RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths Exercise 16.2 Chapter 16 Tangents and Normals is provided here. Highly experienced subject experts at BYJU’S, having vast knowledge of concepts, prepare the answers matching the understanding ability of the students. This exercise, available in PDF format, explains the equation of tangent and normal to a given curve.
A straight line or plane that touches a curve or curved surface at a point but, if extended, does not cross it at that point is called a tangent. RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 16 Tangents and Normals Exercise 16.2 can be used as their reference material. Some of the important topics of this exercise are listed below.
- Equations of tangents and normal
- Finding the equations of tangent and normal to a curve at a given point
- Finding tangent and normal parallel or perpendicular to a given line
- Finding tangent or normal passing through a given point
- Miscellaneous applications of tangents and normals
RD Sharma Solutions For Class 12 Tangents and Normals Exercise 16.2:
Access other exercises of RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 16 – Tangents and Normals
Access answers to Maths RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Chapter 16 – Tangents and Normals Exercise 16.2
Exercise 16.2 Page No: 15.27
1. Find the equation of the tangent to the curve √x + √y = a, at the point (a2/4, a2/4).
Solution:

2. Find the equation of the normal to y = 2x3 – x2 + 3 at (1, 4).
Solution:


3. Find the equation of the tangent and the normal to the following curves at the indicated points:
(i) y = x4 – 6x3 + 13x2 – 10x + 5 at (0, 5)
Solution:

(ii) y = x4 – 6x3 + 13x2 – 10x + 5 at x = 1 y = 3
Solution:

(iii) y = x2 at (0, 0)
Solution:
Given y = x2 at (0, 0)
By differentiating the given curve, we get the slope of the tangent

m (tangent) at (x = 0) = 0
Normal is perpendicular to tangent so, m1m2 = – 1

We can see that the slope of normal is not defined
Equation of tangent is given by y – y1 = m (tangent) (x – x1)
y = 0
Equation of normal is given by y – y1 = m (normal) (x – x1)
x = 0
(iv) y = 2x2 – 3x – 1 at (1, – 2)
Solution:
Given y = 2x2 – 3x – 1 at (1, – 2)
By differentiating the given curve, we get the slope of the tangent

m (tangent) at (1, – 2) = 1
Normal is perpendicular to tangent. So, m1m2 = – 1
m (normal) at (1, – 2) = – 1
Equation of tangent is given by y – y1 = m (tangent) (x – x1)
y + 2 = 1(x – 1)
y = x – 3
Equation of normal is given by y – y1 = m (normal) (x – x1)
y + 2 = – 1(x – 1)
y + x + 1 = 0

Solution:

Equation of tangent is given by y – y1 = m (tangent) (x – x1)
y + 2 = – 2(x – 2)
y + 2x = 2
Equation of normal is given by y – y1 = m (normal) (x – x1)

2y + 4 = x – 2
2y – x + 6 = 0
4. Find the equation of the tangent to the curve x = θ + sin θ, y = 1 + cos θ at θ = π/4.
Solution:

5. Find the equation of the tangent and the normal to the following curves at the indicated points:
(i) x = θ + sin θ, y = 1 + cos θ at θ = π/2
Solution:
Given x = θ + sin θ, y = 1 + cos θ at θ = π/2
By differentiating the given equation with respect to θ, we get the slope of the tangent


Solution:


(iii) x = at2, y = 2at at t = 1.
Solution:


(iv) x = a sec t, y = b tan t at t.
Solution:


(v) x = a (θ + sin θ), y = a (1 – cos θ) at θ
Solution:


(vi) x = 3 cos θ – cos3 θ, y = 3 sin θ – sin3θ
Solution:

6. Find the equation of the normal to the curve x2 + 2y2 – 4x – 6y + 8 = 0 at the point whose abscissa is 2.
Solution:

Finding y co – ordinate by substituting x in the given curve
2y2 – 6y + 4 = 0
y2 – 3y + 2 = 0
y = 2 or y = 1
m (tangent) at x = 2 is 0
Normal is perpendicular to tangent. So, m1m2 = – 1
m (normal) at x = 2 is 1/0, which is undefined
Equation of normal is given by y – y1 = m (normal) (x – x1)
x = 2
7. Find the equation of the normal to the curve ay2 = x3 at the point (am2, am3).
Solution:


8. The equation of the tangent at (2, 3) on the curve y2 = ax3 + b is y = 4x – 5. Find the values of a and b.
Solution:
Given y2 = ax3 + b is y = 4x – 5
By differentiating the given curve, we get the slope of the tangent

m (tangent) at (2, 3) = 2a
Equation of tangent is given by y – y1 = m (tangent) (x – x1)
Now comparing the slope of a tangent with the given equation
2a = 4
a = 2
Now (2, 3) lies on the curve, these points must satisfy
32 = 2 × 23 + b
b = – 7
9. Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve y = x2 + 4x – 16 which is parallel to the line 3x – y + 1 = 0.
Solution:
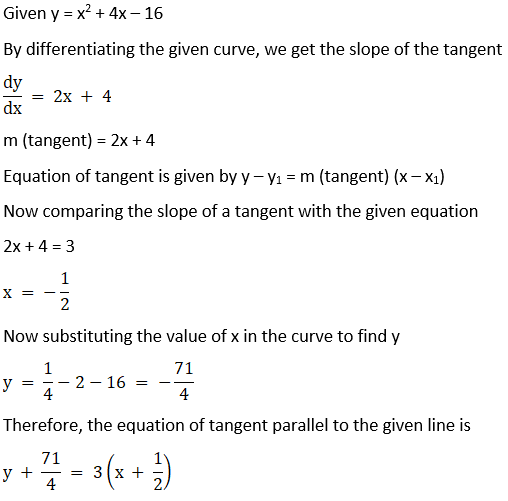

10. Find the equation of normal line to the curve y = x3 + 2x + 6 which is parallel to the line x + 14y + 4 = 0.
Solution:
















Comments