“Asexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of male and female gametes and produces individuals that are genetically identical to the parent.”
Table of Contents
Asexual Reproduction In Plants
Asexual reproduction in plants occurs through budding, fragmentation, vegetative propagation, and spore formation. No flowers are required for this method. The plants produced by asexual reproduction thrive well in stable environments.
Also Read: Reproduction in Plants
Read on to explore the different types of asexual reproduction in plants in complete detail.
Types Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants
Asexual reproduction in plants takes place in two ways:
- Naturally
- Artificially
Natural Methods
Natural methods of asexual reproduction include self-propagation. The different ways in which a plant self propagates are mentioned below:
- Plants such as ginger, onion, dahlia, potato, grow from the buds present on the surface of the stem. A stem tuber has several eyes on the surface. Under favourable conditions, these eyes sprout producing leafy shoots.
- In sweet potato, new plants can grow from the adventitious buds or stolons.
- In Byophyllum, the small buds o the margin of the leaves gets detached and grows into an independent plant.
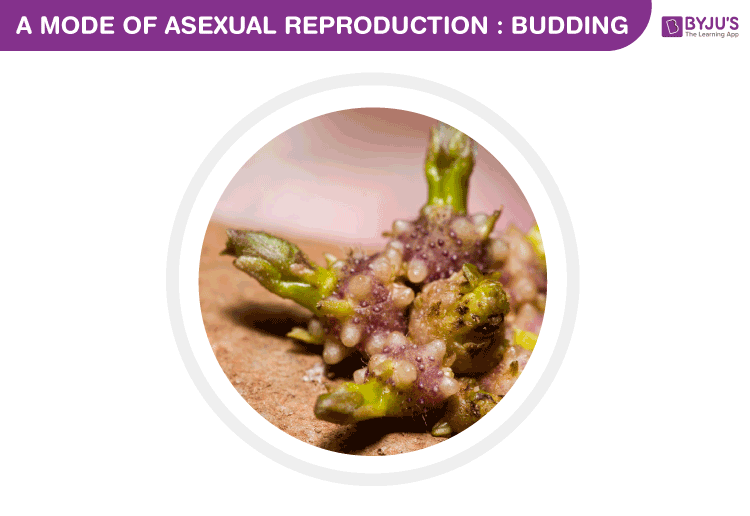
Budding
Budding is the mode of asexual reproduction wherein a new plant is developed from an outgrowth known as the bud. A bud is generally formed due to cell division at one particular site.
For example, if you keep a potato for a long time, you can notice a number of small outgrowths, which are commonly referred to as ‘eyes’. Each of them can be planted which will grow up like a clone of an original potato plant.
Explore more: Budding
Budding
For More Information On Budding, Watch The Below Video:

Vegetative Propagation
It is any form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants, in which new plants are produced from the vegetative parts of the plants, i.e. roots, stems or buds. Vegetative propagation in plants can occur both by naturally or also can be artificially induced by horticulturists.
The most common techniques of vegetative propagation are:
Stems – Runners are the stems which usually grow in a horizontal form above the ground. They have the nodes where the buds are formed. These buds usually grow into a new plant.
Roots – A new plant is developed from modified roots called tubers. Example: Sweet Potato
Leaves – In some plants, detached leaves from the parent plant can be used to grow a new plant. They exhibit growth of small plants, called plantlets, on the edge of their leaves. Example: Bryophyllum.
Fragmentation
This is a mode of asexual reproduction in which a new plant is produced from a portion of the parent plant. Each section or a part of the plants develop into a mature, fully grown individual. Some plants possess specialized structures for reproduction through fragmentation. This type of reproduction happens naturally where the small part of the plant fall off onto soil and then begin to grow up into a new plant. This mode is often used by nurseries and greenhouses to produce plants quickly.
Spore Formation
Many plants and algae form spores in their life cycle. A spore is an asexual reproductive body, surrounded by a hard protective cover to withstand unfavourable conditions such as high temperature and low humidity. Under favourable conditions, the spores germinate and grow into new plants. Plants like moss and ferns use this mode of reproduction.
Also Read: Plant Tissue Culture
Recommended Videos:
Artificial Methods
Following are the artificial methods of asexual reproduction in plants:
Cutting
- In this method, a part of a plant is cut along with the node and is buried in the soil.
- The cutting is watered regularly.
- this is the cheapest method of vegetative propagation in plants.
Grafting
- In this method, the parts of two different plants are joined together such that they continue to grow as a single plant.
- The rooted plant is known as the stock. The other plant is known as the graft.
Layering
It is the method in which a stem attached to a plant is lowered in the ground and covered with soil. The stem grows roots while attached to the parent plant and then detaches as an independent plant.
Micropropagation
This is the method of producing a large number of plants from an explant under laboratory conditions within a short time interval. This facilitates the growth of rare and endangered plant species that are difficult to grow under natural conditions.
Also Read: Micropropagation
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to know more about asexual reproduction in plants.

Frequently Asked Questions
Do strawberries reproduce asexually?
Strawberries reproduce asexually by allowing plantlets at the ends of stolons to grow in soil. Actual strawberries are the result of sexual reproduction.
Name some plants that reproduce asexually.
Banana, sugarcane, ginger, sweet potato, are some of the plants that reproduce asexually.

Thank you so much Byju’s 😊
It’s usefull