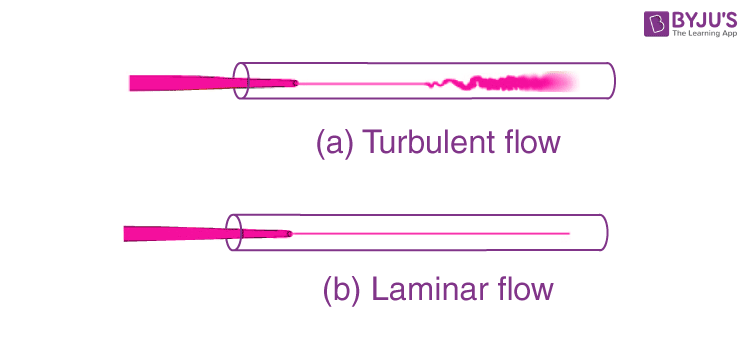
What is Streamline Flow?
Streamline flow in fluids is defined as the flow in which the fluids flow in parallel layers such that there is no disruption or intermixing of the layers and at a given point, the velocity of each fluid particle passing by remains constant with time. Here, at low fluid velocities, there are no turbulent velocity fluctuations and the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing. Here, the motion of particles of the fluid follows a particular order with respect to the particles moving in a straight line parallel to the wall of the pipe such that the adjacent layers slide past each other like playing cards.
To understand the liquid flow pattern better, click on the links provided below:
What are Streamlines?
Streamlines are defined as the path taken by particles of fluid under steady flow conditions. If we represent the flow lines as curves, then the tangent at any point on the curve gives the direction of the fluid velocity at that point.
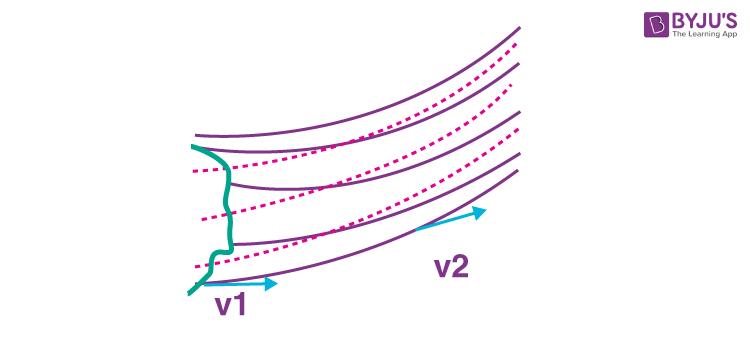
As can be seen in the image above, the curves describe how the fluid particles move with respect to time. The curve provides a map for the flow of this given fluid, and for a steady flow. This map is stationary with time i.e., every particle passing a point behaves exactly like the previous particle that has just passed that point.
The streamlines in a laminar flow follow the equation of continuity, i.e., Av = constant, where, A is the cross-sectional area of the fluid flow, and v is the velocity of the fluid at that point. Av is defined as the volume flux or the flow rate of the fluid, which remains constant for steady flow. When the area of the cross-section is greater, the velocity of the liquid is lesser and vice versa.
To learn more about the streamline flow or other related topics, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.

Comments