Frogs are a diverse group of tailless amphibians. Their unique features include a stout, tailless body, anteriorly placed tongue, protruding eyes, etc. Hoplobatrachus tigrinus (old name – Rana tigrina) is the most common variety of frogs found in the Indian subcontinent. It is also known as the Indian bullfrog.
Let’s learn more about the external description of the Indian bullfrog with a labelled diagram.
Frog – Classification
|
Kingdom |
Animalia |
|
Phylum |
Chordata |
|
Subphylum |
Vertebrata |
|
Class |
Amphibia |
|
Order |
Anura |
|
Genus |
Hoplobatrachus |
|
Species |
tigrinus |
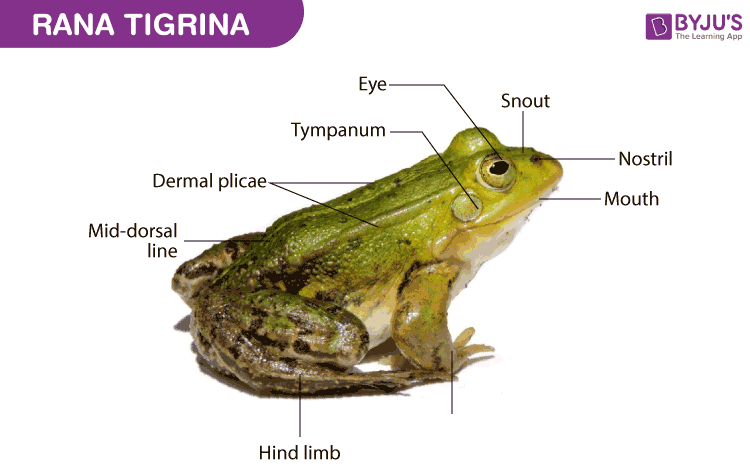
Labelled Diagram of Frog
Habitat and Distribution
Hoplobatrachus tigrinus, or Rana tigrina, is also known as the Asian bullfrog or Indian bullfrog. It is one of the diverse species of frog and is distributed in India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Afghanistan. It has also been introduced in the islands of Andaman, Maldives and Madagascar.
Frogs are amphibians and thus live in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Even on land, they prefer relatively damp areas. They lay eggs in water bodies like ponds and the tadpoles exclusively thrive in water.
Description
- Rana tigrina or Hoplobatrachus tigrinus measures about 12-20 cm in length. They are stout and roughly triangular in shape.
- They have moist, smooth and slippery skin. The dorsal skin is typically olive or green in colour with dark patches while the ventral region is whitish. The back of the skin is thickened or folded longitudinally as dermal plicae.
- The body is distinguished into head and trunk only. They have no neck and tail.
- The head has two small openings near the anterior end of the snout called the external nares.
- The eyes are large, protuberant, bright with black pupils and golden iris. Each of them has a small lower mobile eyelid and an upper large stationary eyelid.
- The upper portion of the lower eyelid forms the transparent nictitating membrane.
- The tympanic membrane or tympanum is a circular area present posterior to each eye. It marks the external border of the middle ear. Also, it lacks an external ear.
- The vocal sacs in male frogs are present under the head.
- The trunk portion contains the forelimbs anteriorly and hindlimbs posteriorly. Typically, the hindlimbs are longer than the forelimbs and thus aid in hopping and leaping.
- The forelimbs have the forearm, upper arm and hand with palm, wrist and four digits. The digits have articular and copulatory pads.
- The copulatory pads are a distinguishing feature present in the hands of male frogs.
- The hind limbs comprise the shank, thigh and foot. The foot includes the sole, ankle and five digits.
- The cloacal opening is present at the posterior end of the trunk.
Significance
Frogs are widely studied vertebrates and are used for pharmacological and physiological research studies. They are used as baits to catch fish. Also, they feed on small molluscs and insects and thus protect crops from harmful insects.
Also Read:

Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments