The Cyclostomata are the modified and degenerate offshoot of the primitive vertebrate stalk. Due to their circular mouth, they are named Cyclostomata.
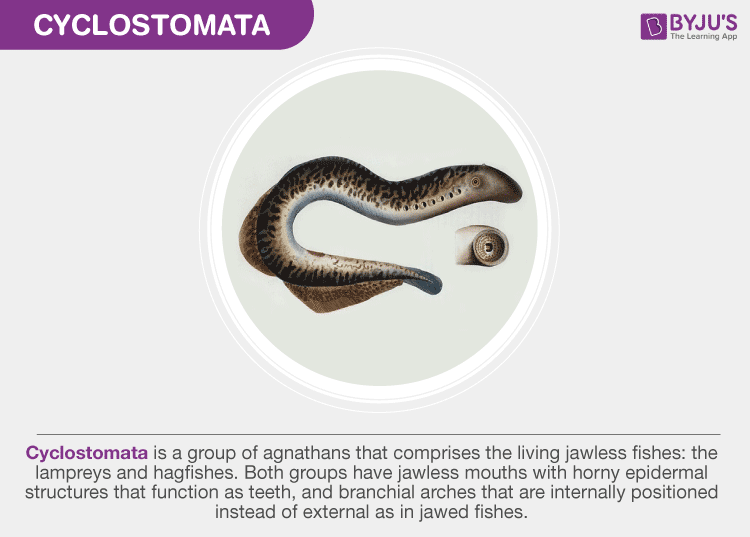
They are parasitic, usually feeding on fish in their adult stage. Morphologically, they resemble eels. They are known to be the only living vertebrates without true jaws, hence called Agnatha. Cyclostomata includes hagfishes and lampreys.
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- The body is round and elongated like an eel.
- The paired fins are absent.
- Median fins with cartilaginous fin rays.
- No paired appendages.
- The skin is soft and smooth, devoid of any scales.
- Spleen is absent.
- The exoskeleton is absent. The endoskeleton is cartilaginous with no bones.
- The notochord is present throughout their lives.
- The digestive system is devoid of any stomach.
- The nostril is single and median.
- The gills are five to sixteen in pairs.
- The heart is two-chambered.
- The brain is visible.
- The lateral line acts as a sense organ.
- About ten pairs of cranial nerves are present.
- The sexes are separate. Some hagfish species are believed to be hermaphrodite.
- A pair of mesonephric kidneys make up the excretory system.
- Development may be direct or indirect.
- Eg., Petromyzon and Maxine.
Also read: Chordata
Sub-Divisions of Cyclostomata
The cyclostomes are sub-divided into two major orders.
Petromyzontiformes
Lampreys or lamper eels belong to this order.
- They are found in both marine and freshwater.
- They have a ventral mouth with many horny teeth.
- The nostril is present dorsally.
- They possess a well-developed dorsal fin.
- The dorsal and ventral roots of spinal nerves are separate.
- The development is indirect.
- Eg., Petromyzon, Lampetra
Myxiniformes
Hagfishes represent this order.
- They are found exclusively in the marine environment.
- They have a terminal mouth with few teeth.
- They have no buccal cavity.
- The nostril is terminal.
- They possess 6-14 pairs of gill slits.
- The dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal nerves are not separate.
- Eggs are large and few in number.
- The dorsal fin is usually absent, or weak.
- Eg., Myxine, Paramyxine.
Further Reading: Animal Kingdom Classification
For more information on Cyclostomata, visit Byju’s app.

Thanks for the answer
Good
good app for learning
thank you sir for so much good explanation
thnks for nice explination